В.Кондратьев Самолеты первой мировой войны
Миниатюрный одностоечный цельнодеревянный биплан с полотняной обшивкой. Разработан в августе 1916 года конструкторским коллективом авиационного департамента известного британского оружейного концерна "Виккерс лимитед" (Vickers Ltd.) на базе одноместного невооруженного разведчика "Виккерс" ES.2.
Первый серийный FB.19 Mk.I впервые поднялся в воздух в ноябре 1916-го. Вскоре появилась новая модификация Mk.II, у которой верхнее крыло было вынесено вперед с целью улучшения обзора. Однако из-за низкой посадки пилота обзор у этой машины все равно считался неважным, хотя его и пытались улучшить за счет прямоугольного, затянутого прозрачным целлулоидом "окна" в центроплане верхней плоскости.
Вооружение обоих модификаций составлял синхропулемет "Виккерс", установленный в углублении по левому борту фюзеляжа и стрелявший сквозь отверстие в капоте.
Всего построено 65 серийных экземпляров истребителя в обеих модификациях. Несмотря на хорошие скоростные данные FB. 19. военное министерство Великобритании решило отказаться от его дальнейших закупок. Из соображений унификации самолетного парка предпочтение было отдано истребителям фирмы "Сопвич", перед которыми машина "Виккерса" не имела решающих преимуществ.
FB.19 не применялся на Западном фронте. Пять машин поступили в 111-й дивизион RFC в Палестине, семь - в 17-й и 47-й дивизионы в Македонии, Шесть штук зачислили в ПВО метрополии, а еще 12 отправили в летные школы. В английских авиадивизионах "Виккерсы" прослужили до конца 1917 года, после чего были списаны.
В конце 1916-го 20 машин первой модификации были отправлены в Россию. Четыре из них летом 1917-го поступили в британский истребительный авиаотряд, воевавший в составе русской армии на Юго-западном фронте. Остальные до революции простояли на складах. В 1918 году их включили в состав Красного воздушного флота.
Шесть самолетов с Алатырского авиасклада в августе-сентябре принимали участие в боях с войсками поволжской "Народной армии" под Казанью. Данных о боевом применении других российских "Виккерсов" в Гражданской войне не сохранилось. Предположительно, они использовались только в летных школах.
МОДИФИКАЦИИ
Mk.I - верхнее крыло без выноса, межкрыльевые стойки вертикальны.
Mk.II - верхнее крыло вынесено вперед, межкрыльевые стойки установлены под наклоном.
ЛЕТНО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ
Размах, м 7,32
Длина, м 5,53
Площадь крыла, кв.м 20,00
Сухой вес, кг 404
Взлетный вес, кг 670
Скорость максимальная, км/ч 175
Скорость подъема на высоту
3000 м, мин.сек 7,50
Потолок, м 4570
В.Шавров История конструкций самолетов в СССР до 1938 г.
"Виккерс-истребитель" - одностоечный биплан с коротким, относительно толстым фюзеляжем. Двигатель - первоначально "Рон" в 110 л. с. (Виккерс "Скаут", Викфе), позже- "Клерже" в 130 л. с. (Виккерс "Буллит"). Центроплан между лонжеронами прозрачный с целлулоидным покрытием. Из-за глубокой посадки летчика обзор из кабины был плох, что снижало ценность этого самолета как истребителя. По сумме летных данных был близок к самолету "Спад-VII", которому в целом уступал, превосходя только в максимальной скорости (до 200 км/ч с "Клерже"). Всего было до трех десятков экземпляров. Применялся в гражданской войне и летал до 1924 г.
Самолет||
Год выпуска||1916
Двигатель , марка||
мощность, л. с.||130
Длина самолета, м||6,1
Размах крыла, м||7,5
Площадь крыла, м2||20
Масса пустого, кг||485
Масса топлива+ масла, кг||136
Масса полной нагрузки, кг||247
Полетная масса, кг||732
Удельная нагрузка на крыло, кг/м2||36,6
Удельная нагрузка на мощность, кг/лс||6,6
Весовая отдача,%||34
Скорость максимальная у земли, км/ч||190
Время набора высоты||
1000м, мин||2
2000м, мин||4,5
3000м, мин||8
Потолок практический, м||7000
Продолжительность полета, ч.||3,5
C.Andrews Vickers Aircraft since 1908 (Putnam)
<...>
A further development of the Bullet appeared in August 1916 as the F.B.19, in an unstaggered version as the Mk I and later in a staggered version, the Mk II. The former had either the 100 hp Gnome monosoupape or 110 hp Le Rhone and the latter the 110 hp Le Rhone or the 110 hp Clerget. About 50 Mk Is and 12 Mk lis were made at Weybridge and were used in small numbers on the Western Front, in Macedonia and Palestine. A demonstration Mk I was sent to Russia which led to a small batch of Mk IIs being sent to Archangel, but there they remained in their crates when the Revolution intervened, Russia withdrawing from the war, and are believed to have been destroyed by British Forces in 1919.
F.B.19 - Bullet Mk I - One 110 hp Le Rhone. Span 24 ft; length 18 ft 2 in; height 8 ft 3 in; wing area 215 sq ft. Empty weight 900 lb; gross weight 1,485 lb. Max speed 102 mph at 10,000 ft; climb to 10,000 ft - 14 min; service ceiling 15,000 ft; absolute ceiling 17,500 ft; endurance 2 3/4 hr. Armament one Vickers gun.
F.B.19 - Bullet Mk II - One 110 hp Clerget. Span 24 ft; length 18 ft 2 in; height 8 ft 3 in; wing area 215 sq ft. Empty weight 890 lb; gross weight 1,475 lb. Max speed 98 mph at 10,000 ft; climb to 10,000 ft-14 1/2 min; absolute ceiling 16,500 ft; endurance 3 hr. Armament one Vickers gun.
P.Lewis The British Fighter since 1912 (Putnam)
August, 1916, saw the emergence of the F.B.19 Mk.I, another of Vickers Ltd.’s endeavours in single-seat fighter design. The new machine was basically the resuscitation of the E.S.1 and E.S.2 of the previous year but with a slightly smaller span and reduced overall length. The F.B.19 Mk.I’s engine was the 100 h.p. Monosoupape Gnome and the armament provided was a single Vickers gun, mounted to port in a trough in the fuselage, and synchronized with the Vickers-Challenger gear.
A new version then appeared, designated F.B.19 Mk.II, the wings of which embodied sharp stagger, and which used either the 110 h.p. Clerget or the 110 h.p. le Rhone engine.
The Mk.I could also utilize the 110 h.p. le Rhone and both marks of F.B.19 went into limited production against orders for the R.F.C., by which service it was often called the Bullet. After being turned down for full-scale operation in France, the F.B.19 found itself flying in the Middle East and also with Home Defence units in the United Kingdom but was never fortunate enough to make a name.
F.Mason The British Fighter since 1912 (Putnam)
Vickers F.B.19
It will be recalled that the Vickers E.S.1 and E.S.2 single-seaters of 1915 had been criticised and probably rejected for service on account of the very poor field of view from the cockpit caused by the circular section of the fuselage. In other respects the aircraft had been commended in the context of standards existing at that time, and Vickers had been sufficiently encouraged to persist with the basic design. The outcome was the F.B.19, which appeared in August 1916 with an almost flat-sided fuselage aft of the carefully faired circular-section nose.
The single-bay wings were of equal span, and when the aircraft first appeared there was no stagger; it was powered by a 100hp Gnome monosoupape. As well as a cutout in the trailing edge of the upper wing, there was a large clear-view aperture between the spars of the wing centre section.
Armament comprised a single Vickers gun located in a channel set into the port side of the forward fuselage below the upper longeron, firing through a small aperture in the front of the engine cowling and equipped with Vickers-Challenger interrupter gear.
When a much-modified version of the F.B.19 appeared soon afterwards with modified wings rigged with considerable stagger, it was termed the Mark II and the original aircraft became the Mark I retrospectively. Despite a very modest performance the Mark II, which inherited the unofficial name Bullet from the earlier E.S. aircraft, was ordered into limited production, with either 110hp Clerget or Le Rhone engines. Six examples were sent to France for operational trials late in 1916, but were not popular and were soon returned home. One aircraft reached No 14 Squadron in the Middle East in May 1917 and another was issued to No 47 in Greece during June, while No 30 in Mesopotamia flew a third. No 111 Squadron included five amongst its assortment of fighters in Palestine during 1918. The only other Squadron to fly F.B.19s was No 141 which received two at Biggin Hill, also in 1918. It is said that a few were shipped to Russia in 1916 and it seems that these can only have been Mark Is, but no reliable records survive to confirm this, nor the number sent.
The accompanying dimensions, weights and performance data refer to the F.B.19 Mark II with 110hp Le Rhone engine.
Type: Single-engine, single-seat, single-bay biplane fighting scout.
Manufacturer: Vickers Ltd (Aviation Department), Knightsbridge, London.
Powerplant: Mark I. 100hp Gnome monosoupape engine; 110hp Le Rhone. Mark II. 110hp Clerget; 110hp Le Rhone.
Dimensions: Span, 24ft 0in; length, 18ft 2in; height, 8ft 3in; wing area, 215 sq ft.
Weights: Tare, 892lb; all-up, 1,478lb.
Performance: Max speed, 98 mph at sea level; climb to 10,000ft, 14 min 50 sec; service ceiling, 15,000ft; endurance, 3 1/4 hr.
Armament: Single 0.303in Vickers machine gun mounted in trough on port side of nose to fire through the propeller arc, synchronized by Vickers-Challenger gear.
Prototypes: Two Mark Is, A1968 and A1969 (first flown in August 1916).
Production: Records suggest that as many as thirty-six F.B.19s were issued to the RFC, although contract cover has only been confirmed for fourteen (two Mark Is, A2120 and A2992, and twelve Mark Ils, A5225-A5236).
Summary of Service: Surviving records show that single Mark Ils served with No 14 Squadron (Middle East), No 30 (Mesopotamia) and No 47 (Greece); No 111 Squadron received five in Palestine in August 1917, and No 141 Squadron flew two at Biggin Hill in 1918. Some were issued to home-based training units in 1918.
W.Green, G.Swanborough The Complete Book of Fighters
VICKERS F.B.19 UK
Designed in 1916 by G H Challenger and flown for the first time in August of that year, the F.B.19 was a single-bay unstaggered equi-span biplane with a single 0.303-in (7,7-mm) Vickers gun mounted on the port side of the fuselage and a 100 hp Gnome Monosoupape engine. Ordered by the War Office for the RFC, the series version was powered by either the Gnome or the 110 hp Le Rhone. Some 50 F.B.19s were built, and, late in 1916, a batch of six was sent to France where, after operational evaluation, the fighter was deemed unsuited for the fighting conditions then evolving. At this time, some of the F.B.19s were delivered to the Russian government following demonstrations in Petrograd, Moscow, Kiev and Tiflis, but several were still in their crates on the docks at Archangel at the commencement of the Bolshevik revolution. These aircraft were destroyed by the Royal Navy, but a few others assembled prior to the Navy's action were flown in Bolshevik service. A modified version, the F.B.19 Mk II, was developed with wing stagger and either the Le Rhone or Clerget 110 hp rotary. Only 12 Mk IIs were built and several of these were included in a batch of 12 F.B.19s sent to the Middle Eastern theatres of war. These were flown in Palestine and Macedonia from June 1917, but no squadron used the type exclusively and it was not well liked. The following data relate to the Le Rhone-powered F.B.19.
Max speed, 98 mph (158 km/h) at 10.000 ft (3 050 m), 90 mph (145 km/h) at 15,000 ft (4 570 m).
Time to 5,000 ft (1525 m), 5.6 min.
Ceiling, 17.000 ft (5180 m).
Endurance, 3.25 hrs.
Empty weight, 892 lb (405 kg).
Loaded weight, 1,478 lb (670 kg).
Span, 24 ft 0 in (7,31 m).
Length, 18 ft 2 in (5,54 m).
Height, 8 ft 3 in (2,51m).
Wing area, 215 sq ft (19,97 m2).
J.Bruce British Aeroplanes 1914-1918 (Putnam)
Vickers F.B. 19
THE Vickers F.B.19 was a single-seat fighter which was a direct descendant of the E.S.1 and E.S.2 scouts of 1915. The F.B.19 first appeared in August, 1916, and in its original form was powered by the 100 h.p. Gnome Monosoupape engine and had unstaggered wings.
It was a single-bay equal-span biplane of conventional appearance. The fuselage was deep and stumpy. The engine cowling was faired into the fuselage sides, but abaft the cockpit the sides were quite flat; there was a deep, rounded top-decking. The fin and rudder were typical of Vickers design, and the tailplane was rectangular. An alternative power unit was the 110 h.p. Le Rhone.
A single Vickers machine-gun, synchronised by the Vickers-Challenger interrupter gear, was mounted on the port side of the fuselage, just below the upper longeron. This weapon installation anticipated that which was used in single-seat fighters of much later date, for the gun lay in a trough in the fuselage side-fairing, and its line of fire ran inside the engine cowling: there was a small hole in the front of the cowling through which the bullets passed.
The mainplanes had straight, slightly raked tips; and ailerons were fitted to upper and lower wings. In order to give the pilot a reasonable upwards view, a very large cut-out was made in the centre-section.� The design was modified by giving the wings a pronounced stagger; additional structural members were introduced in the fuselage sides to meet the new positions of the lower wing spars. The engine of the modified aircraft was either a 110 h.p. Clerget or a 110 h.p. Le Rhone. Otherwise the airframe was unchanged, and in its modified form the machine was designated Vickers F.B.19 Mark II. The original F.B.19 without stagger was the Vickers F.B.19 Mark I.
Both Marks of F.B.19 went into small-scale production for the R.F.C., and deliveries began in 1916. Before the end of that year six had gone to France for operational trials. It is possible that the type may have been flown for a short time by No. 11 Squadron, R.F.C., but it was not regarded as good enough for the aerial fighting on the Western Front and was withdrawn. The F.B.19 was known to the R.F.C. as the Vickers Bullet, a name inherited from the E.S.1 and E.S.2.
In 1917 twelve F.B.19s were sent to the Middle East, and there the type was used operationally by No. 111 Squadron in Palestine and by Nos. 17 and 47 Squadrons in Macedonia. None of these units had more than a few F.B.19s: on October 27th, 1917, No.111 Squadron had five as part of their motley collection of aircraft, the remainder of which consisted of six Bristol Fighters, three D.H.2s, two Bristol M.1c monoplanes and one Bristol Scout. The Vickers F.B.19s had arrived in Palestine in June, 1917. There they had a certain limited usefulness as interceptors. Writing to General John Salmond in December 1917, Major-General W. S. Brancker said: “The Bristol Monoplanes and Vickers Bullets are not very much good except to frighten the Hun; they always seem to lose the enemy as soon as he starts manoeuvring.” In Macedonia the F.B.19 was no more successful.
At home, a few were used on Home Defence duties, but did not distinguish themselves in any way; the remainder went to training units.
Late in 1916 a few F.B.19s were supplied to Russia, and were presumably used on the Eastern Front.
SPECIFICATION
Manufacturers: Vickers Ltd. (Aviation Department). Imperial Court, Basil Street, Knightsbridge, London, S.W.
Power: Mk. 1: 100 h.p. Gnome Monosoupape; 110 h.p. Le Rhone. Mk. II: 110 h.p. Clerget; 110 h.p. Le Rhone. Dimensions: Span: 24 ft. Length: 18 ft 2 in. Height: 8 ft 3 in. Chord: 5 ft. Gap: 4 ft. Stagger: Mk. I, nil; Mk. II, 1 ft 10 in. Dihedral: 1°. Incidence: 0° 15'.
Areas: Wings: upper 113 sq ft, lower 102 sq ft, total 215 sq ft. Ailerons: each 6-3 sq ft, total 25-2 sq ft. Tailplane: 17-5 sq ft. Elevators: 12-5 sq ft. Fin: 5-25 sq ft. Rudder: 6-5 sq ft.
Weights (lb) and Performance:
Aircraft F.B.19 Mk. I F.B.19 Mk. II F.B.19 Mk. II
Engine Monosoupape Clerget Le Rhone
No. of Trial Report - - M.97
Date of Trial Report - - May, 1917
Type of airscrew used on trial - - Vickers 2496
Weight empty 900 890 892
Military load 80 80 80
Pilot 180 180 180
Fuel and oil 325 325 326
Loaded 1,485 1,475 1,478
Maximum speed (m.p.h.) at
10,000 ft 102 98 98
15,000 ft - - 90
m. s. m. s. m. s.
Climb to
5,000 ft 5 20 5 30 - -
6,500 ft - - - - 7 50
10,000 ft 14 00 14 30 14 50
15,000 ft - - - - 37 10
Ceiling: service (feet) - - 15,000
absolute (feet) 17,500 16,500 17,000
Endurance (hours) 2 3/4 3 3 1/4
Armament: One fixed, forward-firing Vickers machine-gun on port side of fuselage, synchronised by Vickers-Challenger interrupter gear to fire through the airscrew.
Service Use: Western Front: probably used by No. 11 Squadron, R.F.C. Palestine: No. 111 Squadron. Macedonia: Nos. 17 and 47 Squadrons. Eastern Front: used by Russian air service.
Production and Allocation: The total number built is not known, but official records show that thirty-six Vickers
F.B.19s were distributed to units of the R.F.C. Six went to France in 1916, and twelve to the Middle East Brigade in 1917; six went to Home Defence squadrons, and twelve to training units.
Serial Numbers: A.1968-A.1969, A.2122 and A.2992: F.B.19s Mk. I ordered under Contract No. 87/A/536. A.5225-A.5236: F.B.19s Mk. II ordered under Contract No. 87/A/1345 and built at Weybridge.
H.King Armament of British Aircraft (Putnam)
F.B.19. This derivative of the E.S.1 (1916) differed from its predecessor in respect of the Vickers gun installation. The gun was recessed as formerly but was mounted much lower in the fuselage side. The Vickers synchronizing gear was retained.
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919
F.B.19. TRACTOR BIPLANE. SINGLE SEATER.
Fighter of 1916 appearance, capable of 109 mph. Only 36 built for RFC and used in Palestine, Russia, Macedonia and in UK for home defence. Fitted with 110 h.p. Clerget or Le Rhone rotary engine.
Armament: One Vickers' gun with Vickers' syncronised firing gear.
Журнал Flight
Flight, June 12, 1919.
"MILESTONES"
THE VICKERS MACHINES
The F.B. 19. (Aug., 1916)
This was a modified type of single-seater tractor scout produced in August, 1916, the visibility being greatly improved, whilst maintaining the excellent performance and manceuvreability of its predecessor, the E.S. 2.
Several of these machines were supplied to Russia towards the close of 1916
 |
В.Кондратьев - Самолеты первой мировой войны
|
| "Виккерс" FB.19 Mk1, Московская авиашкола РККВФ, Ходынский аэродром, осень 1919г.
|
 |
В.Кондратьев - Самолеты первой мировой войны
|
| Виккерс F.B.19, 111-й дивизион RFC, июнь 1917г.
|
 |
В.Кондратьев - Самолеты первой мировой войны
|
| Виккерс F.B.19, Россия, 1917 год.
|
 |
J.Bruce - British Aeroplanes 1914-1918 /Putnam/
|
| Vickers F.B.19 Mk. I.
|
 |
W.Green, G.Swanborough - The Complete Book of Fighters
|
| An F.B.19 Mk I being started up at Brooklands with Harold Barnwell in the cockpit and Stan Cockerell leaning against the starboard wing.
|
 |
В.Кондратьев - Самолеты первой мировой войны
|
Один из двух "Виккерсов", поступивших летом 1917 года в Россию. Предположительно, снимки сделаны летом 1918 года во время боев под Казанью. На самолеты еще не нанесены опознавательные знаки.
More than twenty of the Vickers F.B.19 fighters sent to Russia were taken over by the RKKVF.
|
 |
В.Кондратьев - Самолеты первой мировой войны
|
|
|
 |
C.Andrews - Vickers Aircraft since 1908 /Putnam/
|
| A Vickers F.B.19 Mk I in service with Soviet forces in company with a Sopwith Triplane.
|
 |
В.Шавров - История конструкций самолетов в СССР до 1938 г.
|
| Английский самолет "Виккерс"
|
 |
C.Andrews - Vickers Aircraft since 1908 /Putnam/
|
| A Weybridge-built F.B.19 Mk II Bullet, 1917.
|
 |
F.Mason - The British Fighter since 1912 /Putnam/
|
| This photograph of an F.B.19 Mk II well illustrates the efforts made to improve the pilot’s field of view from the cockpit.
|
 |
J.Bruce - British Aeroplanes 1914-1918 /Putnam/
|
| Readily distinguishable from the original FB 19, of August 1916, by its forward staggered upper wing, the Vickers FB 19 Mk II entered service in small numbers staring in June 1917. FB 19 Mk IIs served with No 17 Squadron, RFC, in Macedonia, while examples of this 100hp or 110hp rotary engined, single Vickers-gunned, single seater were known to have been flown by No.s 14 and 111 Squadrons in Palestine. As only 12 Mk IIs are known to have been built, it is clear that only sections of each squadron operated the type. Top level speed of the Mk II was 102mph at 10.000 feet, but its all-round performance was held to be unimpressive.
|
 |
Журнал - Flight за 1919 г.
|
| THE VICKERS F.B. 19. - This was really a development of the "Barnwell Bullet," and has a 110 h.p. Clerget engine
|
 |
W.Green, G.Swanborough - The Complete Book of Fighters
|
| In its Mk II form, the F.B.19 was produced in small numbers for RFC service.
|
 |
P.Lewis - The British Fighter since 1912 /Putnam/
|
| Vickers F.B.19 Mk.II.
|
 |
P.Lewis - British Bomber since 1914 /Putnam/
|
| Prototype F.B.27 B9952 with original elevators fitted with horn balances and Hispano Suiza engines before its first flight, made by Gordon Bell on 30 November, 1917; the F.B.19 Mk II was presumably one of the first known chase planes.
|
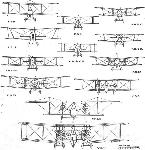 |
Журнал - Flight за 1919 г.
|
| Front Elevations of the Vickers machines
|
 |
Журнал - Flight за 1919 г.
|
| Side elevations ot fhe Vickers machines
|
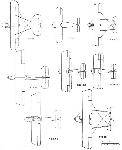 |
Журнал - Flight за 1919 г.
|
| Plan views of the Vickers machines
|
 |
C.Andrews - Vickers Aircraft since 1908 /Putnam/
|
| F.B.19 Mk.II
|
 |
W.Green, G.Swanborough - The Complete Book of Fighters
|
|
|
 |
В.Кондратьев - Самолеты первой мировой войны
|
| Vickers F.B.19 Mk.II
|























