
| Самолеты (сортировка по:) | |||||
| Страна | Конструктор | Название | Год | Фото | Текст |
Schutte-Lanz G.I

|
Страна: Германия Год: 1915
|
| Schutte-Lanz - D.I - 1915 - Германия | <– | –> | Schutte-Lanz - D.III - 1917 - Германия |
 |
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919 /Jane's/ |
| An early (1914-15) Schutte-Lanz Experimental Type G.I Twin-engined Biplane, possessing many features betraying its relationship lighter-than-air craft. Two 160 h.p. Mercedes D.III engine. |
 |
J.Herris - German Aircraft of Minor Manufacturers in WW1. Volume II /Centennial Perspective/ (50) |
| Designed as a battle plane, only one Schutte-Lanz G.I was built. |
 |
J.Herris - German Aircraft of Minor Manufacturers in WW1. Volume II /Centennial Perspective/ (50) |
| This view shows the unusual cross-section of the Schutte-Lanz G.I fuselage. |
 |
Форум - Breguet's Aircraft Challenge /WWW/ |
| Publicity picture for the strength of the wings (a la Fokker ...) |
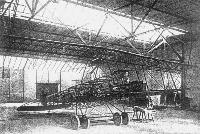 |
Форум - Breguet's Aircraft Challenge /WWW/ |
| The machine half built |
 |
J.Herris - German Aircraft of Minor Manufacturers in WW1. Volume II /Centennial Perspective/ (50) |
| The heavy, drag-creating propeller extension shafts and their supports, clearly seen in this view, were the result of deciding to use a pusher configuration and did nothing to enhance performance or load-carrying capability. |
 |
J.Herris - German Aircraft of Minor Manufacturers in WW1. Volume II /Centennial Perspective/ (50) |
| Drawing for proposed Schutte-Lanz G.II/G.III that was not built. The main difference from the G.I appears to be the streamlined engine cowlings. |