Jane's All The World Aircraft 1913
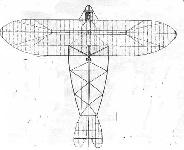
DORNER III. Monoplane. Length.--34-1/2 feet (10.50 m.) Span.--39-1/3 feet (12 m.) Surface.--280 sq. feet (126 m^2.) Weight.--882 lbs. (400 kgs.)
Type II: Length.--32-3/4 feet (10 m.) Span.--38 feet (11.60 m.) Surface.--268-1/2 sq. feet (25 m^2.) Weight.--661 lbs. (300 kgs) See Flugsport, No. 5, 1911.
C.Owers, J.Herris Hannover Aircraft of WWI (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 46)
Hermann Dorner was born on 27 May 1882 in the Luther-Haus in Wittenberg. His father, a professor of theology, was transferred to Konigsberg/Ostpreussen (nowadays Kaliningrad) and the young Dorner made his first attempts at gliding as a teenager at Cranz on the Baltic coast. After carrying out his military service by serving for a year in the navy he obtained his Diplom-Ingenieur in shipbuilding at the Technical University of Charlottenburg in 1906. A year later he resumed his flight tests in Deutschwusterhausen near Berlin with a self-made monoplane glider with three wheels. Unlike Lilienthal, who used gravity as the propulsion for his gliding flights down the slope of a hill, he chose horizontal flight and let himself be pulled by a galloping horse with a long rope. Initial failures and crashes did not discourage him and finally he managed flights up to 80 m in length and 7 m in height with subsequent flawless landings, first in a lying position, and then sitting.
He then desired to achieve powered flight. As there was no commercially available engine suitable for his needs, he designed his own, an air-cooled four-cylinder engine with combined intake and exhaust valve, that was built in 1908 by the Schwager Company. His new high wing monoplane made a few successful aerial jumps and this encouraged him to register for the Johannisthal "International Flight Week" in September 1909. He could not achieve much with his untested monoplane, the prizes were taken by the French pilots taking part, but he learned a lot from them.
The 1909 monoplane had an 18-hp Dorner engine in the fuselage nose with a chain driven airscrew above. The wing was adjustable in flight and spanned 11.80 m. The tail surfaces were carried on a slender boom.
With an improved monoplane, which was equipped with a redesigned 22-hp water-cooled engine, Dorner won the "3rd Lanz Prize of the Skies" on 11 July 1910, amounting to 3,000 marks and immediately thereafter his pilot's license (No. 18). In September of the same year he founded the Dorner Flugzeug GmbH and moved to the aeroplane shed No. 9 in Johannisthal where he started a flight school. He trained a few student pilots, and employed the Swiss pioneer aviator Robert Gsell. He continued to develop larger and more powerful versions of his monoplane. Accidents and the lack of military orders to abandon aeroplane manufacturing in 1912, and the following spring, Goetze, his chief executive officer took over the facility. The company was liquidated in the summer of 1913.
Dorner Aircraft
The T II monoplane had a 22-hp Dorner water-cooled engine and the frontal radiators were mounted on a low tubular steel frame with the spring-loaded wooden chassis axle. The pilot's seat was behind the engine. The wing was supported by struts and used wing warping control. The rear section of the fuselage was open. The drive shaft from the engine passed under the pilot's seat and a long chain transmission drove the pusher propeller mounted high behind the wing. This machine was built in 1910 but it burned after a few flights when a cylinder head tore off in the shed during a test run.
Span 11.6 m; Empty weight 320 kg; AUW 430 kg; Speed 65 km/h.
The T.III monoplane had a 40-hp NAG, 40-hp Korting or 50-hp Dixi engine. It was similar to the T II but a two-seater with dual controls. On 6 June 1911, Georg Schendel (pilot's license No 63) crashed fatally at Aldershof with his mechanic Voss, in a T III. In December 1911, Robert Gsell demonstrated a machine with a 50 hp Daimler in Doberitz for the military administration, which ordered a more powerful prototype.
Span 12.35 m; Speed 85 km/h.
The monoplane that was built to the military order by Dorner was similar to the T III but had a 70-hp Daimler engine and an enclosed fuselage for the engine and seats. Delivered in 1912, there were no further orders because the chain transmission repeatedly led to malfunctions and accidents.
Speed quoted as 110 km/h.