Книги
Jane's
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1913
258
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1913 /Jane's/
AUSTRIAN AEROPLANES.
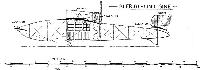
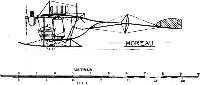
ETRICH Monoplanes. Etrich Flieger Werke, Wiener Neustadt. Igo Etric was a very early experimenter in conjunction with Wels. In 1909 he produced on his own account the first Etrich monoplane, a characteristic machine, which except for detail improvement, varying dimensions, etc., has not been appreciably altered since. (See Historical Section.)
VIII 1911-12 1912-13.
Model and date. VII 1911. 2-Seater Limousine 2-seater.
Length.............feet(m.) 37 (11.30) 30? (9.30) 26? (8)
Span...............feet(m.) 48 (14.60) 42 (12.80) 31? (9.50)
Area...........sq.feet(m^2.) 380 (35 ) 323 (30) 280 (26)
(total...lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Weight..
(useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor..................h.p. 120 Daimler 100 60 Daimler
Speed...........m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Number built during 1912 5 2 2
Remarks.--A number of VII & VIII have been sold for military purposes to the Austrian, Russian, German, and other governments.
GERMAN AEROPLANES.
ETRICH. Etrich Fliegerwerke, G.m.b. H. Dittersbach b. Liebau (Schlesien). Capacity: 50 a year.
1913.
Etrich (original) Taube.
monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 31 (9.5)
Span..............feet(m.) 47-1/2 (14.40)
Area........sq. feet(m^2.) 301 (28)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1323 (600)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor.................h.p. 100 Mercedes or Argus
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) 71 to 75 (115 to 120)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance.............hrs. 6
Remarks.--
ETRICH Monoplanes. Etrich Flieger Werke, Wiener Neustadt. Igo Etric was a very early experimenter in conjunction with Wels. In 1909 he produced on his own account the first Etrich monoplane, a characteristic machine, which except for detail improvement, varying dimensions, etc., has not been appreciably altered since. (See Historical Section.)
VIII 1911-12 1912-13.
Model and date. VII 1911. 2-Seater Limousine 2-seater.
Length.............feet(m.) 37 (11.30) 30? (9.30) 26? (8)
Span...............feet(m.) 48 (14.60) 42 (12.80) 31? (9.50)
Area...........sq.feet(m^2.) 380 (35 ) 323 (30) 280 (26)
(total...lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Weight..
(useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor..................h.p. 120 Daimler 100 60 Daimler
Speed...........m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Number built during 1912 5 2 2
Remarks.--A number of VII & VIII have been sold for military purposes to the Austrian, Russian, German, and other governments.
GERMAN AEROPLANES.
ETRICH. Etrich Fliegerwerke, G.m.b. H. Dittersbach b. Liebau (Schlesien). Capacity: 50 a year.
1913.
Etrich (original) Taube.
monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 31 (9.5)
Span..............feet(m.) 47-1/2 (14.40)
Area........sq. feet(m^2.) 301 (28)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1323 (600)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor.................h.p. 100 Mercedes or Argus
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) 71 to 75 (115 to 120)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance.............hrs. 6
Remarks.--
Clerget-Etrich Taube "Aman" (France, 1910) Slightly modified version of the Etrich IV Taube license-built by Clerget in France for whose name appeared on the tail, Gustave Aman. Powered by an inline Clerget engine, it was completed in August but first flown in October 1910.
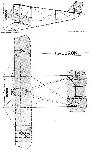
LOHNER-DAIMLER. This firm is now amalgamated with Etrich.
1912-13.
1911. Lohner Daimler
Pfeilflieger.
Length......feet (m.) ... 32 (9.70)
Span........feet (m.) ... 44? (13.50)
Area...sq. feet (m?.) ... 450 (42)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) ... 926 (420)
useful ..lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor............h.p. 60 Aust. 125 Aust.
Daimler Daimler
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 50 (80) 62 (100)
Number built
during 1912 ... ? 4
Remarks.--Staggered and V shape. Late in 1911 one was purchased for the Austrian Army. In 1912 made a world's altitude. Passenger record, 4,530 metres (14,862 feet.)
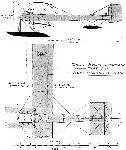
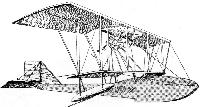
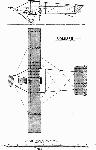
MERCEP Monoplanes. Mihalis Mercep, Aeroplanwerkstatte, Agram, Hungary. Russjan was connected with this firm, which built biplanes to his designs in 1909. Russjan was killed in the second of these. In 1911, a Mercep was built.
1911. 1912-13.
Length feet (m.) 29-1/2 9 23 7
Span feet (m.) 34-1/3 10.50 32-1/2 10
Area sq. feet (m^2) 204 19
(machine, etc. lbs. (kgs.) 617 280
Weight
(useful lbs. (kgs.) 661 300
Motor h.p. 50 Gnome
Number built 1 1
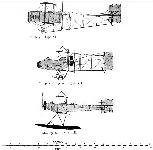
[Illustration: Mercep. 1912-13.]
1911. 1912-13.
Length feet (m.) 29-1/2 9 23 7
Span feet (m.) 34-1/3 10.50 32-1/2 10
Area sq. feet (m^2) 204 19
(machine, etc. lbs. (kgs.) 617 280
Weight
(useful lbs. (kgs.) 661 300
Motor h.p. 50 Gnome
Number built 1 1
[Illustration: Mercep. 1912-13.]
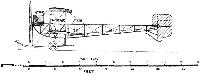
1910 Mercep-Rusjan monoplane
Country of Origin: Slovenia (in 1910 Austro-Hungarian Empire) Designed and built by M.Mercep and E.and J. Rusjan
Span: 46'
Country of Origin: Slovenia (in 1910 Austro-Hungarian Empire) Designed and built by M.Mercep and E.and J. Rusjan
Span: 46'
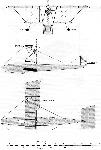
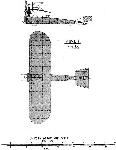
WARCHALOWSKI, Biplane. Karl Warchalowski, Autoplan Werke, Odoakergasse 35, Vienna XVI.
A machine generally on M. Farman lines, but with different shaped ailerons and corners of the leading edge rounded.
A machine generally on M. Farman lines, but with different shaped ailerons and corners of the leading edge rounded.
AUSTRIAN AEROPLANES.
ZIEGLER Monoplane. Flugzengwerke Johann Ziegler, Vienna.
1912-13.
Length........feet (m.) 59 (18)
Span..........feet (m.) 42? (13)
Area.......sq.feet(m^2.) 586 (55)
( total 1656 (750)
Weight (
( useful ...
Motor............. h.p. 100 Mercedes
Speed......m.p.h.(k.m.) 50 (80)
Number built during 1912 2
GERMAN AEROPLANES.
ZIEGLER. Ziegler, Potsdam. Established late in 1912.
1912-13.
Monoplane.
Length.........feet (m.) 31 (9.50)
Span...........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12)
Area......sq. feet (m?.) 344 (32)
Weight,
total...lbs. (kgs.) 881 (400)
useful...lbs. (kgs.) 992 (450)
Motor...............h.p. 100 N.A.G.
Speed, max...m.p.h.(km.) 60 (90)
min..m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance...........hrs. 2
Number built in 1912... 1
Type 1911. 1912.
Bleriot-Hanriot type. Bleriot type.
Length.............. 26? feet (8.15 m.) 28 feet (8.47 m.)
Span................ 29 feet (8.80 m.) 30 feet (9.35 m.)
Area................ 206 sq.ft. (19.20 m^2.) 194 sq.ft. (18 m^2.)
Weight (total)...... 705 lbs. (320 kgs.) 617 lbs. (280 kgs.)
Motor (h.p.)........ 25 Anzani 50 Gnome
Speed (p.h.)........ 46? m. (75 km.) 50 m. (80 km.)
Note. Both fly well. Description in Boletin de Ae.C. Argentino.
BEHUEGHE (Bron), in Herseun. Built in 1912. A monoplane that flew very well at camp of Casteau Aerodrome during May--October. Motor.--25. h.p. type Morane. New designs in wing construction, landing chassis, etc.
A. BRACKE (formerly Bracke, Missyon & Co.), Casteau, Mons. In 1910, constructed the first aeroplane built by a Belgium firm--a monoplane with planes at 120. This machine has not been duplicated: but the firm have since built machines to private specifications. The only firm which has in Belgium the speciality of aeronautical patents.
DE BROUCKERE, 23 rue Joardens, Brussels. Biplane. H. Farman. type. Built in 1911, modified in 1912.
DE LA HAULT Adhemar de la Hault, 214 rue Royale, Brussels. In 1906, built a flapper of novel design. This was followed in 1910, by a machine on monoplane lines with one fixed plane and two flapping wings. This failed to fly, and in August, 1911, was altered into a biplane. It did not succeed, however. M. Hault is still pursuing the ornithopter question.
Janes, 1913.
DE LA HAULT Adhemar de la Hault, 214 rue Royale, Brussels. In 1906, built a flapper of novel design. This was followed in 1910, by a machine on monoplane lines with one fixed plane and two flapping wings. This failed to fly, and in August, 1911, was altered into a biplane. It did not succeed, however. M. Hault is still pursuing the ornithopter question.
DE LA HAULT Adhemar de la Hault, 214 rue Royale, Brussels. In 1906, built a flapper of novel design. This was followed in 1910, by a machine on monoplane lines with one fixed plane and two flapping wings. This failed to fly, and in August, 1911, was altered into a biplane. It did not succeed, however. M. Hault is still pursuing the ornithopter question.
HAREL I. Biplane. Length.--49? feet (15 m.) Surface.--344-1/3 sq. feet (32 m^2.) Weight.--771 lbs. (350 kgs.), flying order. Warping wings. Monoplane tail. Motor.--50 h.p. Gnome, mounted just under and forward of the upper wing. Tractor.-- 1 Chauviere. Elevator placed 1 in front and 1 in rear, H. Farman style. Rudders, 2 in rear. Completed May, 1911. For further details see Conquete de l'Air, July 1st, 1911. Property of M. Van der Stegen.
WILLIAMS. Biplane. Motor.--70 h.p. E.N.V. Generally of headless Voisin type on a Farman body. Completed 1911. Has flown fairly well.
AVRO (1906). This 24 h.p. biplane, designed by A.V. Roe, was the first British machine to leave the ground.
1908 AVROE biplane - was longtime considered the first flying British plane
Country of Origin: U.K. Designed and built by A.V.Roe
Span: 33'3" Length: 23' Weight: 600 lb
Country of Origin: U.K. Designed and built by A.V.Roe
Span: 33'3" Length: 23' Weight: 600 lb
AVRO. Aeroplanes. A.V. Roe & Co., Clifton Street, Miles Platting, Manchester; also Shoreham, Sussex. A.V. Roe designed his first machine, a biplane, in 1906. It was the first British machine to leave the ground. He then experimented with triplanes in Lea Marshes, where he managed to fly with only 9 h.p. in 1908-9. In August, 1910, built Roe III, and in September, Roe IV, also triplanes (see 1911 edition for full details). In 1911 he abandoned triplanes for the Avro biplane. School: Shoreham.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
AVRO. Aeroplanes. A.V. Roe & Co., Clifton Street, Miles Platting, Manchester; also Shoreham, Sussex. A.V. Roe designed his first machine, a biplane, in 1906. It was the first British machine to leave the ground. He then experimented with triplanes in Lea Marshes, where he managed to fly with only 9 h.p. in 1908-9. In August, 1
910, built Roe III, and in September, Roe IV, also triplanes (see 1911 edition for full details). In 1911 he abandoned triplanes for the Avro biplane. School: Shoreham.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
910, built Roe III, and in September, Roe IV, also triplanes (see 1911 edition for full details). In 1911 he abandoned triplanes for the Avro biplane. School: Shoreham.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
AVRO. Aeroplanes. A.V. Roe & Co., Clifton Street, Miles Platting, Manchester; also Shoreham, Sussex. A.V. Roe designed his first machine, a biplane, in 1906. It was the first British machine to leave the ground. He then experimented with triplanes in Lea Marshes, where he managed to fly with only 9 h.p. in 1908-9. In August, 1910, built Roe III, and in September, Roe IV, also triplanes (see 1911 edition for full details). In 1911 he abandoned triplanes for the Avro biplane. School: Shoreham.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
AVRO. Aeroplanes. A.V. Roe & Co., Clifton Street, Miles Platting, Manchester; also Shoreham, Sussex. A.V. Roe designed his first machine, a biplane, in 1906. It was the first British machine to leave the ground. He then experimented with triplanes in Lea Marshes, where he managed to fly with only 9 h.p. in 1908-9. In August, 1910, built Roe III, and in September, Roe IV, also triplanes (see 1911 edition for full details). In 1911 he abandoned triplanes for the Avro biplane. School: Shoreham.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
D 1911-12. E 1912. F 1912. G 1912-13. E 1912-13.
Model. 2-seater 2-seater Totally Totally Hydro-biplane.
biplane. biplane. enclosed enclosed
mono. biplane.
Length.....feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29 (8.84) 23 (7) 29 (8.84) 33 (10)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 30 (11) 28 (8.50) 36 (11) 47-1/2 (14.50)
Area....sq.ft.(m^2.) 279 (26) 335 (32) 158 (14-1/2) 335 (32) 478 (34-1/2)
Weight, empty lbs.(kgs.) 800 (363) 900 (482) 550 (249) 1191 (540) 1740 (789)
Weight, fully loaded, lbs. (kgs.) ... 1300 (589) 800 (363) 1700 (771) 2700 (1224)
Motor...........h.p. 35, any 50 Gnome 40 Viale 60 Green 100 Gnome
make
Speed....m.p.h. (km.) 48 (78) 61 (97) 65 (105) 61.8 (100) 55 (90)
Number built
during 1912....... several 6 1 1 1
Remarks.--Of the above, 4 of the 50 Gnome E type were purchased by the British Royal Flying Corps, and one by the Portuguese Government; the other went to Windermere on January, 1913, for hydro experiments. Climbing speed of this type is 440 feet per min. (134 m.) Dual control fitted. D type are no longer being built. Climbing speed of F type, 300 feet per min. (91.5 m.) Gliding angle, 1 in 6. G has a gliding angle 1 in 6.5. On October 24th, 1912, made British record to date, 7'31-1/2" (=450 miles). The hydro. was delivered to the British R.F.C. naval wing early in 1913.
The Avro Type G cabin biplane, 60 hp Green engine, at Larkhill at the Military Trials in August 1912.
The latest type 60-h.p, Gnome Blackburn monoplane with which Mr. Cyril Foggin, together with Mr. Harold Blackburn, has been giving exhibitions in Leeds at Easter. This new Blackburn model has shown some excellent flying qualities, and is very stable in adverse winds. It is a quick climber, and has a fine turn of speed.
BLACKBURN Aeroplanes. Blackburn Aeroplane Co., Balm Road, Leeds. Blackburn produced his first machine early in 1910 (see 1911 edition for details). In the latter part of that year he designed the machine which ultimately developed into the Blackburn military. In 1911 other types were produced, all being fitted with the patent Blackburn triple control. School at Filey. Hucks has been the principal Blackburn flyer. The type has also been very successfully flown by naval officers. Capacity of works: about 24 a year.
1912-13 1912-13 1913.
Military. 2-seater. Military. 1-seater Hydro-biplane.
2-seater
Length.............. 32 feet (9.75 m.) 5 feet (7.60 m.) 33 feet (10 m.)
Span................ 40 feet (12.20 m.) 32 feet (9.75 m.) 44 & 36 ft
(13.4 & 11 m.)
Area ............... 276 sq.ft. (26 m?.) 195 sq.ft. (18 m?.) 410 sq.ft. (38 m?.)
Weight (total)...... ... 750 lbs. (340 kgs.) 1250 lbs. (507 kgs.)
Motor...........h.p. ... 50 Gnome. 80 Gnome or
100 Anzani
Speed............... 55-65 m. 60 m. (97 km.) 65 m. (105 km.)
(90-105 km.)
Notes.--Petrol for 5 hours (higher endurances can be fitted). Specially designed for military work--all steel construction. All parts unwelded to admit of rapid displacement. Clear observation provided for.
Fuselage.--The fuselage is V shaped and constructed of weldless steel tubing in the form of a lattice girder. The main longitudinals are of round section; cross members, oval section. Connections are not welded but made with strong steel clips so that should any member become damaged a new one can be readily arranged. The front portion is covered with sheet metal giving additional strength and reducing the head resistance. Stream line form tapering towards the rear which is covered with fabric.
Chassis.--Two long skids connected up to fuselage by metal struts. Each skid borne by a pair of wheels, axle held down by elastic shock absorbers. On the axle of the wheels are fitted steel springs which take side thrust. Each pair of wheels held by radius rods forming a bogie.
Control.--Patent Blackburn triple, independent or simultaneous on hand wheel, but special foot control for rudder is fitted if desired.
In 1912, five machines were built, of which two were of the mil. model. Others, non-military models (see last edition.)
1912-13 1912-13 1913.
Military. 2-seater. Military. 1-seater Hydro-biplane.
2-seater
Length.............. 32 feet (9.75 m.) 5 feet (7.60 m.) 33 feet (10 m.)
Span................ 40 feet (12.20 m.) 32 feet (9.75 m.) 44 & 36 ft
(13.4 & 11 m.)
Area ............... 276 sq.ft. (26 m?.) 195 sq.ft. (18 m?.) 410 sq.ft. (38 m?.)
Weight (total)...... ... 750 lbs. (340 kgs.) 1250 lbs. (507 kgs.)
Motor...........h.p. ... 50 Gnome. 80 Gnome or
100 Anzani
Speed............... 55-65 m. 60 m. (97 km.) 65 m. (105 km.)
(90-105 km.)
Notes.--Petrol for 5 hours (higher endurances can be fitted). Specially designed for military work--all steel construction. All parts unwelded to admit of rapid displacement. Clear observation provided for.
Fuselage.--The fuselage is V shaped and constructed of weldless steel tubing in the form of a lattice girder. The main longitudinals are of round section; cross members, oval section. Connections are not welded but made with strong steel clips so that should any member become damaged a new one can be readily arranged. The front portion is covered with sheet metal giving additional strength and reducing the head resistance. Stream line form tapering towards the rear which is covered with fabric.
Chassis.--Two long skids connected up to fuselage by metal struts. Each skid borne by a pair of wheels, axle held down by elastic shock absorbers. On the axle of the wheels are fitted steel springs which take side thrust. Each pair of wheels held by radius rods forming a bogie.
Control.--Patent Blackburn triple, independent or simultaneous on hand wheel, but special foot control for rudder is fitted if desired.
In 1912, five machines were built, of which two were of the mil. model. Others, non-military models (see last edition.)
BLACKBURN Aeroplanes. Blackburn Aeroplane Co., Balm Road, Leeds. Blackburn produced his first machine early in 1910 (see 1911 edition for details). In the latter part of that year he designed the machine which ultimately developed into the Blackburn military. In 1911 other types were produced, all being fitted with the patent Blackburn triple control. School at Filey. Hucks has been the principal Blackburn flyer. The type has also been very successfully flown by naval officers. Capacity of works: about 24 a year.
1912-13 1912-13 1913.
Military. 2-seater. Military. 1-seater Hydro-biplane.
2-seater
Length.............. 32 feet (9.75 m.) 5 feet (7.60 m.) 33 feet (10 m.)
Span................ 40 feet (12.20 m.) 32 feet (9.75 m.) 44 & 36 ft
(13.4 & 11 m.)
Area ............... 276 sq.ft. (26 m?.) 195 sq.ft. (18 m?.) 410 sq.ft. (38 m?.)
Weight (total)...... ... 750 lbs. (340 kgs.) 1250 lbs. (507 kgs.)
Motor...........h.p. ... 50 Gnome. 80 Gnome or
100 Anzani
Speed............... 55-65 m. 60 m. (97 km.) 65 m. (105 km.)
(90-105 km.)
Notes.--Petrol for 5 hours (higher endurances can be fitted). Specially designed for military work--all steel construction. All parts unwelded to admit of rapid displacement. Clear observation provided for.
Fuselage.--The fuselage is V shaped and constructed of weldless steel tubing in the form of a lattice girder. The main longitudinals are of round section; cross members, oval section. Connections are not welded but made with strong steel clips so that should any member become damaged a new one can be readily arranged. The front portion is covered with sheet metal giving additional strength and reducing the head resistance. Stream line form tapering towards the rear which is covered with fabric.
Chassis.--Two long skids connected up to fuselage by metal struts. Each skid borne by a pair of wheels, axle held down by elastic shock absorbers. On the axle of the wheels are fitted steel springs which take side thrust. Each pair of wheels held by radius rods forming a bogie.
Control.--Patent Blackburn triple, independent or simultaneous on hand wheel, but special foot control for rudder is fitted if desired.
In 1912, five machines were built, of which two were of the mil. model. Others, non-military models (see last edition.)
1912-13 1912-13 1913.
Military. 2-seater. Military. 1-seater Hydro-biplane.
2-seater
Length.............. 32 feet (9.75 m.) 5 feet (7.60 m.) 33 feet (10 m.)
Span................ 40 feet (12.20 m.) 32 feet (9.75 m.) 44 & 36 ft
(13.4 & 11 m.)
Area ............... 276 sq.ft. (26 m?.) 195 sq.ft. (18 m?.) 410 sq.ft. (38 m?.)
Weight (total)...... ... 750 lbs. (340 kgs.) 1250 lbs. (507 kgs.)
Motor...........h.p. ... 50 Gnome. 80 Gnome or
100 Anzani
Speed............... 55-65 m. 60 m. (97 km.) 65 m. (105 km.)
(90-105 km.)
Notes.--Petrol for 5 hours (higher endurances can be fitted). Specially designed for military work--all steel construction. All parts unwelded to admit of rapid displacement. Clear observation provided for.
Fuselage.--The fuselage is V shaped and constructed of weldless steel tubing in the form of a lattice girder. The main longitudinals are of round section; cross members, oval section. Connections are not welded but made with strong steel clips so that should any member become damaged a new one can be readily arranged. The front portion is covered with sheet metal giving additional strength and reducing the head resistance. Stream line form tapering towards the rear which is covered with fabric.
Chassis.--Two long skids connected up to fuselage by metal struts. Each skid borne by a pair of wheels, axle held down by elastic shock absorbers. On the axle of the wheels are fitted steel springs which take side thrust. Each pair of wheels held by radius rods forming a bogie.
Control.--Patent Blackburn triple, independent or simultaneous on hand wheel, but special foot control for rudder is fitted if desired.
In 1912, five machines were built, of which two were of the mil. model. Others, non-military models (see last edition.)
BLACKBURN Aeroplanes. Blackburn Aeroplane Co., Balm Road, Leeds. Blackburn produced his first machine early in 1910 (see 1911 edition for details). In the latter part of that year he designed the machine which ultimately developed into the Blackburn military. In 1911 other types were produced, all being fitted with the patent Blackburn triple control. School at Filey. Hucks has been the principal Blackburn flyer. The type has also been very successfully flown by naval officers. Capacity of works: about 24 a year.
1912-13 1912-13 1913.
Military. 2-seater. Military. 1-seater Hydro-biplane.
2-seater
Length.............. 32 feet (9.75 m.) 5 feet (7.60 m.) 33 feet (10 m.)
Span................ 40 feet (12.20 m.) 32 feet (9.75 m.) 44 & 36 ft
(13.4 & 11 m.)
Area ............... 276 sq.ft. (26 m?.) 195 sq.ft. (18 m?.) 410 sq.ft. (38 m?.)
Weight (total)...... ... 750 lbs. (340 kgs.) 1250 lbs. (507 kgs.)
Motor...........h.p. ... 50 Gnome. 80 Gnome or
100 Anzani
Speed............... 55-65 m. 60 m. (97 km.) 65 m. (105 km.)
(90-105 km.)
Notes.--Petrol for 5 hours (higher endurances can be fitted). Specially designed for military work--all steel construction. All parts unwelded to admit of rapid displacement. Clear observation provided for.
Fuselage.--The fuselage is V shaped and constructed of weldless steel tubing in the form of a lattice girder. The main longitudinals are of round section; cross members, oval section. Connections are not welded but made with strong steel clips so that should any member become damaged a new one can be readily arranged. The front portion is covered with sheet metal giving additional strength and reducing the head resistance. Stream line form tapering towards the rear which is covered with fabric.
Chassis.--Two long skids connected up to fuselage by metal struts. Each skid borne by a pair of wheels, axle held down by elastic shock absorbers. On the axle of the wheels are fitted steel springs which take side thrust. Each pair of wheels held by radius rods forming a bogie.
Control.--Patent Blackburn triple, independent or simultaneous on hand wheel, but special foot control for rudder is fitted if desired.
In 1912, five machines were built, of which two were of the mil. model. Others, non-military models (see last edition.)
1912-13 1912-13 1913.
Military. 2-seater. Military. 1-seater Hydro-biplane.
2-seater
Length.............. 32 feet (9.75 m.) 5 feet (7.60 m.) 33 feet (10 m.)
Span................ 40 feet (12.20 m.) 32 feet (9.75 m.) 44 & 36 ft
(13.4 & 11 m.)
Area ............... 276 sq.ft. (26 m?.) 195 sq.ft. (18 m?.) 410 sq.ft. (38 m?.)
Weight (total)...... ... 750 lbs. (340 kgs.) 1250 lbs. (507 kgs.)
Motor...........h.p. ... 50 Gnome. 80 Gnome or
100 Anzani
Speed............... 55-65 m. 60 m. (97 km.) 65 m. (105 km.)
(90-105 km.)
Notes.--Petrol for 5 hours (higher endurances can be fitted). Specially designed for military work--all steel construction. All parts unwelded to admit of rapid displacement. Clear observation provided for.
Fuselage.--The fuselage is V shaped and constructed of weldless steel tubing in the form of a lattice girder. The main longitudinals are of round section; cross members, oval section. Connections are not welded but made with strong steel clips so that should any member become damaged a new one can be readily arranged. The front portion is covered with sheet metal giving additional strength and reducing the head resistance. Stream line form tapering towards the rear which is covered with fabric.
Chassis.--Two long skids connected up to fuselage by metal struts. Each skid borne by a pair of wheels, axle held down by elastic shock absorbers. On the axle of the wheels are fitted steel springs which take side thrust. Each pair of wheels held by radius rods forming a bogie.
Control.--Patent Blackburn triple, independent or simultaneous on hand wheel, but special foot control for rudder is fitted if desired.
In 1912, five machines were built, of which two were of the mil. model. Others, non-military models (see last edition.)
BRISTOL. The British & Colonial Aeroplane Co., Ltd., Filton House, Bristol. Founded 1910. Capital (1913), Have very extensive works (area. sq. feet) on the outskirts of Bristol, employing over 300 men, where they manufacture to their own designs practically every type of flying machine. Flying grounds: Salisbury Plain, Brooklands. 105 Royal Aero Club certificates won on Bristol machines during 1912 (of which 86 were officers of His Majesty's Forces).
Military Military Tractor School
mono. mono. biplane mono.
2-seater. 2-seater. 1913 Side by side.
80 h.p. 50 h.p.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Length feet (m.) 28-1/4 8.60 23-2/3 7.20 27-3/4 8.47
Span feet (m.) 42-1/3 12.90 39-1/3 12 34-1/3 10.44
Area sq. feet (m^2.) 221 20.6 226 22 370 34.4
Total weight, machine, lbs. (kgs.) 1719 771 1323 600 1764 800
Total weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) 710 322 551 250 1200 544
Motor h.p. 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Renault 50 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 73 118 62 100 70 112
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... ... ...
Endurance hrs. 4 3-4 ...
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Notes.--Monoplane: Box section fuselage convex on bottom side to minimise resistance. Mounted on 2 wheels and 2 skids with smaller wheels attached at the forward end. Bristol tractor. Biplane: Box section fuselage, convex on top and bottom sides. Mounted as monoplane. Bristol tractor. This machine is the latest production of the Bristol Co., and has proved an exceptionally successful flyer. Designed by M. Coanda.
Military Military Tractor School
mono. mono. biplane mono.
2-seater. 2-seater. 1913 Side by side.
80 h.p. 50 h.p.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Length feet (m.) 28-1/4 8.60 23-2/3 7.20 27-3/4 8.47
Span feet (m.) 42-1/3 12.90 39-1/3 12 34-1/3 10.44
Area sq. feet (m^2.) 221 20.6 226 22 370 34.4
Total weight, machine, lbs. (kgs.) 1719 771 1323 600 1764 800
Total weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) 710 322 551 250 1200 544
Motor h.p. 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Renault 50 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 73 118 62 100 70 112
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... ... ...
Endurance hrs. 4 3-4 ...
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Notes.--Monoplane: Box section fuselage convex on bottom side to minimise resistance. Mounted on 2 wheels and 2 skids with smaller wheels attached at the forward end. Bristol tractor. Biplane: Box section fuselage, convex on top and bottom sides. Mounted as monoplane. Bristol tractor. This machine is the latest production of the Bristol Co., and has proved an exceptionally successful flyer. Designed by M. Coanda.
BRISTOL. The British & Colonial Aeroplane Co., Ltd., Filton House, Bristol. Founded 1910. Capital (1913), Have very extensive works (area. sq. feet) on the outskirts of Bristol, employing over 300 men, where they manufacture to their own designs practically every type of flying machine. Flying grounds: Salisbury Plain, Brooklands. 105 Royal Aero Club certificates won on Bristol machines during 1912 (of which 86 were officers of His Majesty's Forces).
Military Military Tractor School
mono. mono. biplane mono.
2-seater. 2-seater. 1913 Side by side.
80 h.p. 50 h.p.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Length feet (m.) 28-1/4 8.60 23-2/3 7.20 27-3/4 8.47
Span feet (m.) 42-1/3 12.90 39-1/3 12 34-1/3 10.44
Area sq. feet (m^2.) 221 20.6 226 22 370 34.4
Total weight, machine, lbs. (kgs.) 1719 771 1323 600 1764 800
Total weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) 710 322 551 250 1200 544
Motor h.p. 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Renault 50 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 73 118 62 100 70 112
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... ... ...
Endurance hrs. 4 3-4 ...
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Notes.--Monoplane: Box section fuselage convex on bottom side to minimise resistance. Mounted on 2 wheels and 2 skids with smaller wheels attached at the forward end. Bristol tractor. Biplane: Box section fuselage, convex on top and bottom sides. Mounted as monoplane. Bristol tractor. This machine is the latest production of the Bristol Co., and has proved an exceptionally successful flyer. Designed by M. Coanda.
Military Military Tractor School
mono. mono. biplane mono.
2-seater. 2-seater. 1913 Side by side.
80 h.p. 50 h.p.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Length feet (m.) 28-1/4 8.60 23-2/3 7.20 27-3/4 8.47
Span feet (m.) 42-1/3 12.90 39-1/3 12 34-1/3 10.44
Area sq. feet (m^2.) 221 20.6 226 22 370 34.4
Total weight, machine, lbs. (kgs.) 1719 771 1323 600 1764 800
Total weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) 710 322 551 250 1200 544
Motor h.p. 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Renault 50 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 73 118 62 100 70 112
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... ... ...
Endurance hrs. 4 3-4 ...
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Notes.--Monoplane: Box section fuselage convex on bottom side to minimise resistance. Mounted on 2 wheels and 2 skids with smaller wheels attached at the forward end. Bristol tractor. Biplane: Box section fuselage, convex on top and bottom sides. Mounted as monoplane. Bristol tractor. This machine is the latest production of the Bristol Co., and has proved an exceptionally successful flyer. Designed by M. Coanda.
CODY (1909). Development of a much earlier machine. This one was a general laughing stock for a long time; but it was the direct predecessor of the machine (not very materially different) which was an easy first in the British Army aeroplane trials, 1912.
CODY. Cody flying school, Farnborough. Cody commenced experiments with kites in very early days on behalf of the British Admiralty. Subsequently built the first British Army dirigible, and an experimental Army aeroplane. In 1909, his direct connection with the Army ceased. A Cody I was built in 1908. A Cody II was completed June 1910. The special features of both were: very strong construction, great size (II had area of 857 sq feet), ailerons. Later types, except that warping is substituted for ailerons, do not differ very materially except in minor details. All wood construction.
1911. 1913. Model.
4-seater 4-seater May, 1912.
biplane. biplane. Monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60)
Span..............feet(m.) 43 (13) 43 (13) 43? (13.25)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 484 (44.75) 483 (44.97) 260 (19)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1900 (862) 1900 (862) 2400 (1088)
Weight,useful...lbs.(kgs.) 1000 (453) 1000 (453) 7O0
Motor................... 60 Green, 120 Aust. 120 Aust.
later a Daimler Daimler
100 Green
Speed, max......m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) 75 (120) 83 (135)
min......m.p.h.(km.) 47 (75) 47 (75) 58 (95)
Number built to
end of last year......... 1 1 1
Remarks.--The 1911 is the famous Cody, which, as a 60 h.p., won both Michelin 1911 prizes, and completed the Daily Mail circuit. As a 100 h.p. it won the 1912 Michelin cross-country. By the end of 1912 it is said to have flown a total of 7000 miles. The 1913 is practically a duplicate with a more powerful engine. Special features of the biplanes, maximum camber to lower plane. Both planes equal span. Very strong landing gear. Propeller chain driven: 1-3/4 to 1 gearing. In February, 1913, four biplanes were ordered for the British Army.
Cody lists a mono. for 1913 a trifle longer than the above; also five variations on the biplane of from 35 to 160 h.p., which can be built if required.
1911. 1913. Model.
4-seater 4-seater May, 1912.
biplane. biplane. Monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60)
Span..............feet(m.) 43 (13) 43 (13) 43? (13.25)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 484 (44.75) 483 (44.97) 260 (19)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1900 (862) 1900 (862) 2400 (1088)
Weight,useful...lbs.(kgs.) 1000 (453) 1000 (453) 7O0
Motor................... 60 Green, 120 Aust. 120 Aust.
later a Daimler Daimler
100 Green
Speed, max......m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) 75 (120) 83 (135)
min......m.p.h.(km.) 47 (75) 47 (75) 58 (95)
Number built to
end of last year......... 1 1 1
Remarks.--The 1911 is the famous Cody, which, as a 60 h.p., won both Michelin 1911 prizes, and completed the Daily Mail circuit. As a 100 h.p. it won the 1912 Michelin cross-country. By the end of 1912 it is said to have flown a total of 7000 miles. The 1913 is practically a duplicate with a more powerful engine. Special features of the biplanes, maximum camber to lower plane. Both planes equal span. Very strong landing gear. Propeller chain driven: 1-3/4 to 1 gearing. In February, 1913, four biplanes were ordered for the British Army.
Cody lists a mono. for 1913 a trifle longer than the above; also five variations on the biplane of from 35 to 160 h.p., which can be built if required.
CODY. Cody flying school, Farnborough. Cody commenced experiments with kites in very early days on behalf of the British Admiralty. Subsequently built the first British Army dirigible, and an experimental Army aeroplane. In 1909, his direct connection with the Army ceased. A Cody I was built in 1908. A Cody II was completed June 1910. The special features of both were: very strong construction, great size (II had area of 857 sq feet), ailerons. Later types, except that warping is substituted for ailerons, do not differ very materially except in minor details. All wood construction.
1911. 1913. Model.
4-seater 4-seater May, 1912.
biplane. biplane. Monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60)
Span..............feet(m.) 43 (13) 43 (13) 43? (13.25)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 484 (44.75) 483 (44.97) 260 (19)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1900 (862) 1900 (862) 2400 (1088)
Weight,useful...lbs.(kgs.) 1000 (453) 1000 (453) 7O0
Motor................... 60 Green, 120 Aust. 120 Aust.
later a Daimler Daimler
100 Green
Speed, max......m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) 75 (120) 83 (135)
min......m.p.h.(km.) 47 (75) 47 (75) 58 (95)
Number built to
end of last year......... 1 1 1
Remarks.--The 1911 is the famous Cody, which, as a 60 h.p., won both Michelin 1911 prizes, and completed the Daily Mail circuit. As a 100 h.p. it won the 1912 Michelin cross-country. By the end of 1912 it is said to have flown a total of 7000 miles. The 1913 is practically a duplicate with a more powerful engine. Special features of the biplanes, maximum camber to lower plane. Both planes equal span. Very strong landing gear. Propeller chain driven: 1-3/4 to 1 gearing. In February, 1913, four biplanes were ordered for the British Army.
Cody lists a mono. for 1913 a trifle longer than the above; also five variations on the biplane of from 35 to 160 h.p., which can be built if required.
1911. 1913. Model.
4-seater 4-seater May, 1912.
biplane. biplane. Monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60) 38 (11.60)
Span..............feet(m.) 43 (13) 43 (13) 43? (13.25)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 484 (44.75) 483 (44.97) 260 (19)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1900 (862) 1900 (862) 2400 (1088)
Weight,useful...lbs.(kgs.) 1000 (453) 1000 (453) 7O0
Motor................... 60 Green, 120 Aust. 120 Aust.
later a Daimler Daimler
100 Green
Speed, max......m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) 75 (120) 83 (135)
min......m.p.h.(km.) 47 (75) 47 (75) 58 (95)
Number built to
end of last year......... 1 1 1
Remarks.--The 1911 is the famous Cody, which, as a 60 h.p., won both Michelin 1911 prizes, and completed the Daily Mail circuit. As a 100 h.p. it won the 1912 Michelin cross-country. By the end of 1912 it is said to have flown a total of 7000 miles. The 1913 is practically a duplicate with a more powerful engine. Special features of the biplanes, maximum camber to lower plane. Both planes equal span. Very strong landing gear. Propeller chain driven: 1-3/4 to 1 gearing. In February, 1913, four biplanes were ordered for the British Army.
Cody lists a mono. for 1913 a trifle longer than the above; also five variations on the biplane of from 35 to 160 h.p., which can be built if required.
COVENTRY ORDNANCE. The Coventry Ordnance Works, Ltd., Coventry. London office: 28, Broadway, Westminster, S.W. Established 1912. Capacity: 50 machines a year without difficulty.
1912.
Model 10.
----------------------------------------------------
Length...............feet(m.) 29 (8.80)
Span.................feet(m.) 56 (17)
Area............sq. feet(m?.) 630 (58)
Weight, total......lbs.(kgs.) 1900 (861)
useful.....lbs.(kgs.) 800 (362)
Motor....................h.p. 100 Gnome
Speed, max........m.p.h.(km.) 60 (97)
min........m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance................hrs. ...
Number Built during 1912 .... 2
Remarks.--Experimental machines.
1912.
Model 10.
----------------------------------------------------
Length...............feet(m.) 29 (8.80)
Span.................feet(m.) 56 (17)
Area............sq. feet(m?.) 630 (58)
Weight, total......lbs.(kgs.) 1900 (861)
useful.....lbs.(kgs.) 800 (362)
Motor....................h.p. 100 Gnome
Speed, max........m.p.h.(km.) 60 (97)
min........m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance................hrs. ...
Number Built during 1912 .... 2
Remarks.--Experimental machines.
DUNNE. The Blair Atholl Aeroplane Syndicate, Ltd., 1, Queen Victoria Street, London, E.C. School: Eastchurch. In 1906 Lieut. Dunne was employed by the British Army authorities for secret aeroplane experiments. He had at that time patented a monoplane of arrow type. In 1907 Dunne I was tried on the Duke of Atholl's estate in Scotland, but failed to fly, being smashed on the starting apparatus. Dunne III, a glider, 1908, was experimented with successfully by Lieut. Gibbs. In the same year Dunne IV, a larger power driven edition made hops of 50 yards or so. Early in 1910 the War Office abandoned the experiments. Dunne II, a triplane of 1906 design, was, by consent of the War Office, assigned to Prof. Huntingdon, who made one or two short flights with it at Sastchurch in 1910. At the same time the above syndicate was formed, and Dunne V, built by Short Bros., was completed in June, 1910. In 1912-13 the Huntingdon, modified, was flying well.
50 Gnome.
1912-13 1912-13 1912-13 1912-13
Model and Date. single-seat 2-seater biplane biplane
mono. mono D8. D9.
D7. D7<i>bis.</i>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Length........feet(m.) <i>not given</i> ... ... ...
Span..........feet(m.) 35 (10.66) 85 (10.66) 46 (14) 45 (13.70)
Area......sq.feet(m?.) 200 (18.5) 200 (18.5) 552 (51) 448 (42)
Weight, total,
............lbs.(kgs.) 1050 (476) 1200 (544) 1700 (774) 1693 (768)
Weight, useful
............lbs.(kgs.) 359 (161) 528 (230) 414 (187) 509 (231)
Motor.............h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 60 Green 80 Gnome
Speed......m.p.h.(km.) 60 (95) 60 (95) 45 (70) 50 (80)
Number built during 1912 1 1 1 5
building
('13)
Notes.--Biplane D 8 is identical with the original pattern Dunne V, except that it has only one propeller instead of two. It has been flown completely uncontrolled in a 20 m.p.h. wind, carrying a R.Ae.C. observer as passenger.
50 Gnome.
1912-13 1912-13 1912-13 1912-13
Model and Date. single-seat 2-seater biplane biplane
mono. mono D8. D9.
D7. D7<i>bis.</i>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Length........feet(m.) <i>not given</i> ... ... ...
Span..........feet(m.) 35 (10.66) 85 (10.66) 46 (14) 45 (13.70)
Area......sq.feet(m?.) 200 (18.5) 200 (18.5) 552 (51) 448 (42)
Weight, total,
............lbs.(kgs.) 1050 (476) 1200 (544) 1700 (774) 1693 (768)
Weight, useful
............lbs.(kgs.) 359 (161) 528 (230) 414 (187) 509 (231)
Motor.............h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 60 Green 80 Gnome
Speed......m.p.h.(km.) 60 (95) 60 (95) 45 (70) 50 (80)
Number built during 1912 1 1 1 5
building
('13)
Notes.--Biplane D 8 is identical with the original pattern Dunne V, except that it has only one propeller instead of two. It has been flown completely uncontrolled in a 20 m.p.h. wind, carrying a R.Ae.C. observer as passenger.
DUNNE. The Blair Atholl Aeroplane Syndicate, Ltd., 1, Queen Victoria Street, London, E.C. School: Eastchurch. In 1906 Lieut. Dunne was employed by the British Army authorities for secret aeroplane experiments. He had at that time patented a monoplane of arrow type. In 1907 Dunne I was tried on the Duke of Atholl's estate in Scotland, but failed to fly, being smashed on the starting apparatus. Dunne III, a glider, 1908, was experimented with successfully by Lieut. Gibbs. In the same year Dunne IV, a larger power driven edition made hops of 50 yards or so. Early in 1910 the War Office abandoned the experiments. Dunne II, a triplane of 1906 design, was, by consent of the War Office, assigned to Prof. Huntingdon, who made one or two short flights with it at Sastchurch in 1910. At the same time the above syndicate was formed, and Dunne V, built by Short Bros., was completed in June, 1910. In 1912-13 the Huntingdon, modified, was flying well.
50 Gnome.
1912-13 1912-13 1912-13 1912-13
Model and Date. single-seat 2-seater biplane biplane
mono. mono D8. D9.
D7. D7<i>bis.</i>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Length........feet(m.) <i>not given</i> ... ... ...
Span..........feet(m.) 35 (10.66) 85 (10.66) 46 (14) 45 (13.70)
Area......sq.feet(m?.) 200 (18.5) 200 (18.5) 552 (51) 448 (42)
Weight, total,
............lbs.(kgs.) 1050 (476) 1200 (544) 1700 (774) 1693 (768)
Weight, useful
............lbs.(kgs.) 359 (161) 528 (230) 414 (187) 509 (231)
Motor.............h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 60 Green 80 Gnome
Speed......m.p.h.(km.) 60 (95) 60 (95) 45 (70) 50 (80)
Number built during 1912 1 1 1 5
building
('13)
Notes.--Biplane D 8 is identical with the original pattern Dunne V, except that it has only one propeller instead of two. It has been flown completely uncontrolled in a 20 m.p.h. wind, carrying a R.Ae.C. observer as passenger.
50 Gnome.
1912-13 1912-13 1912-13 1912-13
Model and Date. single-seat 2-seater biplane biplane
mono. mono D8. D9.
D7. D7<i>bis.</i>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Length........feet(m.) <i>not given</i> ... ... ...
Span..........feet(m.) 35 (10.66) 85 (10.66) 46 (14) 45 (13.70)
Area......sq.feet(m?.) 200 (18.5) 200 (18.5) 552 (51) 448 (42)
Weight, total,
............lbs.(kgs.) 1050 (476) 1200 (544) 1700 (774) 1693 (768)
Weight, useful
............lbs.(kgs.) 359 (161) 528 (230) 414 (187) 509 (231)
Motor.............h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 60 Green 80 Gnome
Speed......m.p.h.(km.) 60 (95) 60 (95) 45 (70) 50 (80)
Number built during 1912 1 1 1 5
building
('13)
Notes.--Biplane D 8 is identical with the original pattern Dunne V, except that it has only one propeller instead of two. It has been flown completely uncontrolled in a 20 m.p.h. wind, carrying a R.Ae.C. observer as passenger.
HUNTINGDON (DUNNE II) (1910). One of the earliest aeroplanes in existence--designed by Captain Dunne about 1905-06, previous to the secret experiments of the British War Office in Scotland, on the Duke of Atholl's estate. Assigned to Prof. Huntingdon in 1910. Made a few short flights.
FERGUSON. J.B. Ferguson, Ltd., Belfast.
This machine first appeared in 1910. Owing to an accident to Mr. Ferguson it was laid up for a long time. About the end of 1912 it re-appeared. Principal details:-- Span.--40 feet (12.20 m.) Area.--230 sq. feet (21 m?.) H.P. 40.
This machine first appeared in 1910. Owing to an accident to Mr. Ferguson it was laid up for a long time. About the end of 1912 it re-appeared. Principal details:-- Span.--40 feet (12.20 m.) Area.--230 sq. feet (21 m?.) H.P. 40.
HOWARD-FLANDERS. L. Howard-Flanders, Ltd., 31, Townsend Terrace, Richmond, Surrey. School: Brooklands. Established February, 1912, by Howard-Flanders, whose connection with aviation dates from the pioneer days. Richmond Works opened April, 1912. Capacity of the works at end of 1912 was sufficient to turn out from 25 to 35 machines a year.
F 4 1912. B 2 1912. S 2 1913. F 5 1913. B 3 1913.
2-seater 2-seater single-seat 2-seater 2-seater
military biplane. monoplane. monoplane. biplane.
monoplane.
Length...feet(m) 31? (9.50) 31? (9.50) 28 (8.50) 31 (9.45) 31 (9.45)
Span....feet(m) 40 (12) 40 (12) 35 (10.70) 39 (11.90) 40 (12)
Are..sq.ft.(m?) 240 (22) 390 (36) 190 (17.75) 250 (30) 390 (36)
Weight,total...
.......lbs.(kgs) 1850 (839) 1500 (680) 1180 (585) 1600 (726) 1650 (748)
Weight, useful...
......lbs.(kgs) 500 (227) 450 (204) 350 (159) 600 (272) 600 (272)
Motor......h.p. 70 Renault 40 A.B.C. 80 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max...
.....m.p.h.(km) 67 (108) 56 (90) 82 (132) 70 (115) 68 (110)
Speed, min...
.....m.p.h.(km) 41 (66) 38 (61 ) 45 (73) 42 (68) 40 (65)
Number built
during 1912 4 1 - - -
Remarks.--F 4 climbing speed 1000 feet (305 m.) in 3? minutes, 1500 in 5? mins., 2000 in 8 mins. B 2 climbing speed 200 feet (61 m.) per minute.
The four F 4 type were bought by the British Army during 1912.
F 4 1912. B 2 1912. S 2 1913. F 5 1913. B 3 1913.
2-seater 2-seater single-seat 2-seater 2-seater
military biplane. monoplane. monoplane. biplane.
monoplane.
Length...feet(m) 31? (9.50) 31? (9.50) 28 (8.50) 31 (9.45) 31 (9.45)
Span....feet(m) 40 (12) 40 (12) 35 (10.70) 39 (11.90) 40 (12)
Are..sq.ft.(m?) 240 (22) 390 (36) 190 (17.75) 250 (30) 390 (36)
Weight,total...
.......lbs.(kgs) 1850 (839) 1500 (680) 1180 (585) 1600 (726) 1650 (748)
Weight, useful...
......lbs.(kgs) 500 (227) 450 (204) 350 (159) 600 (272) 600 (272)
Motor......h.p. 70 Renault 40 A.B.C. 80 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max...
.....m.p.h.(km) 67 (108) 56 (90) 82 (132) 70 (115) 68 (110)
Speed, min...
.....m.p.h.(km) 41 (66) 38 (61 ) 45 (73) 42 (68) 40 (65)
Number built
during 1912 4 1 - - -
Remarks.--F 4 climbing speed 1000 feet (305 m.) in 3? minutes, 1500 in 5? mins., 2000 in 8 mins. B 2 climbing speed 200 feet (61 m.) per minute.
The four F 4 type were bought by the British Army during 1912.
HOWARD-FLANDERS. L. Howard-Flanders, Ltd., 31, Townsend Terrace, Richmond, Surrey. School: Brooklands. Established February, 1912, by Howard-Flanders, whose connection with aviation dates from the pioneer days. Richmond Works opened April, 1912. Capacity of the works at end of 1912 was sufficient to turn out from 25 to 35 machines a year.
F 4 1912. B 2 1912. S 2 1913. F 5 1913. B 3 1913.
2-seater 2-seater single-seat 2-seater 2-seater
military biplane. monoplane. monoplane. biplane.
monoplane.
Length...feet(m) 31? (9.50) 31? (9.50) 28 (8.50) 31 (9.45) 31 (9.45)
Span....feet(m) 40 (12) 40 (12) 35 (10.70) 39 (11.90) 40 (12)
Are..sq.ft.(m?) 240 (22) 390 (36) 190 (17.75) 250 (30) 390 (36)
Weight,total...
.......lbs.(kgs) 1850 (839) 1500 (680) 1180 (585) 1600 (726) 1650 (748)
Weight, useful...
......lbs.(kgs) 500 (227) 450 (204) 350 (159) 600 (272) 600 (272)
Motor......h.p. 70 Renault 40 A.B.C. 80 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max...
.....m.p.h.(km) 67 (108) 56 (90) 82 (132) 70 (115) 68 (110)
Speed, min...
.....m.p.h.(km) 41 (66) 38 (61 ) 45 (73) 42 (68) 40 (65)
Number built
during 1912 4 1 - - -
Remarks.--F 4 climbing speed 1000 feet (305 m.) in 3? minutes, 1500 in 5? mins., 2000 in 8 mins. B 2 climbing speed 200 feet (61 m.) per minute.
The four F 4 type were bought by the British Army during 1912.
F 4 1912. B 2 1912. S 2 1913. F 5 1913. B 3 1913.
2-seater 2-seater single-seat 2-seater 2-seater
military biplane. monoplane. monoplane. biplane.
monoplane.
Length...feet(m) 31? (9.50) 31? (9.50) 28 (8.50) 31 (9.45) 31 (9.45)
Span....feet(m) 40 (12) 40 (12) 35 (10.70) 39 (11.90) 40 (12)
Are..sq.ft.(m?) 240 (22) 390 (36) 190 (17.75) 250 (30) 390 (36)
Weight,total...
.......lbs.(kgs) 1850 (839) 1500 (680) 1180 (585) 1600 (726) 1650 (748)
Weight, useful...
......lbs.(kgs) 500 (227) 450 (204) 350 (159) 600 (272) 600 (272)
Motor......h.p. 70 Renault 40 A.B.C. 80 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max...
.....m.p.h.(km) 67 (108) 56 (90) 82 (132) 70 (115) 68 (110)
Speed, min...
.....m.p.h.(km) 41 (66) 38 (61 ) 45 (73) 42 (68) 40 (65)
Number built
during 1912 4 1 - - -
Remarks.--F 4 climbing speed 1000 feet (305 m.) in 3? minutes, 1500 in 5? mins., 2000 in 8 mins. B 2 climbing speed 200 feet (61 m.) per minute.
The four F 4 type were bought by the British Army during 1912.
GRAHAME-WHITE. The Grahame-White Aviation Co., Ltd., 166 Piccadilly, London, W. Works and Flying Ground: Hendon. Founded by C. Grahame-White, the well-known aviator, who in 1909 commenced operations with a school at Pau. Later this was removed to England, and a general agency for the sale of aeroplanes, etc., established. This developed, and early in 1911 the firm was handling a special British agency for the U.S. Burgess type known as "The Baby." The Hendon Aerodrome was acquired, and a factory established, which has grown continually ever since. In April, 1912, a monoplane to special design was completed. By the close of the same year biplanes of advanced design were constructed. Capacity of the works, March, 1913, was equal to 150 machines a year if necessary.
| 1913. |1913. |1913. |1913 |1913.
|Military |"Popular" |"Popular" |Tractor |Monoplane.
|biplane. | biplane |biplane |hydro- |Type IX.
|Type VI. |Type VII. |Type VII. |biplane | single-
|2-seater |2-seater. |2-seater. |2-seater.| seat.
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-------------|---------|----------
Length...feet(m.)|33? (10.10)|20-5/6 (6.40)|26-5/6 (8.22)|25 (7.60)|21 (6.40)Span.....feet(m.}|42 (12.80)|29-1/6 (8.85)|38 (11.60)|42? (13) |32 (9.75)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.)|435 (40?) |230 (21) |475 (44) |380 (35) |208 (19)
Weight, total ...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)|2200 (997) | ... | ... |850 (385)| ... Weight, useful...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)| 750 (340) | ... | ... |450 (204)| ...
Motor | 120 Aust. | 50 Gnome | 50 Gnome |80 Gnome |50 Gnome
| Daimler | | | |
Speed, max... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|70 (110) |60 (95) |50 (80) |65 (105) |65 (105)
Speed, min... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|55 (90) |50 (80) |40 (65) |50 (80) | ... Endurance....hrs.| 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4
Number built | | | | |
during 1912 | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ...
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------------|-----------
|Also built | Also built | |Also built|Also built
|with a 90 | with a 35 | |with a 60 |with a 35
|Aust.Daimler.| Anzani. | |Anzani. |Anzani. Two
|Designed to| | | |main floats
|carry a gun| | | |with 12?
|on the bow.| | | |ft. track.
|Very good | | | |Floats are
|view. Very | | | |15 ft.long,
|strong | | | |2 ft. wide,
|landing | | | |1 ft. 3 in.
|carriage. | | | |deep.
| 1913. |1913. |1913. |1913 |1913.
|Military |"Popular" |"Popular" |Tractor |Monoplane.
|biplane. | biplane |biplane |hydro- |Type IX.
|Type VI. |Type VII. |Type VII. |biplane | single-
|2-seater |2-seater. |2-seater. |2-seater.| seat.
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-------------|---------|----------
Length...feet(m.)|33? (10.10)|20-5/6 (6.40)|26-5/6 (8.22)|25 (7.60)|21 (6.40)Span.....feet(m.}|42 (12.80)|29-1/6 (8.85)|38 (11.60)|42? (13) |32 (9.75)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.)|435 (40?) |230 (21) |475 (44) |380 (35) |208 (19)
Weight, total ...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)|2200 (997) | ... | ... |850 (385)| ... Weight, useful...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)| 750 (340) | ... | ... |450 (204)| ...
Motor | 120 Aust. | 50 Gnome | 50 Gnome |80 Gnome |50 Gnome
| Daimler | | | |
Speed, max... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|70 (110) |60 (95) |50 (80) |65 (105) |65 (105)
Speed, min... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|55 (90) |50 (80) |40 (65) |50 (80) | ... Endurance....hrs.| 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4
Number built | | | | |
during 1912 | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ...
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------------|-----------
|Also built | Also built | |Also built|Also built
|with a 90 | with a 35 | |with a 60 |with a 35
|Aust.Daimler.| Anzani. | |Anzani. |Anzani. Two
|Designed to| | | |main floats
|carry a gun| | | |with 12?
|on the bow.| | | |ft. track.
|Very good | | | |Floats are
|view. Very | | | |15 ft.long,
|strong | | | |2 ft. wide,
|landing | | | |1 ft. 3 in.
|carriage. | | | |deep.
GRAHAME-WHITE. The Grahame-White Aviation Co., Ltd., 166 Piccadilly, London, W. Works and Flying Ground: Hendon. Founded by C. Grahame-White, the well-known aviator, who in 1909 commenced operations with a school at Pau. Later this was removed to England, and a general agency for the sale of aeroplanes, etc., established. This developed, and early in 1911 the firm was handling a special British agency for the U.S. Burgess type known as "The Baby." The Hendon Aerodrome was acquired, and a factory established, which has grown continually ever since. In April, 1912, a monoplane to special design was completed. By the close of the same year biplanes of advanced design were constructed. Capacity of the works, March, 1913, was equal to 150 machines a year if necessary.
| 1913. |1913. |1913. |1913 |1913.
|Military |"Popular" |"Popular" |Tractor |Monoplane.
|biplane. | biplane |biplane |hydro- |Type IX.
|Type VI. |Type VII. |Type VII. |biplane | single-
|2-seater |2-seater. |2-seater. |2-seater.| seat.
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-------------|---------|----------
Length...feet(m.)|33? (10.10)|20-5/6 (6.40)|26-5/6 (8.22)|25 (7.60)|21 (6.40)Span.....feet(m.}|42 (12.80)|29-1/6 (8.85)|38 (11.60)|42? (13) |32 (9.75)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.)|435 (40?) |230 (21) |475 (44) |380 (35) |208 (19)
Weight, total ...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)|2200 (997) | ... | ... |850 (385)| ... Weight, useful...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)| 750 (340) | ... | ... |450 (204)| ...
Motor | 120 Aust. | 50 Gnome | 50 Gnome |80 Gnome |50 Gnome
| Daimler | | | |
Speed, max... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|70 (110) |60 (95) |50 (80) |65 (105) |65 (105)
Speed, min... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|55 (90) |50 (80) |40 (65) |50 (80) | ... Endurance....hrs.| 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4
Number built | | | | |
during 1912 | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ...
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------------|-----------
|Also built | Also built | |Also built|Also built
|with a 90 | with a 35 | |with a 60 |with a 35
|Aust.Daimler.| Anzani. | |Anzani. |Anzani. Two
|Designed to| | | |main floats
|carry a gun| | | |with 12?
|on the bow.| | | |ft. track.
|Very good | | | |Floats are
|view. Very | | | |15 ft.long,
|strong | | | |2 ft. wide,
|landing | | | |1 ft. 3 in.
|carriage. | | | |deep.
| 1913. |1913. |1913. |1913 |1913.
|Military |"Popular" |"Popular" |Tractor |Monoplane.
|biplane. | biplane |biplane |hydro- |Type IX.
|Type VI. |Type VII. |Type VII. |biplane | single-
|2-seater |2-seater. |2-seater. |2-seater.| seat.
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-------------|---------|----------
Length...feet(m.)|33? (10.10)|20-5/6 (6.40)|26-5/6 (8.22)|25 (7.60)|21 (6.40)Span.....feet(m.}|42 (12.80)|29-1/6 (8.85)|38 (11.60)|42? (13) |32 (9.75)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.)|435 (40?) |230 (21) |475 (44) |380 (35) |208 (19)
Weight, total ...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)|2200 (997) | ... | ... |850 (385)| ... Weight, useful...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)| 750 (340) | ... | ... |450 (204)| ...
Motor | 120 Aust. | 50 Gnome | 50 Gnome |80 Gnome |50 Gnome
| Daimler | | | |
Speed, max... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|70 (110) |60 (95) |50 (80) |65 (105) |65 (105)
Speed, min... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|55 (90) |50 (80) |40 (65) |50 (80) | ... Endurance....hrs.| 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4
Number built | | | | |
during 1912 | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ...
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------------|-----------
|Also built | Also built | |Also built|Also built
|with a 90 | with a 35 | |with a 60 |with a 35
|Aust.Daimler.| Anzani. | |Anzani. |Anzani. Two
|Designed to| | | |main floats
|carry a gun| | | |with 12?
|on the bow.| | | |ft. track.
|Very good | | | |Floats are
|view. Very | | | |15 ft.long,
|strong | | | |2 ft. wide,
|landing | | | |1 ft. 3 in.
|carriage. | | | |deep.
GRAHAME-WHITE. The Grahame-White Aviation Co., Ltd., 166 Piccadilly, London, W. Works and Flying Ground: Hendon. Founded by C. Grahame-White, the well-known aviator, who in 1909 commenced operations with a school at Pau. Later this was removed to England, and a general agency for the sale of aeroplanes, etc., established. This developed, and early in 1911 the firm was handling a special British agency for the U.S. Burgess type known as "The Baby." The Hendon Aerodrome was acquired, and a factory established, which has grown continually ever since. In April, 1912, a monoplane to special design was completed. By the close of the same year biplanes of advanced design were constructed. Capacity of the works, March, 1913, was equal to 150 machines a year if necessary.
| 1913. |1913. |1913. |1913 |1913.
|Military |"Popular" |"Popular" |Tractor |Monoplane.
|biplane. | biplane |biplane |hydro- |Type IX.
|Type VI. |Type VII. |Type VII. |biplane | single-
|2-seater |2-seater. |2-seater. |2-seater.| seat.
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-------------|---------|----------
Length...feet(m.)|33? (10.10)|20-5/6 (6.40)|26-5/6 (8.22)|25 (7.60)|21 (6.40)Span.....feet(m.}|42 (12.80)|29-1/6 (8.85)|38 (11.60)|42? (13) |32 (9.75)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.)|435 (40?) |230 (21) |475 (44) |380 (35) |208 (19)
Weight, total ...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)|2200 (997) | ... | ... |850 (385)| ... Weight, useful...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)| 750 (340) | ... | ... |450 (204)| ...
Motor | 120 Aust. | 50 Gnome | 50 Gnome |80 Gnome |50 Gnome
| Daimler | | | |
Speed, max... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|70 (110) |60 (95) |50 (80) |65 (105) |65 (105)
Speed, min... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|55 (90) |50 (80) |40 (65) |50 (80) | ... Endurance....hrs.| 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4
Number built | | | | |
during 1912 | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ...
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------------|-----------
|Also built | Also built | |Also built|Also built
|with a 90 | with a 35 | |with a 60 |with a 35
|Aust.Daimler.| Anzani. | |Anzani. |Anzani. Two
|Designed to| | | |main floats
|carry a gun| | | |with 12?
|on the bow.| | | |ft. track.
|Very good | | | |Floats are
|view. Very | | | |15 ft.long,
|strong | | | |2 ft. wide,
|landing | | | |1 ft. 3 in.
|carriage. | | | |deep.
| 1913. |1913. |1913. |1913 |1913.
|Military |"Popular" |"Popular" |Tractor |Monoplane.
|biplane. | biplane |biplane |hydro- |Type IX.
|Type VI. |Type VII. |Type VII. |biplane | single-
|2-seater |2-seater. |2-seater. |2-seater.| seat.
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-------------|---------|----------
Length...feet(m.)|33? (10.10)|20-5/6 (6.40)|26-5/6 (8.22)|25 (7.60)|21 (6.40)Span.....feet(m.}|42 (12.80)|29-1/6 (8.85)|38 (11.60)|42? (13) |32 (9.75)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.)|435 (40?) |230 (21) |475 (44) |380 (35) |208 (19)
Weight, total ...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)|2200 (997) | ... | ... |850 (385)| ... Weight, useful...| | | | |
.......lbs.(kgs.)| 750 (340) | ... | ... |450 (204)| ...
Motor | 120 Aust. | 50 Gnome | 50 Gnome |80 Gnome |50 Gnome
| Daimler | | | |
Speed, max... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|70 (110) |60 (95) |50 (80) |65 (105) |65 (105)
Speed, min... | | | | |
...m.p.h (k.p.h.)|55 (90) |50 (80) |40 (65) |50 (80) | ... Endurance....hrs.| 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4
Number built | | | | |
during 1912 | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ...
-----------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------------|-----------
|Also built | Also built | |Also built|Also built
|with a 90 | with a 35 | |with a 60 |with a 35
|Aust.Daimler.| Anzani. | |Anzani. |Anzani. Two
|Designed to| | | |main floats
|carry a gun| | | |with 12?
|on the bow.| | | |ft. track.
|Very good | | | |Floats are
|view. Very | | | |15 ft.long,
|strong | | | |2 ft. wide,
|landing | | | |1 ft. 3 in.
|carriage. | | | |deep.
PLANES. Planes, Ltd, 6, Lord Street, Liverpool. Works: Duke Street & Cleveland Street, Birkenhead. Not building at present. In October, 1910, the firm produced a biplane, designed by W.P. Thompson, fitted with a special pendulum stabilising device. This was followed a year or so later by a monoplane.
HANDLEY-PAGE Monoplanes. Handley Page, 72,Victoria Street, S.W. Works: 110, Cricklewood Lane, N.W. Flying ground: Hendon. Established at the end of 1908. In June, 1909, it was turned into a Limited Liability Co. Since then it has been busily employed in producing its own machines, also others to inventor's specifications. About the end of 1911 the firm bought up and sold all the machines of the Aeronautical Syndicate--Valkyrie and Viking types. It is doubtful whether any of these V type still exist--in any case it does not matter. Four were presented to the R. Flying Corps. Of these one was smashed up, the others, one army and two navy, were used to teach mechanics to take down and reassemble engines, etc. Handley-Page also bought up the Radley-Moorhouse machines (Bleriot copies), and disposed of them.
The 1912-13 Handley-Page type is as follows--a development along regular lines of the original H.P. machine:---
Length, 27? feet (8.40 m.) span, 42 feet (12.95 m.) area, 240 sq. feet,(22? m?.)
Weight.--Total, 1300 lbs. (590 kgs.) Empty, 800 lbs. (363 kgs.)
Motor.--50 h.p. Gnome. Speed. 55 m.p.h. (90 km.)
Remarks.--The fixed tail area is 32 sq. feet. Body is entirely enclosed, stream line form. The passenger sits behind the pilot. Mounted on wheels and one long skid forward. Full description and details, Flight, 26th October, 1912.
Principal pilots have been the late E. Petre (who made in it the only flight through London), the late Lieut. Parke, R.N., S. Pickles, and L.R. Whitehouse. The machine has been flown with two passengers, in addition to the pilot.
Military work.--During 1912 five biplanes of the B.E. type were ordered by the British War Office.
Several monoplanes were ordered by foreign governments.
The 1912-13 Handley-Page type is as follows--a development along regular lines of the original H.P. machine:---
Length, 27? feet (8.40 m.) span, 42 feet (12.95 m.) area, 240 sq. feet,(22? m?.)
Weight.--Total, 1300 lbs. (590 kgs.) Empty, 800 lbs. (363 kgs.)
Motor.--50 h.p. Gnome. Speed. 55 m.p.h. (90 km.)
Remarks.--The fixed tail area is 32 sq. feet. Body is entirely enclosed, stream line form. The passenger sits behind the pilot. Mounted on wheels and one long skid forward. Full description and details, Flight, 26th October, 1912.
Principal pilots have been the late E. Petre (who made in it the only flight through London), the late Lieut. Parke, R.N., S. Pickles, and L.R. Whitehouse. The machine has been flown with two passengers, in addition to the pilot.
Military work.--During 1912 five biplanes of the B.E. type were ordered by the British War Office.
Several monoplanes were ordered by foreign governments.
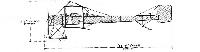
HP Type E (HP5) in original 1912 form as a two-seater. The 'bird-like' origins of some of the early designs can clearly be seen in the wing design of the Handley Page 'Yellow Peril'. No type ol this design entered service with the British military because of the monoplane ban.
The Humphreys Waterplane, built at Wivenhoe, Essex, during 1908/9 by Mr Jack Humphreys, who is said to have been known locally as 'the mad dentist'.
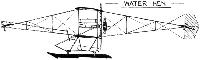
LAKE FLYING Co. Windermere. Established 1911, by E.W. Wakefield, with a view to hydro-aeroplane experiments. The first machine was a Curtiss type built by A.V. Roe, which flew in November, 1911. In 1912, a special biplane generally of Farman type but with more camber to the planes, was built.
Length.--36-1/2 feet (11 m.) Span.--42 feet (12.80 m.) Area.--270 sq. feet (25 m.?) Motor.--Gnome.
Speed.--45.33 m.p.h. (72.54 k.p.h.)
The single float is 6 feet wide, flexibly connected. Balancers mounted on a spring board. Water rudders for steering at slow speed. Fuller details see Flight, December 7th, 1912. Early in 1913, an Avro was purchased for further experiments.
Length.--36-1/2 feet (11 m.) Span.--42 feet (12.80 m.) Area.--270 sq. feet (25 m.?) Motor.--Gnome.
Speed.--45.33 m.p.h. (72.54 k.p.h.)
The single float is 6 feet wide, flexibly connected. Balancers mounted on a spring board. Water rudders for steering at slow speed. Fuller details see Flight, December 7th, 1912. Early in 1913, an Avro was purchased for further experiments.
MARTINSYDE. Messrs. Martin & Handasyde, Brooklnnds, Weybridge, Surrey. Output capacity: about 20 per annum.
1912. 1913.
Model and date. Mono. 2-seater. Mono. 2-seater.
Length.................feet(m.) 35-1/3 (10.75) 35 (10.65)
Span...................feet(m.) 42? (12.95) 42? (13)
Area...............sq.feet(m?.) 290 (27) 285 (26.50)
Weight, total........lbs.(kgs.) ... 1212 (550)
Weight, useful.......lbs.(kgs.) ... 551 (250)
Motor......................h.p. 65 Antoinette 80 Laviator
Speed, max..........m.p.h.(km.) 63 (102) 78 (125)
Speed,min...........m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Landing: wheels and one skid. Controls: warping wings and rear elevator. Triangular body. The two models are very nearly identical.
1912. 1913.
Model and date. Mono. 2-seater. Mono. 2-seater.
Length.................feet(m.) 35-1/3 (10.75) 35 (10.65)
Span...................feet(m.) 42? (12.95) 42? (13)
Area...............sq.feet(m?.) 290 (27) 285 (26.50)
Weight, total........lbs.(kgs.) ... 1212 (550)
Weight, useful.......lbs.(kgs.) ... 551 (250)
Motor......................h.p. 65 Antoinette 80 Laviator
Speed, max..........m.p.h.(km.) 63 (102) 78 (125)
Speed,min...........m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Landing: wheels and one skid. Controls: warping wings and rear elevator. Triangular body. The two models are very nearly identical.
THE "MARTINSYDE" 120 H.P. TWO-SEATER, MILITARY TYPE MONOPLANE. Fuel Capacity for 6 HOURS' FLIGHT, at 85 miles per hour.
PIGGOTT. Piggott Bros. & Co., Ltd., 220, 222 & 224, Bishopsgate, London, E.C. This well-known firm of shed makers built a novel biplane in May, 1910 (details Flight, May 21st, 1910), and in 1911 a monoplane with enclosed body (Flight, April 1st, 1911). In 1912, both were disposed of, and the firm is not proceeding with its experiments. It has, however, a staff of skilled mechanics and a great deal of floor space for the construction of aeroplanes to specifications.
PIGGOTT. Piggott Bros. & Co., Ltd., 220, 222 & 224, Bishopsgate, London, E.C. This well-known firm of shed makers built a novel biplane in May, 1910 (details Flight, May 21st, 1910), and in 1911 a monoplane with enclosed body (Flight, April 1st, 1911). In 1912, both were disposed of, and the firm is not proceeding with its experiments. It has, however, a staff of skilled mechanics and a great deal of floor space for the construction of aeroplanes to specifications.
PORTE (1908). Designed by Lieut. Porte, R.N., in conjunction with Lieut. Pirie, R.N. This machine, on which the former well known aviator commenced his flying career, was smashed up in preliminary trials as a glider on Portsdown Hill, Portsmouth. Its design apparently preceded the Goupy in the use of staggered planes.
RADLEY-ENGLAND. This is not an aeroplane firm, but a special hydro built by two well-known aviators for the Daily Mail competition. Length, 22 feet. Span, 50 feet. 2 floats, 15 feet long by 1 foot 5 inches wide. Pilot in starboard float. Weight, with petrol for 12 hours, 1,380 lbs. Motor, 150 h.p., made up of 3--50 h.p. Gnomes, but two Greens to be fitted for competition. One 4-bladed propeller in rear. Speed, 60 m.p.h., with 100 h.p.
AIRCRAFT FACTORY. Royal Aircraft Factory, Farnborough, near Aldershot. For a long time this establishment had been engaged in dirigible construction and repairs. In 1911 it was decided to expand it in connection with the Royal Flying Corps. Its precise functions are somewhat uncertain. Its nominal main purpose is the repair, etc., of Service Aircraft. During 1912, however, it turned out several machines to a design of its own, known as the "B.E." This design was at one time regarded as confidential; but subsequently duplicates were built by private contractors, and the design illustrated below, published by the Advisory Committee for Aeronautics.
Length, 29-1/2 feet (9 m.)
Span.--36-3/4 feet (11.20 m.)
Area.--374 sq. feet (34-3/4 m^2.)
Weight.--
Motor.--75 h.p. Renault and others.
Speed.--
Length, 29-1/2 feet (9 m.)
Span.--36-3/4 feet (11.20 m.)
Area.--374 sq. feet (34-3/4 m^2.)
Weight.--
Motor.--75 h.p. Renault and others.
Speed.--
SHORT BROS. Works and flying grounds: Eastchurch, Isle of Sheppey, Kent. London office: Queen's Circus, Battersea Park. Took up construction at a very early date. Wright agents in 1909. Have built numerous biplanes and monoplanes to specifications. Produced their own first machine (see 1911 edition) in 1910.
S 34. Standard School.
50 h.p. 70 h.p.
2-seater. 2-seater.
Length................feet(m.) 42 (12.85) 42 (12.85)
Span..................feet(m.) 46? (14.20) 46? (14.20)
Area.............sq. feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight, machine......lbs.(kg.) 1100 (500) 1150 (523)
useful.......lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed, max............(m.p.h.) 39 (63) 48 (78)
min............(m.p.h.) 34 (55) 38 (61)
Endurance.................hrs. 4 5
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Solely designed for school work. Seats side by side.
S 34. Standard School.
50 h.p. 70 h.p.
2-seater. 2-seater.
Length................feet(m.) 42 (12.85) 42 (12.85)
Span..................feet(m.) 46? (14.20) 46? (14.20)
Area.............sq. feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight, machine......lbs.(kg.) 1100 (500) 1150 (523)
useful.......lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed, max............(m.p.h.) 39 (63) 48 (78)
min............(m.p.h.) 34 (55) 38 (61)
Endurance.................hrs. 4 5
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Solely designed for school work. Seats side by side.
SHORT BROS. Works and flying grounds: Eastchurch, Isle of Sheppey, Kent. London office: Queen's Circus, Battersea Park. Took up construction at a very early date. Wright agents in 1909. Have built numerous biplanes and monoplanes to specifications. Produced their own first machine (see 1911 edition) in 1910.
1911-12. 1911-12.
1-seater, Tandem
mono. tractor
biplane
Length................feet(m.) 25 (7.60) 35? (10.80)
Span..................feet(m.) 29? (9) 42 (12.90)
Area.............sq. feet(m?.) 186 (17) ...
Weight, machine......lbs.(kg.) ... 850 (385)
useful.......lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 50 Gnome. 50 Gnome.
Speed, max............(m.p.h.) ... 58 (94)
min............(m.p.h.) ... ...
Endurance.................hrs. 5 5
Number built during 1912 ... ...
No longer built, but still in existence.
S 45. 1913. Military Tractor
Biplane.
70 h.p. 80 h.p. 160 h.p.
2-seater. 2-seater. 4-seater.
Length..............feet(m.) 35? (10.80) 35? (10.80) 40 (13.70)
Span................feet(m.) 42 (12.90) 45 (13.70) 50 (15.25)
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight, machine....lbs.(kg.) 1080 (490) 1100 (500) 1890 (860)
useful.....lbs.(kg.) ... ... ...
Motor...................h.p. 70 Gnome 80 Gnome 160 Gnome
Speed, max..........(m.p.h.) 60 (97) 70 (113) 74 (120)
min..........(m.p.h.) 50 (80) 50 (80) 56 (90)
Endurance...............hrs. 5 5 6
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Tandem seats, pilot in front. Fittings for maps, etc.
1911-12. 1911-12.
1-seater, Tandem
mono. tractor
biplane
Length................feet(m.) 25 (7.60) 35? (10.80)
Span..................feet(m.) 29? (9) 42 (12.90)
Area.............sq. feet(m?.) 186 (17) ...
Weight, machine......lbs.(kg.) ... 850 (385)
useful.......lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 50 Gnome. 50 Gnome.
Speed, max............(m.p.h.) ... 58 (94)
min............(m.p.h.) ... ...
Endurance.................hrs. 5 5
Number built during 1912 ... ...
No longer built, but still in existence.
S 45. 1913. Military Tractor
Biplane.
70 h.p. 80 h.p. 160 h.p.
2-seater. 2-seater. 4-seater.
Length..............feet(m.) 35? (10.80) 35? (10.80) 40 (13.70)
Span................feet(m.) 42 (12.90) 45 (13.70) 50 (15.25)
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight, machine....lbs.(kg.) 1080 (490) 1100 (500) 1890 (860)
useful.....lbs.(kg.) ... ... ...
Motor...................h.p. 70 Gnome 80 Gnome 160 Gnome
Speed, max..........(m.p.h.) 60 (97) 70 (113) 74 (120)
min..........(m.p.h.) 50 (80) 50 (80) 56 (90)
Endurance...............hrs. 5 5 6
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Tandem seats, pilot in front. Fittings for maps, etc.
SHORT BROS. Works and flying grounds: Eastchurch, Isle of Sheppey, Kent. London office: Queen's Circus, Battersea Park. Took up construction at a very early date. Wright agents in 1909. Have built numerous biplanes and monoplanes to specifications. Produced their own first machine (see 1911 edition) in 1910.
S 38. 1913.
Military Nacelle Biplane.
50 h.p. 80 h.p.
2-seater. 3-seater.
Length...............feet(m.) 35? (10.80) 35? (10.80)
Span.................feet(m.) 52 (15.85) 52 (15.85)
[**Note: Typo in chart. Using metric and changing 32 to 52]
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) ... ..
Weight, machine.....lbs.(kg.) 950 (432) 1050 (480)
useful......lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor................... h.p. 50 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max...........(m.p.h.) 42 (68) 58 (94)
min...........(m.p.h.) 35 (57) 39 (63)
Endurance................hrs. 4 5
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Specially designed for reconnaissance. Tandem seats, pilot in front. An
extra passenger can be accommodated.
S 38. 1913.
Military Nacelle Biplane.
50 h.p. 80 h.p.
2-seater. 3-seater.
Length...............feet(m.) 35? (10.80) 35? (10.80)
Span.................feet(m.) 52 (15.85) 52 (15.85)
[**Note: Typo in chart. Using metric and changing 32 to 52]
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) ... ..
Weight, machine.....lbs.(kg.) 950 (432) 1050 (480)
useful......lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor................... h.p. 50 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max...........(m.p.h.) 42 (68) 58 (94)
min...........(m.p.h.) 35 (57) 39 (63)
Endurance................hrs. 4 5
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Specially designed for reconnaissance. Tandem seats, pilot in front. An
extra passenger can be accommodated.
SHORT BROS. Works and flying grounds: Eastchurch, Isle of Sheppey, Kent. London office: Queen's Circus, Battersea Park. Took up construction at a very early date. Wright agents in 1909. Have built numerous biplanes and monoplanes to specifications. Produced their own first machine (see 1911 edition) in 1910.
S 41. 1913. Hydro Biplane.
80 h.p. 100 h.p. 160 h.p.
2-seater. 2-seater. 4-seater.
Length...............feet(m.) 35 (10.67) 39 (11.90) 45 (13.70)
Span.................feet(m.) 40 (13.70) 50 (15.25) 50 (15.25)
Area............sq.feet (m?.) 390 (36) ... ...
Weight, machine.....lbs.(kg.) 1200 (545) 1700 (764) 2000 (09)
useful......lbs.(kg.) 771 (350) ... ...
Motor....................h.p. 80 Gnome 100 Gnome 160 Gnome
Speed, max...........(m.p.h.) 65 (105) 60 (97) 74 (120)
min...........(m.p.h.) 50 (80) 50 (80) 56 (90)
Endurance................hrs. 4 5 6
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.--Floats are two long pontoons. Subsidiary floats at tips of
lower plane, Small tail float with water rudder. W.-t. compartments to floats. Tandem seated, pilot in front. The observer's seat can accommodate two if necessary.
S 41. 1913. Hydro Biplane.
80 h.p. 100 h.p. 160 h.p.
2-seater. 2-seater. 4-seater.
Length...............feet(m.) 35 (10.67) 39 (11.90) 45 (13.70)
Span.................feet(m.) 40 (13.70) 50 (15.25) 50 (15.25)
Area............sq.feet (m?.) 390 (36) ... ...
Weight, machine.....lbs.(kg.) 1200 (545) 1700 (764) 2000 (09)
useful......lbs.(kg.) 771 (350) ... ...
Motor....................h.p. 80 Gnome 100 Gnome 160 Gnome
Speed, max...........(m.p.h.) 65 (105) 60 (97) 74 (120)
min...........(m.p.h.) 50 (80) 50 (80) 56 (90)
Endurance................hrs. 4 5 6
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.--Floats are two long pontoons. Subsidiary floats at tips of
lower plane, Small tail float with water rudder. W.-t. compartments to floats. Tandem seated, pilot in front. The observer's seat can accommodate two if necessary.
SOPWITH. Sopwith Aviation Co. Works: Canbury Park Road, Kingston-on-Thames. School: at Brooklands. Established by T.O.M. Sopwith, the well-known aviator at Brooklands, Autumn of 1911, where during 1912, a 70 h.p. tractor biplane and a 40 h.p. biplane was turned out.
Floor area of the Kingston works in March, 1913, was 30,000 sq. ft. with electric power plant. Works manager: F. Sigrist. General manager: R.O. Cary. Output capacity: at full pressure about 50 machines a year.
1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Bat boat Tractor School Armoured
hydro biplane biplane. warplane.
biplane 3-seater
Length......feet(m.) 30-1/3 (9.20) 29 (8.85) 9 (8.85) 29' 7?" (9)
Span........feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40 (12.20) 40 (12.20) 50 (15.25)
Area.....sq.ft (m?.) 422 (39) 365 (34) 400 (37) 552 (51)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1700 (771) 1750 (794) 1200 (544) 2000 (907)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 500 (227) 750 (340) 400 (181) 800 (362)
Motor......... h.p. 90 Austro- 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 90 Austro-
Daimler Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105) 74 (125) 48 (78) 65 (105)
min.. m.p.h.(km.) 42 (68) 40 (65) 35 (60) 38 (61)
Endurance........hrs. ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Carriage wheels and skids. Control: balanced ailerons.
Floor area of the Kingston works in March, 1913, was 30,000 sq. ft. with electric power plant. Works manager: F. Sigrist. General manager: R.O. Cary. Output capacity: at full pressure about 50 machines a year.
1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Bat boat Tractor School Armoured
hydro biplane biplane. warplane.
biplane 3-seater
Length......feet(m.) 30-1/3 (9.20) 29 (8.85) 9 (8.85) 29' 7?" (9)
Span........feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40 (12.20) 40 (12.20) 50 (15.25)
Area.....sq.ft (m?.) 422 (39) 365 (34) 400 (37) 552 (51)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1700 (771) 1750 (794) 1200 (544) 2000 (907)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 500 (227) 750 (340) 400 (181) 800 (362)
Motor......... h.p. 90 Austro- 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 90 Austro-
Daimler Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105) 74 (125) 48 (78) 65 (105)
min.. m.p.h.(km.) 42 (68) 40 (65) 35 (60) 38 (61)
Endurance........hrs. ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Carriage wheels and skids. Control: balanced ailerons.
SOPWITH. Sopwith Aviation Co. Works: Canbury Park Road, Kingston-on-Thames. School: at Brooklands. Established by T.O.M. Sopwith, the well-known aviator at Brooklands, Autumn of 1911, where during 1912, a 70 h.p. tractor biplane and a 40 h.p. biplane was turned out.
Floor area of the Kingston works in March, 1913, was 30,000 sq. ft. with electric power plant. Works manager: F. Sigrist. General manager: R.O. Cary. Output capacity: at full pressure about 50 machines a year.
1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Bat boat Tractor School Armoured
hydro biplane biplane. warplane.
biplane 3-seater
Length......feet(m.) 30-1/3 (9.20) 29 (8.85) 9 (8.85) 29' 7?" (9)
Span........feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40 (12.20) 40 (12.20) 50 (15.25)
Area.....sq.ft (m?.) 422 (39) 365 (34) 400 (37) 552 (51)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1700 (771) 1750 (794) 1200 (544) 2000 (907)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 500 (227) 750 (340) 400 (181) 800 (362)
Motor......... h.p. 90 Austro- 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 90 Austro-
Daimler Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105) 74 (125) 48 (78) 65 (105)
min.. m.p.h.(km.) 42 (68) 40 (65) 35 (60) 38 (61)
Endurance........hrs. ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Carriage wheels and skids. Control: balanced ailerons.
Floor area of the Kingston works in March, 1913, was 30,000 sq. ft. with electric power plant. Works manager: F. Sigrist. General manager: R.O. Cary. Output capacity: at full pressure about 50 machines a year.
1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Bat boat Tractor School Armoured
hydro biplane biplane. warplane.
biplane 3-seater
Length......feet(m.) 30-1/3 (9.20) 29 (8.85) 9 (8.85) 29' 7?" (9)
Span........feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40 (12.20) 40 (12.20) 50 (15.25)
Area.....sq.ft (m?.) 422 (39) 365 (34) 400 (37) 552 (51)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1700 (771) 1750 (794) 1200 (544) 2000 (907)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 500 (227) 750 (340) 400 (181) 800 (362)
Motor......... h.p. 90 Austro- 80 Gnome 50 Gnome 90 Austro-
Daimler Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105) 74 (125) 48 (78) 65 (105)
min.. m.p.h.(km.) 42 (68) 40 (65) 35 (60) 38 (61)
Endurance........hrs. ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Carriage wheels and skids. Control: balanced ailerons.
VICKERS. Vickers, Ltd., Vickers House, Broadway, Westminster. School: Brooklands. Seven pupils qualified during 1912.
Monoplane. Military
Model and date. 1912-13. biplane.
2-seater. 1913.
Length................feet(m.) 25 (7.60) ...
Span..................feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 40 (12.20)
Area..............sq.feet(m?.) 220 (20) 385 (35)
Weight,total........lbs.(kgs.) 730 (331) ...
Weight, useful......lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 80 Gnome 80 Wolseley
Speed..............m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) ...
Endurance.................hrs. 3 ...
Number built during 1912...... ... ...
Notes.-- Steel construction. Landing shock absorbing: 2 wheels and 1 skid. Rectangular enclosed body. Controls: warping and rear elevator.
Monoplane climbs 300 feet a minute fully loaded.
Biplane is armed with a Vickers R.C. automatic gun in the bow.
Monoplane. Military
Model and date. 1912-13. biplane.
2-seater. 1913.
Length................feet(m.) 25 (7.60) ...
Span..................feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 40 (12.20)
Area..............sq.feet(m?.) 220 (20) 385 (35)
Weight,total........lbs.(kgs.) 730 (331) ...
Weight, useful......lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 80 Gnome 80 Wolseley
Speed..............m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) ...
Endurance.................hrs. 3 ...
Number built during 1912...... ... ...
Notes.-- Steel construction. Landing shock absorbing: 2 wheels and 1 skid. Rectangular enclosed body. Controls: warping and rear elevator.
Monoplane climbs 300 feet a minute fully loaded.
Biplane is armed with a Vickers R.C. automatic gun in the bow.
VICKERS. Vickers, Ltd., Vickers House, Broadway, Westminster. School: Brooklands. Seven pupils qualified during 1912.
Monoplane. Military
Model and date. 1912-13. biplane.
2-seater. 1913.
Length................feet(m.) 25 (7.60) ...
Span..................feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 40 (12.20)
Area..............sq.feet(m?.) 220 (20) 385 (35)
Weight,total........lbs.(kgs.) 730 (331) ...
Weight, useful......lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 80 Gnome 80 Wolseley
Speed..............m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) ...
Endurance.................hrs. 3 ...
Number built during 1912...... ... ...
Notes.-- Steel construction. Landing shock absorbing: 2 wheels and 1 skid. Rectangular enclosed body. Controls: warping and rear elevator.
Monoplane climbs 300 feet a minute fully loaded.
Biplane is armed with a Vickers R.C. automatic gun in the bow.
Monoplane. Military
Model and date. 1912-13. biplane.
2-seater. 1913.
Length................feet(m.) 25 (7.60) ...
Span..................feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 40 (12.20)
Area..............sq.feet(m?.) 220 (20) 385 (35)
Weight,total........lbs.(kgs.) 730 (331) ...
Weight, useful......lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.....................h.p. 80 Gnome 80 Wolseley
Speed..............m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115) ...
Endurance.................hrs. 3 ...
Number built during 1912...... ... ...
Notes.-- Steel construction. Landing shock absorbing: 2 wheels and 1 skid. Rectangular enclosed body. Controls: warping and rear elevator.
Monoplane climbs 300 feet a minute fully loaded.
Biplane is armed with a Vickers R.C. automatic gun in the bow.
WHITE. J. Samuel White & Co., Ltd., shipbuilders and engineers, East Cowes, Isle of Wight. London office: 28, Victoria Street, S.W. This well-known firm of torpedo craft builders, etc., formally opened an aviation department on 1st January, 1913, with Howard T. Wright as general manager and designer.
1913.
Navy plane.
Length.........feet(m.) 30 (9.15)
Span...........feet(m.) 44 (3.10)
Area........sq.ft.(m?.) 500 (46.50)
Weight, total...
...lbs.(kgs.) 2000 (907)
Weight,useful...
...lbs.(kgs.) 650 (295)
Motor..............h.p. 160 Gnome
Speed,max...m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115)
min...m.p.h.(km.) 35 (57)
Number built*......... ...
Remarks.--Hydro-biplane, with Howard T. Wright patent aeroplanes to give wide range of speed. Two patent hydro floats, 21 feet (--m.) long, three steps on each.
1913.
Navy plane.
Length.........feet(m.) 30 (9.15)
Span...........feet(m.) 44 (3.10)
Area........sq.ft.(m?.) 500 (46.50)
Weight, total...
...lbs.(kgs.) 2000 (907)
Weight,useful...
...lbs.(kgs.) 650 (295)
Motor..............h.p. 160 Gnome
Speed,max...m.p.h.(km.) 70 (115)
min...m.p.h.(km.) 35 (57)
Number built*......... ...
Remarks.--Hydro-biplane, with Howard T. Wright patent aeroplanes to give wide range of speed. Two patent hydro floats, 21 feet (--m.) long, three steps on each.
ALBATROS. Albatroswerke G.m.b. H. Flugzeugfabr. u. Fliegerschule, Johannisthal bei Berlin. Established 1910. One of the largest constructors in Germany. Capacity: 150 machines a year.
1911-12. 1912. 1912-13. Hydro. Mono.
2-seat Military Military
tractor tractor tractor.
biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 13? (10.70) 43?-1/2 (10.5) 42? (12.8) ... ...
Spa.......feet(m.) 43-2/3(13.30) 52? (16) 65? (20) ... ...
Are...sq. feet(m?) 430 (40) 576 (54) 624 (58.5) ... ...
Weight, total...
......lbs.(kgs.) 1058 (480) 1543 (700) 1874 (850) ... ...
Weight,useful...
.... .lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) ... ... ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 90 Mercedes 120 N.A.G. or ... ...
or 100 Argus Aust. Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 59 (95) 46 (75) ... ...
min...m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 6 6 7-5 ... ...
Number built
during 1912 about 40 70 30 4 2
Remarks.--In all the upper plane is slightly staggered. In all the control is duplicated.
1911-12. 1912. 1912-13. Hydro. Mono.
2-seat Military Military
tractor tractor tractor.
biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 13? (10.70) 43?-1/2 (10.5) 42? (12.8) ... ...
Spa.......feet(m.) 43-2/3(13.30) 52? (16) 65? (20) ... ...
Are...sq. feet(m?) 430 (40) 576 (54) 624 (58.5) ... ...
Weight, total...
......lbs.(kgs.) 1058 (480) 1543 (700) 1874 (850) ... ...
Weight,useful...
.... .lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) ... ... ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 90 Mercedes 120 N.A.G. or ... ...
or 100 Argus Aust. Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 59 (95) 46 (75) ... ...
min...m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 6 6 7-5 ... ...
Number built
during 1912 about 40 70 30 4 2
Remarks.--In all the upper plane is slightly staggered. In all the control is duplicated.
ALBATROS. Albatroswerke G.m.b. H. Flugzeugfabr. u. Fliegerschule, Johannisthal bei Berlin. Established 1910. One of the largest constructors in Germany. Capacity: 150 machines a year.
1911-12. 1912. 1912-13. Hydro. Mono.
2-seat Military Military
tractor tractor tractor.
biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 13? (10.70) 43?-1/2 (10.5) 42? (12.8) ... ...
Spa.......feet(m.) 43-2/3(13.30) 52? (16) 65? (20) ... ...
Are...sq. feet(m?) 430 (40) 576 (54) 624 (58.5) ... ...
Weight, total...
......lbs.(kgs.) 1058 (480) 1543 (700) 1874 (850) ... ...
Weight,useful...
.... .lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) ... ... ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 90 Mercedes 120 N.A.G. or ... ...
or 100 Argus Aust. Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 59 (95) 46 (75) ... ...
min...m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 6 6 7-5 ... ...
Number built
during 1912 about 40 70 30 4 2
Remarks.--In all the upper plane is slightly staggered. In all the control is duplicated.
1911-12. 1912. 1912-13. Hydro. Mono.
2-seat Military Military
tractor tractor tractor.
biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 13? (10.70) 43?-1/2 (10.5) 42? (12.8) ... ...
Spa.......feet(m.) 43-2/3(13.30) 52? (16) 65? (20) ... ...
Are...sq. feet(m?) 430 (40) 576 (54) 624 (58.5) ... ...
Weight, total...
......lbs.(kgs.) 1058 (480) 1543 (700) 1874 (850) ... ...
Weight,useful...
.... .lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) ... ... ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 90 Mercedes 120 N.A.G. or ... ...
or 100 Argus Aust. Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 59 (95) 46 (75) ... ...
min...m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 6 6 7-5 ... ...
Number built
during 1912 about 40 70 30 4 2
Remarks.--In all the upper plane is slightly staggered. In all the control is duplicated.
ALBATROS. Albatroswerke G.m.b. H. Flugzeugfabr. u. Fliegerschule, Johannisthal bei Berlin. Established 1910. One of the largest constructors in Germany. Capacity: 150 machines a year.
1911-12. 1912. 1912-13. Hydro. Mono.
2-seat Military Military
tractor tractor tractor.
biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 13? (10.70) 43?-1/2 (10.5) 42? (12.8) ... ...
Spa.......feet(m.) 43-2/3(13.30) 52? (16) 65? (20) ... ...
Are...sq. feet(m?) 430 (40) 576 (54) 624 (58.5) ... ...
Weight, total...
......lbs.(kgs.) 1058 (480) 1543 (700) 1874 (850) ... ...
Weight,useful...
.... .lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) ... ... ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 90 Mercedes 120 N.A.G. or ... ...
or 100 Argus Aust. Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 59 (95) 46 (75) ... ...
min...m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 6 6 7-5 ... ...
Number built
during 1912 about 40 70 30 4 2
Remarks.--In all the upper plane is slightly staggered. In all the control is duplicated.
1911-12. 1912. 1912-13. Hydro. Mono.
2-seat Military Military
tractor tractor tractor.
biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 13? (10.70) 43?-1/2 (10.5) 42? (12.8) ... ...
Spa.......feet(m.) 43-2/3(13.30) 52? (16) 65? (20) ... ...
Are...sq. feet(m?) 430 (40) 576 (54) 624 (58.5) ... ...
Weight, total...
......lbs.(kgs.) 1058 (480) 1543 (700) 1874 (850) ... ...
Weight,useful...
.... .lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) ... ... ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 90 Mercedes 120 N.A.G. or ... ...
or 100 Argus Aust. Daimler
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 59 (95) 46 (75) ... ...
min...m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 6 6 7-5 ... ...
Number built
during 1912 about 40 70 30 4 2
Remarks.--In all the upper plane is slightly staggered. In all the control is duplicated.
AVIATIK. Autemobil & Aviatik A.G., Mulhausen i.E. Established 1910. Capacity: 100 a year.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
AVIATIK. Autemobil & Aviatik A.G., Mulhausen i.E. Established 1910. Capacity: 100 a year.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
AVIATIK. Autemobil & Aviatik A.G., Mulhausen i.E. Established 1910. Capacity: 100 a year.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
HANSA-TAUBE. Heinrich Heitmann, Aviatik und Konstructions Werkstotten, Altona.
1912. 1913.
Monoplane. Monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 24? (7.5) 24? (7.5)
Span..............feet(m.) 36? (11.2) 36? (11.2)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 237 (22) 237 (22)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 573 (260)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. 75 or 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed..........m.p.h.(km.) 56-62 (95-100) 62 (100)
Number built during 1912.. 2 2
Remarks.--
1912. 1913.
Monoplane. Monoplane.
Length............feet(m.) 24? (7.5) 24? (7.5)
Span..............feet(m.) 36? (11.2) 36? (11.2)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 237 (22) 237 (22)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 573 (260)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. 75 or 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed..........m.p.h.(km.) 56-62 (95-100) 62 (100)
Number built during 1912.. 2 2
Remarks.--
MARS. Deutsche Flogzeugwerke G.m.b.H., Lindenthal bei Leipzig. Established 1911. This is one of the most important and successful aviation works in Germany. Capacity: from 80 to 100 machines a year.
1911-12. 1912. 1912
Monoplane. Biplane. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 31 (9.7) 31 (9.7)
Span.............feet(m.) 55? (16.8) 57 (17.8)
Are.........sq. feet(m?.) 376 (35) 495 (46)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1234 (560) 1434 (650)
useful, lbs.(kgs.) 1808 (820) 2006 (910) Building
Motor................h.p. 95 N.A.G. 95 Mercedes
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 120 (75) 115 (71)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance............hrs. 5--6 4--6
Number Built during 1912 6 16
Remarks--
1911-12. 1912. 1912
Monoplane. Biplane. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 31 (9.7) 31 (9.7)
Span.............feet(m.) 55? (16.8) 57 (17.8)
Are.........sq. feet(m?.) 376 (35) 495 (46)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1234 (560) 1434 (650)
useful, lbs.(kgs.) 1808 (820) 2006 (910) Building
Motor................h.p. 95 N.A.G. 95 Mercedes
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 120 (75) 115 (71)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance............hrs. 5--6 4--6
Number Built during 1912 6 16
Remarks--
MARS. Deutsche Flogzeugwerke G.m.b.H., Lindenthal bei Leipzig. Established 1911. This is one of the most important and successful aviation works in Germany. Capacity: from 80 to 100 machines a year.
1911-12. 1912. 1912
Monoplane. Biplane. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 31 (9.7) 31 (9.7)
Span.............feet(m.) 55? (16.8) 57 (17.8)
Are.........sq. feet(m?.) 376 (35) 495 (46)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1234 (560) 1434 (650)
useful, lbs.(kgs.) 1808 (820) 2006 (910) Building
Motor................h.p. 95 N.A.G. 95 Mercedes
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 120 (75) 115 (71)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance............hrs. 5--6 4--6
Number Built during 1912 6 16
Remarks--
1911-12. 1912. 1912
Monoplane. Biplane. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 31 (9.7) 31 (9.7)
Span.............feet(m.) 55? (16.8) 57 (17.8)
Are.........sq. feet(m?.) 376 (35) 495 (46)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1234 (560) 1434 (650)
useful, lbs.(kgs.) 1808 (820) 2006 (910) Building
Motor................h.p. 95 N.A.G. 95 Mercedes
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 120 (75) 115 (71)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance............hrs. 5--6 4--6
Number Built during 1912 6 16
Remarks--
DORNER III. Monoplane. Length.--34-1/2 feet (10.50 m.) Span.--39-1/3 feet (12 m.) Surface.--280 sq. feet (126 m^2.) Weight.--882 lbs. (400 kgs.)
Type II: Length.--32-3/4 feet (10 m.) Span.--38 feet (11.60 m.) Surface.--268-1/2 sq. feet (25 m^2.) Weight.--661 lbs. (300 kgs) See Flugsport, No. 5, 1911.
Type II: Length.--32-3/4 feet (10 m.) Span.--38 feet (11.60 m.) Surface.--268-1/2 sq. feet (25 m^2.) Weight.--661 lbs. (300 kgs) See Flugsport, No. 5, 1911.
1910 Dorner Type II pusher monoplane
Country of Origin: Germany Designed and built by Dorner
Span: 32'10" Length: 38'1" Weight w.engine: 661 lbs
Country of Origin: Germany Designed and built by Dorner
Span: 32'10" Length: 38'1" Weight w.engine: 661 lbs
EULER. August Euler, Frankfurt a.M. In 1908 Euler secured Voisin rights for Germany. In 1910 he took out a patent for a design of his own. In the summer of 1911 he built a successful monoplane, in the autumn of the same year a triplane. Existing models are as follows:--
1912. 1912.
Triplane. Monoplane. Military biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) no data no data
Span.............feet(m.) 23 (7)
Area.........sq. feet(m?) ...
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor................h.p. Gnome
Speed,max.... m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance ...........hrs. 3-4
Number Built during 1912 about 70 of various types
1912. 1912.
Triplane. Monoplane. Military biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) no data no data
Span.............feet(m.) 23 (7)
Area.........sq. feet(m?) ...
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor................h.p. Gnome
Speed,max.... m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance ...........hrs. 3-4
Number Built during 1912 about 70 of various types
EULER. August Euler, Frankfurt a.M. In 1908 Euler secured Voisin rights for Germany. In 1910 he took out a patent for a design of his own. In the summer of 1911 he built a successful monoplane, in the autumn of the same year a triplane. Existing models are as follows:--
1912. 1912.
Triplane. Monoplane. Military biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) no data no data
Span.............feet(m.) 23 (7)
Area.........sq. feet(m?) ...
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor................h.p. Gnome
Speed,max.... m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance ...........hrs. 3-4
Number Built during 1912 about 70 of various types
1912. 1912.
Triplane. Monoplane. Military biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) no data no data
Span.............feet(m.) 23 (7)
Area.........sq. feet(m?) ...
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor................h.p. Gnome
Speed,max.... m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance ...........hrs. 3-4
Number Built during 1912 about 70 of various types
EULER. August Euler, Frankfurt a.M. In 1908 Euler secured Voisin rights for Germany. In 1910 he took out a patent for a design of his own. In the summer of 1911 he built a successful monoplane, in the autumn of the same year a triplane. Existing models are as follows:--
1912. 1912.
Triplane. Monoplane. Military biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) no data no data
Span.............feet(m.) 23 (7)
Area.........sq. feet(m?) ...
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor................h.p. Gnome
Speed,max.... m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance ...........hrs. 3-4
Number Built during 1912 about 70 of various types
1912. 1912.
Triplane. Monoplane. Military biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) no data no data
Span.............feet(m.) 23 (7)
Area.........sq. feet(m?) ...
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor................h.p. Gnome
Speed,max.... m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance ...........hrs. 3-4
Number Built during 1912 about 70 of various types
FOKKER. Monoplanes. Fokker-Aeroplanbau, G.m.b.H., 18 Parkstrasse, Johannisthal bei Berlin.
Capacity: 40.
1912. 1912.
A. B.
Length..........feet(m.) 26? (8) 26? (8.25)
Span............feet(m.) 37? (11.50) 39-1/3 (12)
Area.......sq. feet(m?.) 226 (21) 242 (22.50)
Weight, total lbs.(kgs.) 838 (380) 1036 (470)
useful lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...............h.p. 70 Argus 100 Argus
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 56 (90) 68 (108)
min. m.p.h. (km.) ... ...
Endurance...........hrs. 4-6 4-6
Number Built during 1912 3 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1913.
A. B. C. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9) 29? (9) 29? (9) 31 (9.50)
Span........feet(m.) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 2? (16.20)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26) 280 (26) ...
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs.) 970 (440) 1146 (520) 1190 (540) ...
...useful, bs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Argus or 100 Argus 70 Renault 100 Renault
Dixi or Mercedes
Speed,
....max, m.p.h.(km.) 52 (83) 60 (96) 53 (85) 59 (95)
....min, m.p.h.(km.) 43 (70) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 5-8 5-8 4-6 4
Number built
during 1912. 6 5 2 ...
Remarks.--The Fokker is a machine of Dutch origin. (See DUTCH).
Capacity: 40.
1912. 1912.
A. B.
Length..........feet(m.) 26? (8) 26? (8.25)
Span............feet(m.) 37? (11.50) 39-1/3 (12)
Area.......sq. feet(m?.) 226 (21) 242 (22.50)
Weight, total lbs.(kgs.) 838 (380) 1036 (470)
useful lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...............h.p. 70 Argus 100 Argus
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 56 (90) 68 (108)
min. m.p.h. (km.) ... ...
Endurance...........hrs. 4-6 4-6
Number Built during 1912 3 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1913.
A. B. C. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9) 29? (9) 29? (9) 31 (9.50)
Span........feet(m.) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 2? (16.20)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26) 280 (26) ...
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs.) 970 (440) 1146 (520) 1190 (540) ...
...useful, bs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Argus or 100 Argus 70 Renault 100 Renault
Dixi or Mercedes
Speed,
....max, m.p.h.(km.) 52 (83) 60 (96) 53 (85) 59 (95)
....min, m.p.h.(km.) 43 (70) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 5-8 5-8 4-6 4
Number built
during 1912. 6 5 2 ...
Remarks.--The Fokker is a machine of Dutch origin. (See DUTCH).
FOKKER. Monoplanes. Fokker-Aeroplanbau, G.m.b.H., 18 Parkstrasse, Johannisthal bei Berlin.
Capacity: 40.
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1913.
A. B. C. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9) 29? (9) 29? (9) 31 (9.50)
Span........feet(m.) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 2? (16.20)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26) 280 (26) ...
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs.) 970 (440) 1146 (520) 1190 (540) ...
...useful, bs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Argus or 100 Argus 70 Renault 100 Renault
Dixi or Mercedes
Speed,
....max, m.p.h.(km.) 52 (83) 60 (96) 53 (85) 59 (95)
....min, m.p.h.(km.) 43 (70) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 5-8 5-8 4-6 4
Number built
during 1912. 6 5 2 ...
Remarks.--The Fokker is a machine of Dutch origin. (See DUTCH).
Capacity: 40.
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1913.
A. B. C. Hydro-
aeroplane.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9) 29? (9) 29? (9) 31 (9.50)
Span........feet(m.) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 42? (13.2) 2? (16.20)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26) 280 (26) ...
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs.) 970 (440) 1146 (520) 1190 (540) ...
...useful, bs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Argus or 100 Argus 70 Renault 100 Renault
Dixi or Mercedes
Speed,
....max, m.p.h.(km.) 52 (83) 60 (96) 53 (85) 59 (95)
....min, m.p.h.(km.) 43 (70) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 5-8 5-8 4-6 4
Number built
during 1912. 6 5 2 ...
Remarks.--The Fokker is a machine of Dutch origin. (See DUTCH).
GOEDECKER. J. Goedecker, Flugmaschinen-Werke, Niederwalluf a. Rh. Flying School: Flugplatz Grosser Sand bei Mainz.
1912. 1911.
Monoplane Monoplane
"Sturmvogel." "Sturmvogel."
Length............feet(m.) 32? (10) 29? (9)
Span..............feet(m.) 47? (14.5) 47? (14.5)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 387 (36) ...
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 992 (459) 827 (375)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor............... h.p. 100 Dixi 70 Argus
Speed..........m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ...
Number built during 1912.. 8 2
1912. 1911.
Monoplane Monoplane
"Sturmvogel." "Sturmvogel."
Length............feet(m.) 32? (10) 29? (9)
Span..............feet(m.) 47? (14.5) 47? (14.5)
Area..........sq.feet(m?.) 387 (36) ...
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 992 (459) 827 (375)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor............... h.p. 100 Dixi 70 Argus
Speed..........m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ...
Number built during 1912.. 8 2
GRADE. Hans Grade Fliegerwerke, Bork, Post Bruck (Mark). Founded 1910 by H. Grade, who was the first man in Germany to fly with a German machine. During 1911 Grades had a considerable vogue, but since then have not been prominent.
[Illustration: Photograph, from above rear, caption: 1912 racer.]
Model and date. Racer, 1911. Racer, 1912. Racer, 1912.
C. D. E.
Length..............feet(m.) 33 (10) 21 (6.50) 26? (8)
Span................feet(m.) 39? (12) 34? (10.50) 41 (12.50)
Area .........sq. feet(m^[2].) 480 (45) 240 (22) 360 (33)
Weight, machine...
...............lbs.(kgs.) 375 (170) 408 (185) 595 (270)
Weight, useful...
...............lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...................h.p. various ... ...
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 71 (115) 71 (115)
Number built during 1912.... ? 1 or 2 ?
[Illustration: Photograph, from above rear, caption: 1912 racer.]
Model and date. Racer, 1911. Racer, 1912. Racer, 1912.
C. D. E.
Length..............feet(m.) 33 (10) 21 (6.50) 26? (8)
Span................feet(m.) 39? (12) 34? (10.50) 41 (12.50)
Area .........sq. feet(m^[2].) 480 (45) 240 (22) 360 (33)
Weight, machine...
...............lbs.(kgs.) 375 (170) 408 (185) 595 (270)
Weight, useful...
...............lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...................h.p. various ... ...
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 71 (115) 71 (115)
Number built during 1912.... ? 1 or 2 ?
GRADE. Hans Grade Fliegerwerke, Bork, Post Bruck (Mark). Founded 1910 by H. Grade, who was the first man in Germany to fly with a German machine. During 1911 Grades had a considerable vogue, but since then have not been prominent.
[Illustration: Photograph, from above rear, caption: 1912 racer.]
Model and date. Racer, 1911. Racer, 1912. Racer, 1912.
C. D. E.
Length..............feet(m.) 33 (10) 21 (6.50) 26? (8)
Span................feet(m.) 39? (12) 34? (10.50) 41 (12.50)
Area .........sq. feet(m^[2].) 480 (45) 240 (22) 360 (33)
Weight, machine...
...............lbs.(kgs.) 375 (170) 408 (185) 595 (270)
Weight, useful...
...............lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...................h.p. various ... ...
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 71 (115) 71 (115)
Number built during 1912.... ? 1 or 2 ?
[Illustration: Photograph, from above rear, caption: 1912 racer.]
Model and date. Racer, 1911. Racer, 1912. Racer, 1912.
C. D. E.
Length..............feet(m.) 33 (10) 21 (6.50) 26? (8)
Span................feet(m.) 39? (12) 34? (10.50) 41 (12.50)
Area .........sq. feet(m^[2].) 480 (45) 240 (22) 360 (33)
Weight, machine...
...............lbs.(kgs.) 375 (170) 408 (185) 595 (270)
Weight, useful...
...............lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...................h.p. various ... ...
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 71 (115) 71 (115)
Number built during 1912.... ? 1 or 2 ?
HANUSCHKE. Bruno Hanuschke, Flugzeugbau, Johannisthal b. Berlin. Capacity: small.
1912. 1913.
"Typ populaire" Typ II.
Length...........feet(m.) 24? (7.50) 21 (6.50)
Span.............feet m.) 27 (8.25) 26? (8)
Area.........sq.feet(m?.) 183 (17) 172 (16)
Weight, total..lbs.(kgs.) 716 (325) 1102 (500)
Weight, useful.lbs.(kgs.) 385 (175) 600 (275)
Motor................h.p. 35 Anzani 50 Gnome
Speed.........m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 62 (100)
Endurance............hrs. 2 2
Number built during 1912. 2 2
Remarks.--
1912. 1913.
"Typ populaire" Typ II.
Length...........feet(m.) 24? (7.50) 21 (6.50)
Span.............feet m.) 27 (8.25) 26? (8)
Area.........sq.feet(m?.) 183 (17) 172 (16)
Weight, total..lbs.(kgs.) 716 (325) 1102 (500)
Weight, useful.lbs.(kgs.) 385 (175) 600 (275)
Motor................h.p. 35 Anzani 50 Gnome
Speed.........m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 62 (100)
Endurance............hrs. 2 2
Number built during 1912. 2 2
Remarks.--
HARLAN. Harlan Werke, G. m. b. H., 21 Moltkestrasse, Johannisthal bei Berlin. Established 1909, turned into present Company, 1911. Output capacity about 50 machines a year.
1912. 1912-13.
Military monoplane. Military monoplane.
Length.............feet(m.) 26? (8) 30 (9.10)
Span...............feet(m.) 39-1/3 (12) 45? (13.80)
Area...........sq.feet(m?.) 312 (29) 312 (29)
Weight, total....lbs.(kgs.) ... 1984 (900)
Weight, useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... 1323 (600)
Motor..................h.p. 100 Argus or Mercedes 100 Argus
Speed...........m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 69 (110)
Endurance..............hrs. 7-8 7-8
Number built during 1912... 20 15
1912. 1912-13.
Military monoplane. Military monoplane.
Length.............feet(m.) 26? (8) 30 (9.10)
Span...............feet(m.) 39-1/3 (12) 45? (13.80)
Area...........sq.feet(m?.) 312 (29) 312 (29)
Weight, total....lbs.(kgs.) ... 1984 (900)
Weight, useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... 1323 (600)
Motor..................h.p. 100 Argus or Mercedes 100 Argus
Speed...........m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 69 (110)
Endurance..............hrs. 7-8 7-8
Number built during 1912... 20 15
JATHO. Jatho Flugzeugwerke, G.m.b.H., Stader Chaussee 32, Hannover. Karl Jatho built his first aeroplane in 1899, and has produced machines at intervals ever since. Capacity: small.
1913.
Length..............feet(m.) 29? (9)
Span................feet(m.) 49? (15)
Area............sq.feet(m?.) 345 (32)
Weight, total.....lbs.(kgs.) 2116 (960)
Weight, useful....lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450)
Motor..................h.p. 100 N.A.G.
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) 75 (120)
Endurance..............hrs. 3
Number built during 1912... 2
Remarks.--
1913.
Length..............feet(m.) 29? (9)
Span................feet(m.) 49? (15)
Area............sq.feet(m?.) 345 (32)
Weight, total.....lbs.(kgs.) 2116 (960)
Weight, useful....lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450)
Motor..................h.p. 100 N.A.G.
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) 75 (120)
Endurance..............hrs. 3
Number built during 1912... 2
Remarks.--
JEANNIN. Emile Jeannin, Flugzeugbau, G.m.b.H., Stahltauben & Renneindecker Fabrik, Johannisthal b. Berlin. Capacity: small.
1912. 1913.
"Taube" monoplane. Racing monoplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 29? (9) ...
Span.............feet(m.) 42? (13) ...
Area.........sq.feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight, total...lbs.(kg.) ... ...
useful...lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor................h.p. 100-150 Argus 150 Argus
Speed.........m.p.h.(km.) 68 (110) 87 (140)
Endurance............hrs. 5-8 4-7
Number built during 1912. 2 3
Remarks.--The 1913 was building only in March.
1912. 1913.
"Taube" monoplane. Racing monoplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 29? (9) ...
Span.............feet(m.) 42? (13) ...
Area.........sq.feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight, total...lbs.(kg.) ... ...
useful...lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor................h.p. 100-150 Argus 150 Argus
Speed.........m.p.h.(km.) 68 (110) 87 (140)
Endurance............hrs. 5-8 4-7
Number built during 1912. 2 3
Remarks.--The 1913 was building only in March.
KAHNT. Oswald Kahnt, Flugzeugbau, Leipzig. Capacity: small.
K.F. 1913.
"Falke."
Length...............feet(m.) 27? (8.50)
Span.................feet(m.) 42? (13)
Area............sq. feet(m?.) 291 (27)
Weight, total......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Weight, useful.....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor....................h.p. 50-70
Speed.............m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
Number built during 1912.... new firm
K.F. 1913.
"Falke."
Length...............feet(m.) 27? (8.50)
Span.................feet(m.) 42? (13)
Area............sq. feet(m?.) 291 (27)
Weight, total......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Weight, useful.....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor....................h.p. 50-70
Speed.............m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
Number built during 1912.... new firm
KONDOR. Kondor Flugzeugwerke G.m.b.H., Essen, Ruhr. Fabrik auf dem Flugplatz. Rotthausen. Capacity: 30 or so a year.
1912. 1913.
Length.............feet(m.) 33? (10.30) 27 (8.20)
Span...............feet(m.) 48? (14.80) 46 (14)
Area..........sq. feet(m?.) 258 (24) 280 (26)
Weight, total....lbs.(kgs.) 1543 ( 700) 1328 600)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor..................h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed...........m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105) 70 (112)
Number Built during 1912... 2 ...
Remarks.--Both models torpedo body, on 4 skids. Planes dart V form. Constructor: J. Suwelack.
1912. 1913.
Length.............feet(m.) 33? (10.30) 27 (8.20)
Span...............feet(m.) 48? (14.80) 46 (14)
Area..........sq. feet(m?.) 258 (24) 280 (26)
Weight, total....lbs.(kgs.) 1543 ( 700) 1328 600)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor..................h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed...........m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105) 70 (112)
Number Built during 1912... 2 ...
Remarks.--Both models torpedo body, on 4 skids. Planes dart V form. Constructor: J. Suwelack.
MROZINSKI. Bernard Mrozinski, Berlin-Wilmersdorf. Established 1912.
Length, 23 feet (7 m.) span, 32? feet (10 m.) area, 215 sq. feet (20 m?.)
Weight.--661 lbs. (300 kgs.)
Motor.--20 h.p. Anzani.
Speed.--50 m.p.h. (80 km.)
Remarks.--One machine only built in 1912.
Length, 23 feet (7 m.) span, 32? feet (10 m.) area, 215 sq. feet (20 m?.)
Weight.--661 lbs. (300 kgs.)
Motor.--20 h.p. Anzani.
Speed.--50 m.p.h. (80 km.)
Remarks.--One machine only built in 1912.
OERTZ. Max Oertz, Yachtwerft, Reiherstieg b. Hamburg. Famous yacht builder. Commenced aeroplane construction in 1911. Existing models as below. Capacity about 25 machines a year.
M 1911-12. M 1912-13.
Monoplane. Monoplane.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9) 30? (9.2)
Span........feet(m.) 41? (12.75) 41? (12.75)
Area...sq.feet (m?.) 247 (23) 263 (24.5)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 948 (430) 1212 (550)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 70 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 75 (120)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 3 4
Number built
during 1912....... 3 1
M 1911-12. M 1912-13.
Monoplane. Monoplane.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9) 30? (9.2)
Span........feet(m.) 41? (12.75) 41? (12.75)
Area...sq.feet (m?.) 247 (23) 263 (24.5)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 948 (430) 1212 (550)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 70 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 75 (120)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 3 4
Number built
during 1912....... 3 1
OTTO. Gustav Otto, Flugmaschinenwerke, Schleissheimer Str. 135, Munich. Started building in 1911. Present max. capacity about 30 machines a year.
M 1912.
Biplane.
Length.........feet(m.) ...
Span...........feet(m.) ...
Area......sq. feet(m?.) ...
Weight,
total....lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor..............h.p. 100 A. G. Otto.
Speed,
max.....m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance.........hrs. 6-8
Number built during 1912 6
Remarks.--All 1912 machines purchased for German Army.
M 1912.
Biplane.
Length.........feet(m.) ...
Span...........feet(m.) ...
Area......sq. feet(m?.) ...
Weight,
total....lbs.(kgs.) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor..............h.p. 100 A. G. Otto.
Speed,
max.....m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110)
min.....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance.........hrs. 6-8
Number built during 1912 6
Remarks.--All 1912 machines purchased for German Army.
PEGA-EMICH. Flugtechnische und mechanische Werke vorm. Pega & Emich, Falterstrasse 13-15, Griesheim, Frankurt-a-M. Commenced building with a 6-decker in 1910. Capacity: small.
1913.
Buteno monoplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 39? (12)
Span.............feet(m.) 46 (14)
Area........sq. feet(m?.) 355 (33)
Weight, total...lbs.(kg.) 838 (380)
useful...lbs.(kg.) 1102 (500)
Motor................h.p. 70 Argus
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance............hrs. 2
Number built during 1912. ...
1913.
Buteno monoplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 39? (12)
Span.............feet(m.) 46 (14)
Area........sq. feet(m?.) 355 (33)
Weight, total...lbs.(kg.) 838 (380)
useful...lbs.(kg.) 1102 (500)
Motor................h.p. 70 Argus
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ...
Endurance............hrs. 2
Number built during 1912. ...
PIPPART-NOLL. Pippart-Noll-Flugzeugbau, Mannheim.
P.N.1 P.N.2. P.N.3.
Type. Sporting. "Uberland" Military.
1912. 1912. 1913.
Length.....feet (m.) 31 (9.50) 28 (8.50) 28 (8.50 also 7)
Span.......feet (m.) 34? (10.50) 39-1/3 (12) 45? (13.70)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 215 (20) 280 (26) 300 (28)
Weight,
machine, lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 838 (380) 1234 (560)
useful, lbs.(kgs.) 330 (150) 463 (210) 441 (200)
Motor...........h.p. 70 Argus 70 Argus 70 Argus
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95) 62 (100) 68 (110)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... 50 (80)
Endurance.. hrs. ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 1 1 1
P.N.1 P.N.2. P.N.3.
Type. Sporting. "Uberland" Military.
1912. 1912. 1913.
Length.....feet (m.) 31 (9.50) 28 (8.50) 28 (8.50 also 7)
Span.......feet (m.) 34? (10.50) 39-1/3 (12) 45? (13.70)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 215 (20) 280 (26) 300 (28)
Weight,
machine, lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 838 (380) 1234 (560)
useful, lbs.(kgs.) 330 (150) 463 (210) 441 (200)
Motor...........h.p. 70 Argus 70 Argus 70 Argus
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95) 62 (100) 68 (110)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... 50 (80)
Endurance.. hrs. ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 1 1 1
KUHLSTEIN. Kuhlstein Wagenbau, Karosseriefabrik, Salzufer 4, Charlottenburg. This old-established motor car firm commenced to build aeroplanes in 1911. Capacity: 20 a year.
1912. 1912.
Torpedo monoplane. Torpedo monoplane.
I. II.
Length...........feet(m.) 29? (9.10) 27 (8.2)
Span.............feet(m.) 40? (12.4) 35? (10.8)
Area.........sq.feet(m?.) 291 (27) 215 (20)
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) 1984 (900) 2204 (1000)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) 1322 (600) 1543 (700)
Motor................h.p. 100 Argus 96 Mercedes
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
min....m.p.h.(km.) 84 (135) 87 (140)
Endurance............hrs. 3 3
Number Built during 1912 2 2
Remarks.--
1912. 1912.
Torpedo monoplane. Torpedo monoplane.
I. II.
Length...........feet(m.) 29? (9.10) 27 (8.2)
Span.............feet(m.) 40? (12.4) 35? (10.8)
Area.........sq.feet(m?.) 291 (27) 215 (20)
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) 1984 (900) 2204 (1000)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) 1322 (600) 1543 (700)
Motor................h.p. 100 Argus 96 Mercedes
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
min....m.p.h.(km.) 84 (135) 87 (140)
Endurance............hrs. 3 3
Number Built during 1912 2 2
Remarks.--
RUMPLER. E. Rumpler, Luftfahrzeugbau G.m.b.H., Siegfriedstrasse 202, Berlin-Lichtenberg, also Johannisthal b. Berlin. Established 1909 by E. Rumpler and R. Haessner for the construction in Germany of Etrich (see Austria) Monoplanes. These now vary considerably from the original Etrich. Capacity at present about 200 to 300 machines a year. Standard models are as follows:--
1912. 1912. 1913.
Monoplane. "Taube." Hydro.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9.50) 34 (10.30) 33 (10)
Span........feet(m.) 41? (12.65) 46 (14) 49? (15)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 247 (23) 336 (32) 387 (36)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1398 (630) 1190 (540) 1328 (600)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 771 (350) 551 (230) 485 (220)
Motor...........h.p. 95 Mercedes 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 81 (130) 59 (95) 56 (90)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 6-7 4-6 ...
Number built
during 1912, 1 60 3
1912. 1912. 1913.
Monoplane. "Taube." Hydro.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9.50) 34 (10.30) 33 (10)
Span........feet(m.) 41? (12.65) 46 (14) 49? (15)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 247 (23) 336 (32) 387 (36)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1398 (630) 1190 (540) 1328 (600)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 771 (350) 551 (230) 485 (220)
Motor...........h.p. 95 Mercedes 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 81 (130) 59 (95) 56 (90)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 6-7 4-6 ...
Number built
during 1912, 1 60 3
RUMPLER. E. Rumpler, Luftfahrzeugbau G.m.b.H., Siegfriedstrasse 202, Berlin-Lichtenberg, also Johannisthal b. Berlin. Established 1909 by E. Rumpler and R. Haessner for the construction in Germany of Etrich (see Austria) Monoplanes. These now vary considerably from the original Etrich. Capacity at present about 200 to 300 machines a year. Standard models are as follows:--
1912. 1912. 1913.
Monoplane. "Taube." Hydro.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9.50) 34 (10.30) 33 (10)
Span........feet(m.) 41? (12.65) 46 (14) 49? (15)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 247 (23) 336 (32) 387 (36)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1398 (630) 1190 (540) 1328 (600)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 771 (350) 551 (230) 485 (220)
Motor...........h.p. 95 Mercedes 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 81 (130) 59 (95) 56 (90)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 6-7 4-6 ...
Number built
during 1912, 1 60 3
1912. 1912. 1913.
Monoplane. "Taube." Hydro.
Length......feet(m.) 29? (9.50) 34 (10.30) 33 (10)
Span........feet(m.) 41? (12.65) 46 (14) 49? (15)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 247 (23) 336 (32) 387 (36)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1398 (630) 1190 (540) 1328 (600)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 771 (350) 551 (230) 485 (220)
Motor...........h.p. 95 Mercedes 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 81 (130) 59 (95) 56 (90)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.......hrs. 6-7 4-6 ...
Number built
during 1912, 1 60 3
RUTH-ROHDE. Ruth-Rohde, Motorgleitflieger, G.m.b.H., Wandsbeck. Established 1912. Capacity: small.
1912. 1912.
Biplane I. Biplane II.
Length..........feet (m.) 26? (8) 26? (8)
Span............feet (m.) 36 (11) 45 (14)
Area........sq.feet (m?.) 590 (55) 700 (65)
Weight,
total.......lbs.(kgs.) 1653 (750) 1764 (800)
useful......lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor................h.p. 75 Argus 75 Argus
Speed,
max........m.p.h.(km.) 55 (90) 55 (80)
min........m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance............hrs. 3 3-4
Number built during 1912. 1 1
1912. 1912.
Biplane I. Biplane II.
Length..........feet (m.) 26? (8) 26? (8)
Span............feet (m.) 36 (11) 45 (14)
Area........sq.feet (m?.) 590 (55) 700 (65)
Weight,
total.......lbs.(kgs.) 1653 (750) 1764 (800)
useful......lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor................h.p. 75 Argus 75 Argus
Speed,
max........m.p.h.(km.) 55 (90) 55 (80)
min........m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance............hrs. 3 3-4
Number built during 1912. 1 1
SCHELIES. Richard Schelies, Conventstrasse 5 und 5b, Hamburg 23. Flying Station, etc. Dockenhuden a/Elbe.
1913.
Hydro-monoplane.
Length..................feet(m.) 23 7
Span....................feet(m.) 29? 9
Area................sq.feet(m?.) 323 30
Weight, total.........lbs.(kgs.) 705 320
useful........lbs.(kgs.) 220 100
Motor...................h.p. Rheinische Aero 35
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) ...
1913.
Hydro-monoplane.
Length..................feet(m.) 23 7
Span....................feet(m.) 29? 9
Area................sq.feet(m?.) 323 30
Weight, total.........lbs.(kgs.) 705 320
useful........lbs.(kgs.) 220 100
Motor...................h.p. Rheinische Aero 35
Speed............m.p.h.(km.) ...
SCHULZE. Gustav Schulze, Flugzeng Werke, Burg b. Magdeburg. Schulze began to build in 1910 light monoplanes, generally along Santos-Dumont lines. Maximum present capacity about 12 machines a year.
1912. 1912. 1912. 1913.
I. II. III. I.
(2-seater). (2-seater).
Length......feet(m.) 19? (6) 26? (8) 21-1/3(6.50) 23 (7)
Span........feet(m.) 26? (8) 34-1/3(10.5) 28 (8.50) 29-1/3 (9)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 172 (16) 215 (20) 172 (16) 194 (18)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 330 (150) 441 (200) 441 (200) 551 (250)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 24-30 Hilz 24-30 Hilz 35 Haacke 35 Haacke
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 48 (77) 53 (85) 56 (90) 53 (85)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... 43 (70) 50 (80) 46 (75)
Number built
during 1912. 1 3 1 Building.
1912. 1912. 1912. 1913.
I. II. III. I.
(2-seater). (2-seater).
Length......feet(m.) 19? (6) 26? (8) 21-1/3(6.50) 23 (7)
Span........feet(m.) 26? (8) 34-1/3(10.5) 28 (8.50) 29-1/3 (9)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 172 (16) 215 (20) 172 (16) 194 (18)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 330 (150) 441 (200) 441 (200) 551 (250)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 24-30 Hilz 24-30 Hilz 35 Haacke 35 Haacke
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 48 (77) 53 (85) 56 (90) 53 (85)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... 43 (70) 50 (80) 46 (75)
Number built
during 1912. 1 3 1 Building.
SIGISMUND. Prinz Sigismund vein Preussen, Berlin.
Model and date. Monoplane.
Length.............feet m.) 29? (9)
Span...............feet(m.) 42? (13)
Area..........sq. feet(m?.) 323 (30)
Weight, total....lbs.(kgs.) 950 (430)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) 395 (180)
Motor..................... Argus, 100
Speed, max.. ...m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
Number built during 1912... 2
Model and date. Monoplane.
Length.............feet m.) 29? (9)
Span...............feet(m.) 42? (13)
Area..........sq. feet(m?.) 323 (30)
Weight, total....lbs.(kgs.) 950 (430)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) 395 (180)
Motor..................... Argus, 100
Speed, max.. ...m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
Number built during 1912... 2
UNION FLUGZEUGWERKE. Union Flugzeugwerke G.m.b.H. Elsenstrasse 106 & 107, Berlin s.o. 36. Established 1913. Capital 500,000 marks. Capacity of works: 20 machines a year.
Bomhard.
Model and date. Pfeilflieger,
1913.
Length..............feet(m.) 32? (10)
Span................feet(m.) 59 (18)
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) 450 (42)
Weight, total.....lbs.(kgs.) 1235 (560)
Weight, useful....lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280)
Motor...................... 100 Argus
Speed, max.......m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110)
Speed, min.......m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
Number built during 1912... New firm
Bomhard.
Model and date. Pfeilflieger,
1913.
Length..............feet(m.) 32? (10)
Span................feet(m.) 59 (18)
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) 450 (42)
Weight, total.....lbs.(kgs.) 1235 (560)
Weight, useful....lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280)
Motor...................... 100 Argus
Speed, max.......m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110)
Speed, min.......m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
Number built during 1912... New firm
ELLEHAMMER (1905). On 12th September, 1906, this machine made the first free flight in Europe. On 28th June, 1908, it won the prize at Kiel for the first flight in Germany (distance, 47 m.) It was a tractor biplane with a revolving Ellehammer motor. It also had a pendulum seat as a stabilising device.
ANTONI. Soc. di aviazione Antoni, via Vitt. Emanuele, 46, Pisa. School: S. Guisto, Pisa.
Output capacity: about 20 machines a year.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Single seat mono. 2-seater military
mono.
Length............feet(m.) 33 (10) 36 (11)
Span..............feet(m.) 28 (8.50) 28 (8.50)
Area........sq. feet(m^2.) 172 (16) 237 (22)
Weight,machine...lbs.(kg.) 660 (300) 770 (350)
Weight, useful...lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. Gnome or Anzani Gnome and Anzani
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Speed, min.....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance.............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912.. ... ...
Output capacity: about 20 machines a year.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Single seat mono. 2-seater military
mono.
Length............feet(m.) 33 (10) 36 (11)
Span..............feet(m.) 28 (8.50) 28 (8.50)
Area........sq. feet(m^2.) 172 (16) 237 (22)
Weight,machine...lbs.(kg.) 660 (300) 770 (350)
Weight, useful...lbs.(kg.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. Gnome or Anzani Gnome and Anzani
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Speed, min.....m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance.............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912.. ... ...
ASTERIA. Fabbr. Ital. Aeroplani ing. Darbesio e. C., via Salbertrand, 12, Torino (Turin).
School: MIRAFMORI.[*] Capacity: small.
1912-13. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane.
Length..............feet(m.) 21-3/4 (6.50) 29-1/2 (9)
Span................feet(m.) 26-1/2 (8.10) 44 (13.50)
Span................feet(m.) ... 24-1/2 (7.50)
Area..........sq. feet(m^2.) 162 (15) 431 (40)
Weight,.machine...lbs.(kgs.) 530 (240) 110 (500)
Weight, useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...................h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Renault
Speed, max.......m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Speed, min.......m.p.h.(km.) ... ...
Endurance...............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912.... ... ...
1911 Asteria No. 3 pusher biplane - first plane to be used in War during Italian campaign in Bengasi (Oct.1911)
Country of Origin: Italy Designed by Francesco Darbesio, built by Soc.Aeronautica Asteria,Torino
Span: 49'3" Length: 34'5"
Country of Origin: Italy Designed by Francesco Darbesio, built by Soc.Aeronautica Asteria,Torino
Span: 49'3" Length: 34'5"
CALDERARA. Navy hydro-monoplane.
Model 1912-13. "Hydro vol"
Length................feet(m.) 54 (16.50)
Span..................feet(m.) 61 (18.50)
Area.............sq. feet(m?.) 753 (70)
Weight, total.......lbs.(kgs.) 2644 (1200)
useful......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor....................h.p. 150 (formerly 100 Gnome)
Speed, max.........m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
min.........m.p.h.(km.) 50 (80)
Endurance.................hrs. 6?
Number Built during 1912..... 1
Lieut. Calderara's floats consist of a plurality of w.t. compartments with internal lattice frame, well braced. Hull is formed of three skins of wood, sail-cloth between each. Distance between outer floats, 21 feet (6.30 m.) Centre of gravity is only 4? feet (1.40 m.) above water. If necessary wings can be cut away and the central hull used as a boat with emergency sail.
Model 1912-13. "Hydro vol"
Length................feet(m.) 54 (16.50)
Span..................feet(m.) 61 (18.50)
Area.............sq. feet(m?.) 753 (70)
Weight, total.......lbs.(kgs.) 2644 (1200)
useful......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor....................h.p. 150 (formerly 100 Gnome)
Speed, max.........m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
min.........m.p.h.(km.) 50 (80)
Endurance.................hrs. 6?
Number Built during 1912..... 1
Lieut. Calderara's floats consist of a plurality of w.t. compartments with internal lattice frame, well braced. Hull is formed of three skins of wood, sail-cloth between each. Distance between outer floats, 21 feet (6.30 m.) Centre of gravity is only 4? feet (1.40 m.) above water. If necessary wings can be cut away and the central hull used as a boat with emergency sail.
CAPRONI. Soc. di Aviazione Ingg, Caproni e Faccanoni, Vizzola Ticino. School: Vizzola Ticino.
Models 1912-13 Single Seat Single Seat 2-seater 3-seater
mono. A. mono. B. mono. mono.
Length.....feet(m.) 26? (8) 26-1/2 (8) ... ...
Span.......feet(m.) 29 (8.80) 29 (8.80) ... ...
Area...sq. ft.(m?.) 162 (15) 162 (15) 172 (16) 226 (21)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 485 (220) 660 (300) 750 (340) 760 (345) useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 35 Anzani 50 Gnome 60 Anzani 80 Gnome
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 75 (120) 75 (120) 87 (140)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance......hrs. 3? ... ... 4
Number built
during 1912. ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--At the end of 1912, held Italian record for speed, 200-300 k.m. Flown by Cobioni.
CAPRONI-BRISTOL. Caproni also builds under Bristol licence.
Models 1912-13 Single Seat Single Seat 2-seater 3-seater
mono. A. mono. B. mono. mono.
Length.....feet(m.) 26? (8) 26-1/2 (8) ... ...
Span.......feet(m.) 29 (8.80) 29 (8.80) ... ...
Area...sq. ft.(m?.) 162 (15) 162 (15) 172 (16) 226 (21)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 485 (220) 660 (300) 750 (340) 760 (345) useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 35 Anzani 50 Gnome 60 Anzani 80 Gnome
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 75 (120) 75 (120) 87 (140)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance......hrs. 3? ... ... 4
Number built
during 1912. ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--At the end of 1912, held Italian record for speed, 200-300 k.m. Flown by Cobioni.
CAPRONI-BRISTOL. Caproni also builds under Bristol licence.
CHIRIBIRI. A Chiribiri e. C, via Lamarmora 28, and via Don Bosco 68-73. Torino (Turin).
Models 1912-13. 45 h.p. mono. 50 h.p. mono. Racing mono. 80 h.p. mono.
Leng......feet(m.) 23 (7) 23 (7) 24? (7.50) 25? (7.80)
Span......feet(m.) 29? (9) 29? (9) 31 (9.30) 39-2/3 (12.10)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 204 (19) 204 (19) 226 (21) 258 (24)
Weight,
total..lbs.(kgs) 595 (270) 683 (310) 772 (350) 595 (270)
useful..lbs.(kgs) ... ... ... ...
Motor........ h.p. 45 Chiribiri 50 Chiribiri 60 Chiribiri 80 Chiribiri
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 44 (70) 56 (90) 103 (165) 65 (105)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912. ... ... 2 ...
Models 1912-13. 45 h.p. mono. 50 h.p. mono. Racing mono. 80 h.p. mono.
Leng......feet(m.) 23 (7) 23 (7) 24? (7.50) 25? (7.80)
Span......feet(m.) 29? (9) 29? (9) 31 (9.30) 39-2/3 (12.10)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 204 (19) 204 (19) 226 (21) 258 (24)
Weight,
total..lbs.(kgs) 595 (270) 683 (310) 772 (350) 595 (270)
useful..lbs.(kgs) ... ... ... ...
Motor........ h.p. 45 Chiribiri 50 Chiribiri 60 Chiribiri 80 Chiribiri
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 44 (70) 56 (90) 103 (165) 65 (105)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912. ... ... 2 ...
FRIULI. E. Pensuti e E. Calligaro, Pordenone. School: Pordenone. A 30-35 h.p. Anzani motor
monoplane. Area, l50 sq. feet. (14 m^2). Generally of Bleriot type, but Hanriot type landing carriage.
monoplane. Area, l50 sq. feet. (14 m^2). Generally of Bleriot type, but Hanriot type landing carriage.
GRAHAM-BELL II. Flights were made by Dr. Graham-Bell in a tetrahedal type, similar to one described in the 1911 edition.
McCURDY-WILLARD. Biplane.
Maximum length, 26? feet (8 m.) maximum breadth, 31-1/3 feet (9.50 m.) supporting surface, --sq. feet (--m?.)
Total weight.--
Body.-- Central skid in combination with 4 wheels. Triangular body, base of triangle on top. Fuselage entirely enclosed.
Planes.-- Maximum span, 31-1/3 feet (9.50 m.) Chord, 3? feet (1 m.) Gap, 5 feet (1.50 m.) Ailerons at trailing edge of wing tips, 6 feet x 2 feet (1.80 X 0.60 m.)
Moto r--
Speed.--
Tractor.-- Diameter, 7? feet (2.40 m.) Pitch, 6 feet (1.82 m.)
Steering.-- Double elevator placed in rear of tail. Control, push and pull wheel. Rudder in rear. Control, wheel. Ailerons. Control, turning steering-wheel left or right.
Remarks.-- See Aeronautics, U.S.A., August, 1911.
* * * * *
There has been also the Baddeck and other early machines (see 1911 edition), but none of them seem to be in existence at the present time.
Maximum length, 26? feet (8 m.) maximum breadth, 31-1/3 feet (9.50 m.) supporting surface, --sq. feet (--m?.)
Total weight.--
Body.-- Central skid in combination with 4 wheels. Triangular body, base of triangle on top. Fuselage entirely enclosed.
Planes.-- Maximum span, 31-1/3 feet (9.50 m.) Chord, 3? feet (1 m.) Gap, 5 feet (1.50 m.) Ailerons at trailing edge of wing tips, 6 feet x 2 feet (1.80 X 0.60 m.)
Moto r--
Speed.--
Tractor.-- Diameter, 7? feet (2.40 m.) Pitch, 6 feet (1.82 m.)
Steering.-- Double elevator placed in rear of tail. Control, push and pull wheel. Rudder in rear. Control, wheel. Ailerons. Control, turning steering-wheel left or right.
Remarks.-- See Aeronautics, U.S.A., August, 1911.
* * * * *
There has been also the Baddeck and other early machines (see 1911 edition), but none of them seem to be in existence at the present time.
JUNE BUG (1908-09). Famous machine of its era. Built by the Aeronautical Society of America (see Cygnet II). Second machine to fly in the U.S.A. Did 2000 miles before being broken up.
BALDWIN Biplanes. Captain Thos. S. Baldwin, PO Box, 78, Madison Square, N.Y. About half-a-dozen steel biplanes have been produced in 1911 by Captain Baldwin, and he and other aviators, Badger, Hammond, Miss Scott Mass, etc., have flown these at various exhibitions and meets, and are classed with well-known successful American biplanes.
Details of Baldwin ("Red Devil").
Length.--28-1/4 feet (8.60 m.) Span.--28-3/4 feet (8.75 m.) Motor.--50-60 h.p. Hall-Scott Propeller.--One Requa-Gibson in rear of main planes. Diameter, 7 feet (2.13 m.) Pitch, 6 feet (1.82 m.) Speed.--60 m.p.h. (97 k.p.h.)
Details of Baldwin ("Red Devil").
Length.--28-1/4 feet (8.60 m.) Span.--28-3/4 feet (8.75 m.) Motor.--50-60 h.p. Hall-Scott Propeller.--One Requa-Gibson in rear of main planes. Diameter, 7 feet (2.13 m.) Pitch, 6 feet (1.82 m.) Speed.--60 m.p.h. (97 k.p.h.)
BENOIST. Benoist Aircraft Co., 6628, Delmar Boulevard, St. Louis, Mo. (formerly Aeronautic Supply Co.
Model and date. 1912-13. 1913.
"Headless." Flying boat.
Tandem biplane.
Length............feet(m.) 22-1/3 (6.85) 27
Span..............feet(m.) 30 (9.15) 42-1/6 (12.80)
Area.........sq. feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight,total....lbs.(kgs.) ... 1004 (455)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. ... 75 Roberts
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) 68 (110) ...
min.....m.p.h.(km.) 31 (50) ...
Endurance.............hrs. 3
Notes.--The boat of the flying boat is 23-5/6 feet long, by 2 feet 2? inches wide. Shipable wheels. See Aeronautics, January, 1913.
Model and date. 1912-13. 1913.
"Headless." Flying boat.
Tandem biplane.
Length............feet(m.) 22-1/3 (6.85) 27
Span..............feet(m.) 30 (9.15) 42-1/6 (12.80)
Area.........sq. feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight,total....lbs.(kgs.) ... 1004 (455)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. ... 75 Roberts
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) 68 (110) ...
min.....m.p.h.(km.) 31 (50) ...
Endurance.............hrs. 3
Notes.--The boat of the flying boat is 23-5/6 feet long, by 2 feet 2? inches wide. Shipable wheels. See Aeronautics, January, 1913.
1911 Benoist Headless pusher biplane (land and seaplane) St. Louis
Country of Origin: USA Designed by Thomas W.Benoist and built by Benoist Aircraft Co.
Span: 30' Length: 22'6" Range: 180 miles Price: US$ 3950- land; US$4150- with float
Country of Origin: USA Designed by Thomas W.Benoist and built by Benoist Aircraft Co.
Span: 30' Length: 22'6" Range: 180 miles Price: US$ 3950- land; US$4150- with float
BENOIST. Benoist Aircraft Co., 6628, Delmar Boulevard, St. Louis, Mo. (formerly Aeronautic Supply Co.
Model and date. 1912-13. 1913.
"Headless." Flying boat.
Tandem biplane.
Length............feet(m.) 22-1/3 (6.85) 27
Span..............feet(m.) 30 (9.15) 42-1/6 (12.80)
Area.........sq. feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight,total....lbs.(kgs.) ... 1004 (455)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. ... 75 Roberts
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) 68 (110) ...
min.....m.p.h.(km.) 31 (50) ...
Endurance.............hrs. 3
Notes.--The boat of the flying boat is 23-5/6 feet long, by 2 feet 2? inches wide. Shipable wheels. See Aeronautics, January, 1913.
Model and date. 1912-13. 1913.
"Headless." Flying boat.
Tandem biplane.
Length............feet(m.) 22-1/3 (6.85) 27
Span..............feet(m.) 30 (9.15) 42-1/6 (12.80)
Area.........sq. feet(m?.) ... ...
Weight,total....lbs.(kgs.) ... 1004 (455)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.................h.p. ... 75 Roberts
Speed, max.....m.p.h.(km.) 68 (110) ...
min.....m.p.h.(km.) 31 (50) ...
Endurance.............hrs. 3
Notes.--The boat of the flying boat is 23-5/6 feet long, by 2 feet 2? inches wide. Shipable wheels. See Aeronautics, January, 1913.
BOKOR TRIPLANE. - In this American design the double triangular-shaped tail and the swinging aviator's seat, which automatically warps the lower plane, are the main features.
BOKOR (1909). The third American machine to leave the ground; the second purely U.S. one.
BOKOR (1909). The third American machine to leave the ground; the second purely U.S. one.
BOLAND. Boland Aeroplane & Motor Co., 182l, Broadway, New York. Works: Ft. Center St. Newark, N.J.
Model and date. 1913.
"Tailless."
Length................feet(m.) 21-1/6 (6.45)
Span..................feet(m.) 35? (10.80)
Area............sq. feet(m^2.) ...
Weight, total.......lbs.(kgs.) 900 (408)
useful......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor.....................h.p. 60 Boland
Speed..............m.p.h.(km.) 60 (95)
Number built during 1912 1
A refinement of the original machine of the late F.E. Boland, which first flew in 1911. Control by two special jibs which work inward. Designed to be used also as a hydro, with three step floats. No rudder or ailerons. Full details, etc., see Aeronautics, U.S.A., May, 1913, and Aircraft, U.S.A., May, 1913.
Model and date. 1913.
"Tailless."
Length................feet(m.) 21-1/6 (6.45)
Span..................feet(m.) 35? (10.80)
Area............sq. feet(m^2.) ...
Weight, total.......lbs.(kgs.) 900 (408)
useful......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor.....................h.p. 60 Boland
Speed..............m.p.h.(km.) 60 (95)
Number built during 1912 1
A refinement of the original machine of the late F.E. Boland, which first flew in 1911. Control by two special jibs which work inward. Designed to be used also as a hydro, with three step floats. No rudder or ailerons. Full details, etc., see Aeronautics, U.S.A., May, 1913, and Aircraft, U.S.A., May, 1913.
BURGESS. Burgess Co. & Curtis, Marblehead, Mass. Built Wright types under license, also machines of their own.
Model and date. Military Coast defence Naval flying
tractor. hydro. boat.
1912-13. 1913. 1913.
Length.....feet(m.) 37? (8.50) 33-1/3 (9.55) 31 (9.45)
Span.......feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 37? (12) 42 (13.10)
36 (10.97)
Area...sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
useful,lbs.(kgs.) ... 775 (352) ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 60 Sturtevant 70 Renault
muffled
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 45 (70) 59 (95) ...
Endurance......hrs. 4? 4? ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.-- Lumina fabric. Special clear view Boat 29?feet long.
Single screw. for observation. 2--2 step floats.
Details, 2--1 step mahogany Petrol, 48 gallons.
Aeronautics, and copper floats. Details,
(U.S.A.), Useful weight Aeronautics,
May-June,1912. includes floats. (U.S.A.), May,1913.
Details,
Aeronautics,
(U.S.A.), Feb.,1913.
Model and date. Military Coast defence Naval flying
tractor. hydro. boat.
1912-13. 1913. 1913.
Length.....feet(m.) 37? (8.50) 33-1/3 (9.55) 31 (9.45)
Span.......feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 37? (12) 42 (13.10)
36 (10.97)
Area...sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
useful,lbs.(kgs.) ... 775 (352) ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 60 Sturtevant 70 Renault
muffled
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 45 (70) 59 (95) ...
Endurance......hrs. 4? 4? ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.-- Lumina fabric. Special clear view Boat 29?feet long.
Single screw. for observation. 2--2 step floats.
Details, 2--1 step mahogany Petrol, 48 gallons.
Aeronautics, and copper floats. Details,
(U.S.A.), Useful weight Aeronautics,
May-June,1912. includes floats. (U.S.A.), May,1913.
Details,
Aeronautics,
(U.S.A.), Feb.,1913.
BURGESS. Burgess Co. & Curtis, Marblehead, Mass. Built Wright types under license, also machines of their own.
Model and date. Military Coast defence Naval flying
tractor. hydro. boat.
1912-13. 1913. 1913.
Length.....feet(m.) 37? (8.50) 33-1/3 (9.55) 31 (9.45)
Span.......feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 37? (12) 42 (13.10)
36 (10.97)
Area...sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
useful,lbs.(kgs.) ... 775 (352) ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 60 Sturtevant 70 Renault
muffled
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 45 (70) 59 (95) ...
Endurance......hrs. 4? 4? ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.-- Lumina fabric. Special clear view Boat 29?feet long.
Single screw. for observation. 2--2 step floats.
Details, 2--1 step mahogany Petrol, 48 gallons.
Aeronautics, and copper floats. Details,
(U.S.A.), Useful weight Aeronautics,
May-June,1912. includes floats. (U.S.A.), May,1913.
Details,
Aeronautics,
(U.S.A.), Feb.,1913.
Model and date. Military Coast defence Naval flying
tractor. hydro. boat.
1912-13. 1913. 1913.
Length.....feet(m.) 37? (8.50) 33-1/3 (9.55) 31 (9.45)
Span.......feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 37? (12) 42 (13.10)
36 (10.97)
Area...sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
useful,lbs.(kgs.) ... 775 (352) ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 60 Sturtevant 70 Renault
muffled
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 45 (70) 59 (95) ...
Endurance......hrs. 4? 4? ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.-- Lumina fabric. Special clear view Boat 29?feet long.
Single screw. for observation. 2--2 step floats.
Details, 2--1 step mahogany Petrol, 48 gallons.
Aeronautics, and copper floats. Details,
(U.S.A.), Useful weight Aeronautics,
May-June,1912. includes floats. (U.S.A.), May,1913.
Details,
Aeronautics,
(U.S.A.), Feb.,1913.
1913 Burgess I Scout hydroaeroplane pusher biplane
Country of Origin: USA Designed and built by W.Burgess
Span: 39'19" Length: 31'4"
Country of Origin: USA Designed and built by W.Burgess
Span: 39'19" Length: 31'4"
BURGESS. Burgess Co. & Curtis, Marblehead, Mass. Built Wright types under license, also machines of their own.
Model and date. Military Coast defence Naval flying
tractor. hydro. boat.
1912-13. 1913. 1913.
Length.....feet(m.) 37? (8.50) 33-1/3 (9.55) 31 (9.45)
Span.......feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 37? (12) 42 (13.10)
36 (10.97)
Area...sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
useful,lbs.(kgs.) ... 775 (352) ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 60 Sturtevant 70 Renault
muffled
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 45 (70) 59 (95) ...
Endurance......hrs. 4? 4? ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.-- Lumina fabric. Special clear view Boat 29?feet long.
Single screw. for observation. 2--2 step floats.
Details, 2--1 step mahogany Petrol, 48 gallons.
Aeronautics, and copper floats. Details,
(U.S.A.), Useful weight Aeronautics,
May-June,1912. includes floats. (U.S.A.), May,1913.
Details,
Aeronautics,
(U.S.A.), Feb.,1913.
Model and date. Military Coast defence Naval flying
tractor. hydro. boat.
1912-13. 1913. 1913.
Length.....feet(m.) 37? (8.50) 33-1/3 (9.55) 31 (9.45)
Span.......feet(m.) 34? (10.50) 37? (12) 42 (13.10)
36 (10.97)
Area...sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
useful,lbs.(kgs.) ... 775 (352) ...
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 60 Sturtevant 70 Renault
muffled
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 45 (70) 59 (95) ...
Endurance......hrs. 4? 4? ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Remarks.-- Lumina fabric. Special clear view Boat 29?feet long.
Single screw. for observation. 2--2 step floats.
Details, 2--1 step mahogany Petrol, 48 gallons.
Aeronautics, and copper floats. Details,
(U.S.A.), Useful weight Aeronautics,
May-June,1912. includes floats. (U.S.A.), May,1913.
Details,
Aeronautics,
(U.S.A.), Feb.,1913.
CHRISTMAS. Durham Christmas Aeroplane Sales & Exhibition Corporation, Inc. 1913. Capital: $10,000 to $50,000. Claims for it are that it is "automatically balanced." This is attained by the shape of the machine, not through the agency of any auxiliary apparatus.
COOKE. Weldon B. Cooke Aeroplane Co., Sandusky, Ohio. Founded 1913 by the well-known aviator, W.B. Cooke.
Model and date. 1913.
Length.................feet(m.) 25 (7.60)
Span...................feet(m.) 24 (7.30)
Area..............sq. feet(m?.) 240 (22)
Weight, total........lbs.(kgs.) 750 (340)
Weight, useful.......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor......................h.p. 75 Roberts 2 cycle
upside down
Speed...............m.p.h. (km.) ...
Number built during 1912 new firm
Details, Aeronautics, U.S.A., February, 1913.
Model and date. 1913.
Length.................feet(m.) 25 (7.60)
Span...................feet(m.) 24 (7.30)
Area..............sq. feet(m?.) 240 (22)
Weight, total........lbs.(kgs.) 750 (340)
Weight, useful.......lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor......................h.p. 75 Roberts 2 cycle
upside down
Speed...............m.p.h. (km.) ...
Number built during 1912 new firm
Details, Aeronautics, U.S.A., February, 1913.
CURTISS. Curtiss Aeroplane Co., Hammondsport, N.Y. Glenn H. Curtiss in 1907 and 1908 was a member of the Aerial Experiment Association, formed by Dr. and Mrs. Alexander Graham Bell. This Association built four machines, each along the lines of one of the four engineers belong to the Association, F.W. Baldwin, Lieut. T.E. Selfridge, G.H. Curtiss and J.A.D. McCurdy. The last built was the June Bug, designed by Curtiss and was the most successful. In the spring of 1908, the Association was disbanded and The Aeronautical Society gave Curtiss an order for an aeroplane with carte blanche as to design. He produced a 4 cyl. machine, Curtiss engine, and flew it. A duplicate was hurriedly built, 8 cyl. engine installed, and taken to Europe for the first Gordon Bennett, which he won. Returning, the same type was continued with minor improvements. Later the front elevator was brought closer in, finally discarded, and the fan tail adopted and this remains the standard land machine to-day. In April, a military tractor was built and flown.
On January 26th, 1911, first successful flights were made with a hydroaeroplane, at the Winter camp at San Diego, Calif. This had two floats tandem. One was finally adopted and great success was achieved, and remains standard at the present time. With this machine various experiments were made. It was altered in a tractor for one occasion, it was lifted on board warships; made into triplane, etc.
In 1912 he brought out his present type of flying boat. This is being rapidly developed and minor changes in details are made in practically every machine put out.
In May, 1913, he produced a special 4-passenger flying boat for a customer on special order.
Note.--In addition to those tabulated, special small racing machines have been built, as well as similar machines with extra sections simply added either side for Army use.
Model and date. Type D. Type E. Type F.
1913. 1913. 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 26-2/3 (8.1) 27-1/3 (8.33) 27-1/3 (8.33)
Span........feet(m.) 26? (8) 31? (9.50) 38-1/3 (11.70)
Overall.....feet(m.) 33-1/12 (10) 36? (11) 41-2/3 (12.70)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 214 (19?) 288 (26?) 421? (39)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs) ... 1700 (771) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs) ... 500 (227) ...
Motor...........h.p. Curtiss 80 Curtiss Curtiss
Spee.....m.p.h.(km.) ... 59 (95) ...
Remarks.-- Land service, Fitted either Used to date only
but is also with wheels, as military tractor
made with pontons, or boat. or heavy flying boat.
floats. Vilas boat. McCormick boat.
Panels.
Boat 24 ft. long. Boat 25 ft. long 4 ft.
Beam 54? ft. wide. Freeboard 46
Height 41" long. ins. Cockpit 84 ins.
Cockpit 3 ft.long long by 46 ins. wide.
by 4 ft. 2 ins. Length of tail, incl.
wide. elevator 12 feet.
For full details of the tractor (F) see Aeronautics, U.S.A., February, 1913.
FRENCH AEROPLANES.
PAULHAN-CURTISS. Soc. anonyme d'aviation Paulhan, (S.A.P.) 71 boulevard Berthier, Paris. Flying ground: Bois d'Arcy par St. Ayr (S. et O.) Hydro school: Juan-les-Pins, par Antibes (Alpes Maritimes).
Founded by the well-known aviator, L. Paulhan. He first produced biplanes, then triplanes and finally a monoplane type, the Tatin-Paulhan (1911). These are now all abandoned, and the firm devotes itself to building hydro-aeroplanes under Curtiss (U.S.A.) license. Principal type built are:--
Model and date. Flying boat. Flying boat.
Biplanes. Single-seater. 2-seater.
Length..............feet (m.) ... 27 (8.30)
Span................feet (m.) 35? (10.80) 37 (ll.30)
Area...........sq. feet (m?.) ... 290 (26.75)
Weight, machine...lbs. (kgs.) ... 948 (430)
Weight, useful....lbs. (kgs.) ... ...
Motor....................h.p. 75 Curtiss 85 Curtiss
Speed............m.p.h. (km.) ... ...
Number built during 1912.... 2 8
On January 26th, 1911, first successful flights were made with a hydroaeroplane, at the Winter camp at San Diego, Calif. This had two floats tandem. One was finally adopted and great success was achieved, and remains standard at the present time. With this machine various experiments were made. It was altered in a tractor for one occasion, it was lifted on board warships; made into triplane, etc.
In 1912 he brought out his present type of flying boat. This is being rapidly developed and minor changes in details are made in practically every machine put out.
In May, 1913, he produced a special 4-passenger flying boat for a customer on special order.
Note.--In addition to those tabulated, special small racing machines have been built, as well as similar machines with extra sections simply added either side for Army use.
Model and date. Type D. Type E. Type F.
1913. 1913. 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 26-2/3 (8.1) 27-1/3 (8.33) 27-1/3 (8.33)
Span........feet(m.) 26? (8) 31? (9.50) 38-1/3 (11.70)
Overall.....feet(m.) 33-1/12 (10) 36? (11) 41-2/3 (12.70)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 214 (19?) 288 (26?) 421? (39)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs) ... 1700 (771) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs) ... 500 (227) ...
Motor...........h.p. Curtiss 80 Curtiss Curtiss
Spee.....m.p.h.(km.) ... 59 (95) ...
Remarks.-- Land service, Fitted either Used to date only
but is also with wheels, as military tractor
made with pontons, or boat. or heavy flying boat.
floats. Vilas boat. McCormick boat.
Panels.
Boat 24 ft. long. Boat 25 ft. long 4 ft.
Beam 54? ft. wide. Freeboard 46
Height 41" long. ins. Cockpit 84 ins.
Cockpit 3 ft.long long by 46 ins. wide.
by 4 ft. 2 ins. Length of tail, incl.
wide. elevator 12 feet.
For full details of the tractor (F) see Aeronautics, U.S.A., February, 1913.
FRENCH AEROPLANES.
PAULHAN-CURTISS. Soc. anonyme d'aviation Paulhan, (S.A.P.) 71 boulevard Berthier, Paris. Flying ground: Bois d'Arcy par St. Ayr (S. et O.) Hydro school: Juan-les-Pins, par Antibes (Alpes Maritimes).
Founded by the well-known aviator, L. Paulhan. He first produced biplanes, then triplanes and finally a monoplane type, the Tatin-Paulhan (1911). These are now all abandoned, and the firm devotes itself to building hydro-aeroplanes under Curtiss (U.S.A.) license. Principal type built are:--
Model and date. Flying boat. Flying boat.
Biplanes. Single-seater. 2-seater.
Length..............feet (m.) ... 27 (8.30)
Span................feet (m.) 35? (10.80) 37 (ll.30)
Area...........sq. feet (m?.) ... 290 (26.75)
Weight, machine...lbs. (kgs.) ... 948 (430)
Weight, useful....lbs. (kgs.) ... ...
Motor....................h.p. 75 Curtiss 85 Curtiss
Speed............m.p.h. (km.) ... ...
Number built during 1912.... 2 8
CURTISS. Curtiss Aeroplane Co., Hammondsport, N.Y. Glenn H. Curtiss in 1907 and 1908 was a member of the Aerial Experiment Association, formed by Dr. and Mrs. Alexander Graham Bell. This Association built four machines, each along the lines of one of the four engineers belong to the Association, F.W. Baldwin, Lieut. T.E. Selfridge, G.H. Curtiss and J.A.D. McCurdy. The last built was the June Bug, designed by Curtiss and was the most successful. In the spring of 1908, the Association was disbanded and The Aeronautical Society gave Curtiss an order for an aeroplane with carte blanche as to design. He produced a 4 cyl. machine, Curtiss engine, and flew it. A duplicate was hurriedly built, 8 cyl. engine installed, and taken to Europe for the first Gordon Bennett, which he won. Returning, the same type was continued with minor improvements. Later the front elevator was brought closer in, finally discarded, and the fan tail adopted and this remains the standard land machine to-day. In April, a military tractor was built and flown.
On January 26th, 1911, first successful flights were made with a hydroaeroplane, at the Winter camp at San Diego, Calif. This had two floats tandem. One was finally adopted and great success was achieved, and remains standard at the present time. With this machine various experiments were made. It was altered in a tractor for one occasion, it was lifted on board warships; made into triplane, etc.
In 1912 he brought out his present type of flying boat. This is being rapidly developed and minor changes in details are made in practically every machine put out.
In May, 1913, he produced a special 4-passenger flying boat for a customer on special order.
Note.--In addition to those tabulated, special small racing machines have been built, as well as similar machines with extra sections simply added either side for Army use.
Model and date. Type D. Type E. Type F.
1913. 1913. 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 26-2/3 (8.1) 27-1/3 (8.33) 27-1/3 (8.33)
Span........feet(m.) 26? (8) 31? (9.50) 38-1/3 (11.70)
Overall.....feet(m.) 33-1/12 (10) 36? (11) 41-2/3 (12.70)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 214 (19?) 288 (26?) 421? (39)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs) ... 1700 (771) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs) ... 500 (227) ...
Motor...........h.p. Curtiss 80 Curtiss Curtiss
Spee.....m.p.h.(km.) ... 59 (95) ...
Remarks.-- Land service, Fitted either Used to date only
but is also with wheels, as military tractor
made with pontons, or boat. or heavy flying boat.
floats. Vilas boat. McCormick boat.
Panels.
Boat 24 ft. long. Boat 25 ft. long 4 ft.
Beam 54? ft. wide. Freeboard 46
Height 41" long. ins. Cockpit 84 ins.
Cockpit 3 ft.long long by 46 ins. wide.
by 4 ft. 2 ins. Length of tail, incl.
wide. elevator 12 feet.
For full details of the tractor (F) see Aeronautics, U.S.A., February, 1913.
On January 26th, 1911, first successful flights were made with a hydroaeroplane, at the Winter camp at San Diego, Calif. This had two floats tandem. One was finally adopted and great success was achieved, and remains standard at the present time. With this machine various experiments were made. It was altered in a tractor for one occasion, it was lifted on board warships; made into triplane, etc.
In 1912 he brought out his present type of flying boat. This is being rapidly developed and minor changes in details are made in practically every machine put out.
In May, 1913, he produced a special 4-passenger flying boat for a customer on special order.
Note.--In addition to those tabulated, special small racing machines have been built, as well as similar machines with extra sections simply added either side for Army use.
Model and date. Type D. Type E. Type F.
1913. 1913. 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 26-2/3 (8.1) 27-1/3 (8.33) 27-1/3 (8.33)
Span........feet(m.) 26? (8) 31? (9.50) 38-1/3 (11.70)
Overall.....feet(m.) 33-1/12 (10) 36? (11) 41-2/3 (12.70)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 214 (19?) 288 (26?) 421? (39)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs) ... 1700 (771) ...
useful...lbs.(kgs) ... 500 (227) ...
Motor...........h.p. Curtiss 80 Curtiss Curtiss
Spee.....m.p.h.(km.) ... 59 (95) ...
Remarks.-- Land service, Fitted either Used to date only
but is also with wheels, as military tractor
made with pontons, or boat. or heavy flying boat.
floats. Vilas boat. McCormick boat.
Panels.
Boat 24 ft. long. Boat 25 ft. long 4 ft.
Beam 54? ft. wide. Freeboard 46
Height 41" long. ins. Cockpit 84 ins.
Cockpit 3 ft.long long by 46 ins. wide.
by 4 ft. 2 ins. Length of tail, incl.
wide. elevator 12 feet.
For full details of the tractor (F) see Aeronautics, U.S.A., February, 1913.
ENGLISH (1909). In 1909 extraordinary claims were made for this machine and great things expected. On a full power trial in its shed it broke loose, and smashed itself against the roof. No recorded outdoor results.
GALLAUDET. Gallaudet Eng. Co., Norwich Ct.
In 1912 produced a special racer as above. Span, 32 feet (9.75 m.) Area, 200 sq. feet (18? m?.) Speed, 100 m.p.h. (160 k.p.h.) Motor, 100 Gnome.
In 1912 produced a special racer as above. Span, 32 feet (9.75 m.) Area, 200 sq. feet (18? m?.) Speed, 100 m.p.h. (160 k.p.h.) Motor, 100 Gnome.
HULBERT (1910). This strange machine built in Switzerland by Dr. Dane Hulbert, achieved several flights. The planes were placed longitudinally instead of in the usual way.
KIRKHAM Biplanes. Chas. B. Kirkham, Motor Manufacturers, Savona, N.Y. Began to manufacture aeroplanes in 1912, after previous experiments and flights near his factory.
Length, ---- feet (---- m.) span, 34 feet (10.40 m.) surface, ----sq. feet) (---- m?.)
Weight.--Complete, without pilot, 980 lbs. (445 kgs.)
Motor.--50 h.p. Kirkham, located in front under bonnet. 70 h.p. also fitted.
Speed.--56-62 m.p.h. (90-100 k.p.h.)
Remarks.--Rises easily at under 35 m.p.h., and has a full speed radius of 5? hours. Full details in Aeronautics, U.S.A., January, 1912. 1913, no changes.
Length, ---- feet (---- m.) span, 34 feet (10.40 m.) surface, ----sq. feet) (---- m?.)
Weight.--Complete, without pilot, 980 lbs. (445 kgs.)
Motor.--50 h.p. Kirkham, located in front under bonnet. 70 h.p. also fitted.
Speed.--56-62 m.p.h. (90-100 k.p.h.)
Remarks.--Rises easily at under 35 m.p.h., and has a full speed radius of 5? hours. Full details in Aeronautics, U.S.A., January, 1912. 1913, no changes.
SELLERS. Quadruplane. Matthew B. Sellers, R.F., D2, Norwood, Ga. Has been successfully experimenting for a number of years with a staggered quadruplane, and has given the aviation world a number of valuable papers. His aim is to fly successfully with the least possible horse power. For several years he has been making flights with various engines delivering from 5 to 6 h.p. on careful test. The actual thrust has been measured and recorded in late 1911 experiments. Details in Aeronautics, June, 1909; October, 1909; November, 1910; January, 1911; January, 1912. No actual details of the machine are available, but it follows closely the patent drawings (see references). He is one of the few real scientific flying men in the U.S.A. The original machine with slight changes was still flying at end of 1912 with only 5 h.p. B.H.P. The flying speed is 20 m.p.h.
SLOAN. "Bicurve." Sloan & Cie, 17 rue de Louvre, Paris. Works: 9 rue Victor Hugo, Charenton. Flying ground: Port Aviation. Output capacity: small.
Model and date. 1912. 1913.
Length.........feet(m.) 31-1/3 (9.50) 29 (8.70)
Span...........feet(m.) 42? (13) 42? (12.90)
Area.......sq. feet(m?) 527 (49) 473 (44)
Weight, machine.......
.............lbs.(kgs.) 1100 (500) 662 (300)
Weight, useful........
.............lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Gnome 120 Laviator
Speed...max. m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95) 65 (105)
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Wheels and skids landing gear. Control: ailerons and rear elevator.
Model and date. 1912. 1913.
Length.........feet(m.) 31-1/3 (9.50) 29 (8.70)
Span...........feet(m.) 42? (13) 42? (12.90)
Area.......sq. feet(m?) 527 (49) 473 (44)
Weight, machine.......
.............lbs.(kgs.) 1100 (500) 662 (300)
Weight, useful........
.............lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 100 Gnome 120 Laviator
Speed...max. m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95) 65 (105)
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Wheels and skids landing gear. Control: ailerons and rear elevator.
THOMAS Biplanes. Thomas Bros., Bath, N.Y., O.W., and W.T. Thomas began experimenting and flying in 1908 with a machine on the order of a Curtiss. In the winter of 1909-10, a type of their own was produced and was flown during 1911 by Walter Johnson in exhibitions. In 1912 they continued the same type, with refinements. In 1913 they adopted the overhanging top plane type, but of the same general high order of construction.
Model and date. 1912. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Tractor Monoplane. Standard Special Flying
biplane. biplane. biplane. boat.
Length...ft.(m.) ... 30 (9.15) ... 25 (7.62) ...
Span.....ft.(m.) 37(11.27) 32 (9.75) 37 (11.27) 33 (10) 33 (10)
27(8.23) ... 27 (8.23) 23 (7) 23 (7)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) ... ... ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kg.) 900 (408) 750 (340) 900 (408) 850 (385) ...
Weight,
useful, lb.(kg.) ... ... ... 400 (181) ...
Motor, h.p. 65 70 65 65 100
Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Maximotor
muffled
Speed,
m.p.h.(km) 58 (94) ... 58 (94) 60 (97) ...
Endurance, hrs. 2 ... 2 2? ...
Number built
during 1912 1 building ... ... building
Remarks. Control in all: Ailerons, 4 rudders. Elevator operated by rocking post on which wheel is mounted. The 1912 tractor was given up as less efficient than the Standard 1913.
Special: full description Aeronautics, U.S.A., May, 1913.
The move was evolved 1912, but not built till well into 1913.
Model and date. 1912. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Tractor Monoplane. Standard Special Flying
biplane. biplane. biplane. boat.
Length...ft.(m.) ... 30 (9.15) ... 25 (7.62) ...
Span.....ft.(m.) 37(11.27) 32 (9.75) 37 (11.27) 33 (10) 33 (10)
27(8.23) ... 27 (8.23) 23 (7) 23 (7)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) ... ... ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kg.) 900 (408) 750 (340) 900 (408) 850 (385) ...
Weight,
useful, lb.(kg.) ... ... ... 400 (181) ...
Motor, h.p. 65 70 65 65 100
Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Maximotor
muffled
Speed,
m.p.h.(km) 58 (94) ... 58 (94) 60 (97) ...
Endurance, hrs. 2 ... 2 2? ...
Number built
during 1912 1 building ... ... building
Remarks. Control in all: Ailerons, 4 rudders. Elevator operated by rocking post on which wheel is mounted. The 1912 tractor was given up as less efficient than the Standard 1913.
Special: full description Aeronautics, U.S.A., May, 1913.
The move was evolved 1912, but not built till well into 1913.
THOMAS Biplanes. Thomas Bros., Bath, N.Y., O.W., and W.T. Thomas began experimenting and flying in 1908 with a machine on the order of a Curtiss. In the winter of 1909-10, a type of their own was produced and was flown during 1911 by Walter Johnson in exhibitions. In 1912 they continued the same type, with refinements. In 1913 they adopted the overhanging top plane type, but of the same general high order of construction.
Model and date. 1912. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Tractor Monoplane. Standard Special Flying
biplane. biplane. biplane. boat.
Length...ft.(m.) ... 30 (9.15) ... 25 (7.62) ...
Span.....ft.(m.) 37(11.27) 32 (9.75) 37 (11.27) 33 (10) 33 (10)
27(8.23) ... 27 (8.23) 23 (7) 23 (7)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) ... ... ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kg.) 900 (408) 750 (340) 900 (408) 850 (385) ...
Weight,
useful, lb.(kg.) ... ... ... 400 (181) ...
Motor, h.p. 65 70 65 65 100
Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Maximotor
muffled
Speed,
m.p.h.(km) 58 (94) ... 58 (94) 60 (97) ...
Endurance, hrs. 2 ... 2 2? ...
Number built
during 1912 1 building ... ... building
Remarks. Control in all: Ailerons, 4 rudders. Elevator operated by rocking post on which wheel is mounted. The 1912 tractor was given up as less efficient than the Standard 1913.
Special: full description Aeronautics, U.S.A., May, 1913.
The move was evolved 1912, but not built till well into 1913.
Model and date. 1912. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Tractor Monoplane. Standard Special Flying
biplane. biplane. biplane. boat.
Length...ft.(m.) ... 30 (9.15) ... 25 (7.62) ...
Span.....ft.(m.) 37(11.27) 32 (9.75) 37 (11.27) 33 (10) 33 (10)
27(8.23) ... 27 (8.23) 23 (7) 23 (7)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) ... ... ... ... ...
Weight,
total, lbs.(kg.) 900 (408) 750 (340) 900 (408) 850 (385) ...
Weight,
useful, lb.(kg.) ... ... ... 400 (181) ...
Motor, h.p. 65 70 65 65 100
Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Kirkham Maximotor
muffled
Speed,
m.p.h.(km) 58 (94) ... 58 (94) 60 (97) ...
Endurance, hrs. 2 ... 2 2? ...
Number built
during 1912 1 building ... ... building
Remarks. Control in all: Ailerons, 4 rudders. Elevator operated by rocking post on which wheel is mounted. The 1912 tractor was given up as less efficient than the Standard 1913.
Special: full description Aeronautics, U.S.A., May, 1913.
The move was evolved 1912, but not built till well into 1913.
WASHINGTON. Washington Aeroplane Co., Washington, D.C. In 1913 built a flying boat to private order. Length, 29 feet (8.83 m.) Maximum span, 38 feet (11.85 m.) Motor, 80 h.p. Gyro. Boat with eight compartments and one 3 inch step.
WITTEMAN. Witteman Bros., 17, Ocean Terrace and Little Clare Road, Staton Island, N.Y. These people do a considerable business building Curtiss type machines or machines to special designs for others. They built the Baldwin biplanes for Captain Baldwin, to his design, using steel tubing throughout. See Aeronautics, December, 1911, for a Witteman of special design shown by them at the Aero Show.
Unquestinably the most famous aviation photograph ever taken, this study shows the Flyer making the first of its four flights of 17 December 1903, with Orville piloting and Wilbur at the wingtip. Orville had set up the camera on its tripod, and the shutter was operated by John T Daniels of the Kill Devil Life Saving Station.
Orville Wright, the pilot in this historic picture, taken at 10.35am, Thursday, 17 December 1903, claimed this 12-second flight as ‘the first in the history of the world in which a machine carrying a man had raised itself by its own power into the air in full flight, had sailed forward without reduction of speed, and had finally landed at a point as high as that from which it started’.
Orville Wright, the pilot in this historic picture, taken at 10.35am, Thursday, 17 December 1903, claimed this 12-second flight as ‘the first in the history of the world in which a machine carrying a man had raised itself by its own power into the air in full flight, had sailed forward without reduction of speed, and had finally landed at a point as high as that from which it started’.
1904 Wright Flyer 2 - almost identical to Flyer 1 but heavier.
Country of origin: USA. Designed and built by Wilbur & Orville Wright.
Span: 40.3' Length: 21.1' Weight: 925 lbs
Country of origin: USA. Designed and built by Wilbur & Orville Wright.
Span: 40.3' Length: 21.1' Weight: 925 lbs
WRIGHT (1908). Two views of the machine with which Wilbur Wright started all Europe from August, 1908 to April, 1909. First U.S. machine to fly.
WRIGHT (1908). Two views of the machine with which Wilbur Wright started all Europe from August, 1908 to April, 1909. First U.S. machine to fly.
U.S.A. AEROPLANES.
WRIGHT BROS. Biplanes. The Wright Co., Dayton, Ohio. The original type of Wright machine was mounted on skids only, and started along a rail. Its special features were a biplane elevator forward, main planes with warpable tips to trailing edge, small keel in gap, 2 propellers, chain driven in rear of planes, double rudder in rear and no tail. Wilbur Wright flew a machine of this type for 2 h. 20 m. 23? s. in 1908. (Details of early Wrights see previous editions of this book.)
Model and date. B. C. EX. E.
Length......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29? (9) ... ...
Span........feet(m.) 39 (11.90) 38 (ll.58) 32 (9.75) 32 (9.75)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 500 (47) 500 (47) ... ...
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1250 (567) ... ... ...
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 30-35 Wright. 30-35 Wright. 30 or 50 30 or 50
Wright. Wright.
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 45 (75) 45 (75) ... ...
1913 standard. For exhibition 1913
This machine work only. For
as a hydro is Single seater exhibition
fitted with small duplicate work
two 3 step of B. only.
floats. Single seater
duplicate of
EX except
fitted with a
single pro-
peller only.
GERMAN AEROPLANES.
WRIGHT. Flugmaschine Wright, G.m.b.H., Adlershof, bei Berlin. Company formed to trade in German rights for the Wright Bros.' patents. Considerable departures have been made from the U.S. pattern, and some have been built with a single propeller only. Capacity of works 100-150 a year.
1912. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Military. Sporting. Military. Military.
4-seater.
Length.......feet(m.) 28 (8.50) 26? (8.20) 31? (9.65) ...
Sp...........feet(m.) 39? (12.20) 31 (9.60) 40? (12.50) 44? (13.50)
Area....sq. feet(m?.) 452 (42) 323 (30) 463 (45) 463 (43)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450) 837 (380) 1433 (650) 1653 (750)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 882 (400)
Motor...........h.p. 55 N.A.G. 55 N.A.G. 100 Argus or 100
Mercedes
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 50 (80) 60 (95) 60 (95) 60 (95)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912... 10 ? ... ...
WRIGHT BROS. Biplanes. The Wright Co., Dayton, Ohio. The original type of Wright machine was mounted on skids only, and started along a rail. Its special features were a biplane elevator forward, main planes with warpable tips to trailing edge, small keel in gap, 2 propellers, chain driven in rear of planes, double rudder in rear and no tail. Wilbur Wright flew a machine of this type for 2 h. 20 m. 23? s. in 1908. (Details of early Wrights see previous editions of this book.)
Model and date. B. C. EX. E.
Length......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29? (9) ... ...
Span........feet(m.) 39 (11.90) 38 (ll.58) 32 (9.75) 32 (9.75)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 500 (47) 500 (47) ... ...
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1250 (567) ... ... ...
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 30-35 Wright. 30-35 Wright. 30 or 50 30 or 50
Wright. Wright.
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 45 (75) 45 (75) ... ...
1913 standard. For exhibition 1913
This machine work only. For
as a hydro is Single seater exhibition
fitted with small duplicate work
two 3 step of B. only.
floats. Single seater
duplicate of
EX except
fitted with a
single pro-
peller only.
GERMAN AEROPLANES.
WRIGHT. Flugmaschine Wright, G.m.b.H., Adlershof, bei Berlin. Company formed to trade in German rights for the Wright Bros.' patents. Considerable departures have been made from the U.S. pattern, and some have been built with a single propeller only. Capacity of works 100-150 a year.
1912. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Military. Sporting. Military. Military.
4-seater.
Length.......feet(m.) 28 (8.50) 26? (8.20) 31? (9.65) ...
Sp...........feet(m.) 39? (12.20) 31 (9.60) 40? (12.50) 44? (13.50)
Area....sq. feet(m?.) 452 (42) 323 (30) 463 (45) 463 (43)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450) 837 (380) 1433 (650) 1653 (750)
useful...lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 882 (400)
Motor...........h.p. 55 N.A.G. 55 N.A.G. 100 Argus or 100
Mercedes
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 50 (80) 60 (95) 60 (95) 60 (95)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912... 10 ? ... ...
U.S.A. AEROPLANES.
WRIGHT BROS. Biplanes. The Wright Co., Dayton, Ohio. The original type of Wright machine was mounted on skids only, and started along a rail. Its special features were a biplane elevator forward, main planes with warpable tips to trailing edge, small keel in gap, 2 propellers, chain driven in rear of planes, double rudder in rear and no tail. Wilbur Wright flew a machine of this type for 2 h. 20 m. 23? s. in 1908. (Details of early Wrights see previous editions of this book.)
Model and date. B. C. EX. E.
Length......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29? (9) ... ...
Span........feet(m.) 39 (11.90) 38 (ll.58) 32 (9.75) 32 (9.75)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 500 (47) 500 (47) ... ...
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1250 (567) ... ... ...
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 30-35 Wright. 30-35 Wright. 30 or 50 30 or 50
Wright. Wright.
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 45 (75) 45 (75) ... ...
1913 standard. For exhibition 1913
This machine work only. For
as a hydro is Single seater exhibition
fitted with small duplicate work
two 3 step of B. only.
floats. Single seater
duplicate of
EX except
fitted with a
single pro-
peller only.
WRIGHT BROS. Biplanes. The Wright Co., Dayton, Ohio. The original type of Wright machine was mounted on skids only, and started along a rail. Its special features were a biplane elevator forward, main planes with warpable tips to trailing edge, small keel in gap, 2 propellers, chain driven in rear of planes, double rudder in rear and no tail. Wilbur Wright flew a machine of this type for 2 h. 20 m. 23? s. in 1908. (Details of early Wrights see previous editions of this book.)
Model and date. B. C. EX. E.
Length......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29? (9) ... ...
Span........feet(m.) 39 (11.90) 38 (ll.58) 32 (9.75) 32 (9.75)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 500 (47) 500 (47) ... ...
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1250 (567) ... ... ...
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 30-35 Wright. 30-35 Wright. 30 or 50 30 or 50
Wright. Wright.
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 45 (75) 45 (75) ... ...
1913 standard. For exhibition 1913
This machine work only. For
as a hydro is Single seater exhibition
fitted with small duplicate work
two 3 step of B. only.
floats. Single seater
duplicate of
EX except
fitted with a
single pro-
peller only.
U.S.A. AEROPLANES.
WRIGHT BROS. Biplanes. The Wright Co., Dayton, Ohio. The original type of Wright machine was mounted on skids only, and started along a rail. Its special features were a biplane elevator forward, main planes with warpable tips to trailing edge, small keel in gap, 2 propellers, chain driven in rear of planes, double rudder in rear and no tail. Wilbur Wright flew a machine of this type for 2 h. 20 m. 23? s. in 1908. (Details of early Wrights see previous editions of this book.)
Model and date. B. C. EX. E.
Length......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29? (9) ... ...
Span........feet(m.) 39 (11.90) 38 (ll.58) 32 (9.75) 32 (9.75)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 500 (47) 500 (47) ... ...
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1250 (567) ... ... ...
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 30-35 Wright. 30-35 Wright. 30 or 50 30 or 50
Wright. Wright.
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 45 (75) 45 (75) ... ...
1913 standard. For exhibition 1913
This machine work only. For
as a hydro is Single seater exhibition
fitted with small duplicate work
two 3 step of B. only.
floats. Single seater
duplicate of
EX except
fitted with a
single pro-
peller only.
WRIGHT BROS. Biplanes. The Wright Co., Dayton, Ohio. The original type of Wright machine was mounted on skids only, and started along a rail. Its special features were a biplane elevator forward, main planes with warpable tips to trailing edge, small keel in gap, 2 propellers, chain driven in rear of planes, double rudder in rear and no tail. Wilbur Wright flew a machine of this type for 2 h. 20 m. 23? s. in 1908. (Details of early Wrights see previous editions of this book.)
Model and date. B. C. EX. E.
Length......feet(m.) 31 (9.45) 29? (9) ... ...
Span........feet(m.) 39 (11.90) 38 (ll.58) 32 (9.75) 32 (9.75)
Area...sq. feet(m?.) 500 (47) 500 (47) ... ...
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 1250 (567) ... ... ...
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ...
Motor..........h.p. 30-35 Wright. 30-35 Wright. 30 or 50 30 or 50
Wright. Wright.
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 45 (75) 45 (75) ... ...
1913 standard. For exhibition 1913
This machine work only. For
as a hydro is Single seater exhibition
fitted with small duplicate work
two 3 step of B. only.
floats. Single seater
duplicate of
EX except
fitted with a
single pro-
peller only.
1913 Wright Model E - similar to EX, except only one 7' pusher and 2 large 24" balloon tires.
Country of origin: USA. Designed and built by Wilbur & Orville Wright.
Span: 36' Length: 27.9' Weight: 730 lbs.
Country of origin: USA. Designed and built by Wilbur & Orville Wright.
Span: 36' Length: 27.9' Weight: 730 lbs.
ANTOINETTE IV (1909). In this machine Latham made the first attempt to fly the Channel, 19th July, 1909.
ASTRA. "Astra" Soc. de Constructions Aeronautiques, (Anciens Etabs. Surcouf) Soc. An'yme 13 Rue Couchat, Billancourt (Seine). Works: 121-123 Rue de Bellevue, Billancourt. Flying grounds: Issy-les-Molineux Villacoublay (S-&-0). This old established balloon and dirigible firm first took up aviation as French agents for the Wrights in 1909. For a time they built Wrights with certain modifications, but by 1912, little save the Wright system of warping remained. Capacity: about 100 machines a year.
Biplane, Military Biplane, Mil. biplane, Hydro-bi-
type C. biplane Type C. type C.M. plane,type
1912-13. type C.M. 1913. 1913. C.M.
Wood. 1912-13. Wood & Wood & steel. 1913.
Wood steel. Wood & steel
Length..feet(m.) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 32? (10)
Span....feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 39? (12)
Area.sq.feet(m?) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2)
Weight, machine,
......lbs.(kgs.) 1764 (800) 2365 (1073) ... 1411 (640) 1763 (800)
Weight, useful, (unladen)
......lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) 882 (400) ... ... ...
Motor......h.p. 50 Renault 75 Renault 50 Renault 75 Renault 100 Renault
or 75 Chenu
Speed, max.,
....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Speed, min.,
......p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance..hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The 1912-13 and 1913 types differ only in the adoption of metal in the 1913 models, which are consequently considerably lighter.
General features.--Warping wings. Fixed tail planes with two elevators in rear. Single rudder. Single tractor geared down 1 to 2. Type C carries 85 litres petrol; type C.M., 137 litres.
Biplane, Military Biplane, Mil. biplane, Hydro-bi-
type C. biplane Type C. type C.M. plane,type
1912-13. type C.M. 1913. 1913. C.M.
Wood. 1912-13. Wood & Wood & steel. 1913.
Wood steel. Wood & steel
Length..feet(m.) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 32? (10)
Span....feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 39? (12)
Area.sq.feet(m?) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2)
Weight, machine,
......lbs.(kgs.) 1764 (800) 2365 (1073) ... 1411 (640) 1763 (800)
Weight, useful, (unladen)
......lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) 882 (400) ... ... ...
Motor......h.p. 50 Renault 75 Renault 50 Renault 75 Renault 100 Renault
or 75 Chenu
Speed, max.,
....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Speed, min.,
......p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance..hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The 1912-13 and 1913 types differ only in the adoption of metal in the 1913 models, which are consequently considerably lighter.
General features.--Warping wings. Fixed tail planes with two elevators in rear. Single rudder. Single tractor geared down 1 to 2. Type C carries 85 litres petrol; type C.M., 137 litres.
ASTRA. "Astra" Soc. de Constructions Aeronautiques, (Anciens Etabs. Surcouf) Soc. An'yme 13 Rue Couchat, Billancourt (Seine). Works: 121-123 Rue de Bellevue, Billancourt. Flying grounds: Issy-les-Molineux Villacoublay (S-&-0). This old established balloon and dirigible firm first took up aviation as French agents for the Wrights in 1909. For a time they built Wrights with certain modifications, but by 1912, little save the Wright system of warping remained. Capacity: about 100 machines a year.
Biplane, Military Biplane, Mil. biplane, Hydro-bi-
type C. biplane Type C. type C.M. plane,type
1912-13. type C.M. 1913. 1913. C.M.
Wood. 1912-13. Wood & Wood & steel. 1913.
Wood steel. Wood & steel
Length..feet(m.) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 32? (10)
Span....feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 39? (12)
Area.sq.feet(m?) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2)
Weight, machine,
......lbs.(kgs.) 1764 (800) 2365 (1073) ... 1411 (640) 1763 (800)
Weight, useful, (unladen)
......lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) 882 (400) ... ... ...
Motor......h.p. 50 Renault 75 Renault 50 Renault 75 Renault 100 Renault
or 75 Chenu
Speed, max.,
....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Speed, min.,
......p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance..hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The 1912-13 and 1913 types differ only in the adoption of metal in the 1913 models, which are consequently considerably lighter.
General features.--Warping wings. Fixed tail planes with two elevators in rear. Single rudder. Single tractor geared down 1 to 2. Type C carries 85 litres petrol; type C.M., 137 litres.
Biplane, Military Biplane, Mil. biplane, Hydro-bi-
type C. biplane Type C. type C.M. plane,type
1912-13. type C.M. 1913. 1913. C.M.
Wood. 1912-13. Wood & Wood & steel. 1913.
Wood steel. Wood & steel
Length..feet(m.) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 34 (10.40) 36 (10.97) 32? (10)
Span....feet(m.) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 41 (12.50) 40? (12.32) 39? (12)
Area.sq.feet(m?) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2) 519 (48.2)
Weight, machine,
......lbs.(kgs.) 1764 (800) 2365 (1073) ... 1411 (640) 1763 (800)
Weight, useful, (unladen)
......lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) 882 (400) ... ... ...
Motor......h.p. 50 Renault 75 Renault 50 Renault 75 Renault 100 Renault
or 75 Chenu
Speed, max.,
....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Speed, min.,
......p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance..hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The 1912-13 and 1913 types differ only in the adoption of metal in the 1913 models, which are consequently considerably lighter.
General features.--Warping wings. Fixed tail planes with two elevators in rear. Single rudder. Single tractor geared down 1 to 2. Type C carries 85 litres petrol; type C.M., 137 litres.
BERTIN. L. Bertin, 23 rue de Rocroy, Paris. About 1908 Bertin began building helicopters. The machine below was exhibited in the 1913 Paris Salon.
1913.
Monoplane.
2-seater.
Length.........feet(m.) 29 (8.80)
Span...........feet(m.) 34 (10.40)
Area .....sq. feet(m?.) 226 (21)
Weight,machine...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 770 (350)
Weight, useful...
.....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor..............h.p. 100 Bertin
Speed, max...m.p.h.(km.) 71 (115)
Number built during 1912 1
Remarks--Wood and steel construction. On wheels only. Controls: warping and rear elevator.
1913.
Monoplane.
2-seater.
Length.........feet(m.) 29 (8.80)
Span...........feet(m.) 34 (10.40)
Area .....sq. feet(m?.) 226 (21)
Weight,machine...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 770 (350)
Weight, useful...
.....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor..............h.p. 100 Bertin
Speed, max...m.p.h.(km.) 71 (115)
Number built during 1912 1
Remarks--Wood and steel construction. On wheels only. Controls: warping and rear elevator.
BESSON. Marcel Besson, 24 rue Marbeuf, Paris. Capacity: small. Besson first appeared in 1911 with a tail-first mono. In the Paris Salon, 1913, he exhibited an improved machine along similar lines.
1913
Canard 2-seater.
Length...........feet(m.) 22 (6.70)
Span.............feet(m.) 44 (13.40)
Area ......sq. feet (m?.) 323 (30)
Weight, machine...
...lbs.(kgs.) 730 (331.2)
Weight, useful...
...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor.................h.p. 70 Gnome
Speed..........m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95)
Number built during 1912... 1
Remarks.--All steel construction. On wheels and 2 skids. Control: ailerons and front elevator.
1913
Canard 2-seater.
Length...........feet(m.) 22 (6.70)
Span.............feet(m.) 44 (13.40)
Area ......sq. feet (m?.) 323 (30)
Weight, machine...
...lbs.(kgs.) 730 (331.2)
Weight, useful...
...lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor.................h.p. 70 Gnome
Speed..........m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95)
Number built during 1912... 1
Remarks.--All steel construction. On wheels and 2 skids. Control: ailerons and front elevator.
1911 Besson canard monoplane
Country of Origin: France Designed by Marcel Besson Built by Louis Clement
Span: 38' Length: 24'7" Weight empty: 770 lbs
Country of Origin: France Designed by Marcel Besson Built by Louis Clement
Span: 38' Length: 24'7" Weight empty: 770 lbs
In 1909 the famous Bleriot XI was built. This did very well at Reims, 1909. On 25th July, 1909, Bleriot made the first Cross-Channel flight in the machine illustrated below.
BLERIOT XI. This machine had length, 23 feet (7 m.) Span, 25? feet (7.80 m.) Area, 167 sq. feet (15? m?.) Aspect ratio 4? to 1. Motor, 22-25, 3 cylinder Anzani, Speed, about 45 m.p.h. (73 k.m.) Special features: Fixed wings with rounded edges. Twin elevator and fixed surface tail.
BLERIOT XI. This machine had length, 23 feet (7 m.) Span, 25? feet (7.80 m.) Area, 167 sq. feet (15? m?.) Aspect ratio 4? to 1. Motor, 22-25, 3 cylinder Anzani, Speed, about 45 m.p.h. (73 k.m.) Special features: Fixed wings with rounded edges. Twin elevator and fixed surface tail.
BLERIOT Monoplanes. L. Bleriot, "Bleriot-Aeronautique," 39, Route de la Revolte, Paris-Levallois. Flying grounds: Buc Etampes and Pau.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
BLERIOT Monoplanes. L. Bleriot, "Bleriot-Aeronautique," 39, Route de la Revolte, Paris-Levallois. Flying grounds: Buc Etampes and Pau.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
Special types of Bleriots.--In addition to the standard machines, Bleriot from time to time produces special machines, of which the best known is the Limousine, built for M. Deutsch de la Meurthe, built 1911 and still existing. One or two Canards have also been built, including an armoured military.
BLERIOT Monoplanes. L. Bleriot, "Bleriot-Aeronautique," 39, Route de la Revolte, Paris-Levallois. Flying grounds: Buc Etampes and Pau.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
Special types of Bleriots.--Early in 1913 a special experimental military machine was produced with considerable secrecy.
BLERIOT Monoplanes. L. Bleriot, "Bleriot-Aeronautique," 39, Route de la Revolte, Paris-Levallois. Flying grounds: Buc Etampes and Pau.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
L. Bleriot began to experiment in 1906, along Langley lines. By 1909 he was one of the leading French firms; and the first cross Channel flight was made by him.
Details of standard types:--
XI bis. XXI. XXVII. XXVIII. XXVIII. Monocoque
2-seater Military Single Single 2-Seater 2-Seater
mono side by seat seater
(1911 side mono. 1913. 1913. 1913.
onward) 2-seater 1912.
mono. 1912
Length....feet(m) 27(8.40) 27? (8.24) 28 (8.5) 25 (7.60) 27 (8.20) ...
Span......feet(m) 36 (11) 36 (11) 29? (9) 29 (8.80) 32 (9.75) 40(12.25)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 349 (33) 268 (25) 129 (18) 162 (15) 215 (20) 270 (25)
Weight, unladen...
........lbs.(kgs) ... 727 (330) 529 (240) 530 (240) 660 (300) 830 (375)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... 286 (129) 550 (250) ...
Motor.......h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 70 Gnome 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 56 (90) 56 (90) 78 (125) 62 (100) 71 (115) 75 (150)
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Note.--The monos., as usual, are of wood construction; wheels only for landing. Rectangular section bodies. Warping wings, elevator in rear. Chauviere propeller. The monocoque has wood, steel and cork construction. Coque body. Skids to landing chassis. Levasseur propeller. Otherwise as the other monos.
Principal Bleriot flyers are or have been:--Aubrun, Balsan, Bleriot, Busson, Chavez, Cordonnier, Delagrange, Drexel, Efimoff, Gibbs, Hubert, Hamel, Moissant, Paulhan, Prevetau, Prevot, Prier, Radley, Thorup, Tyck, Wienzciers, and many others.
BOREL. G. Borel & Cie, 25 rue Brunel, Paris. Established 1910. Capacity: about 25 machines a year.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
BOREL. G. Borel & Cie, 25 rue Brunel, Paris. Established 1910. Capacity: about 25 machines a year.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
BOREL. G. Borel & Cie, 25 rue Brunel, Paris. Established 1910. Capacity: about 25 machines a year.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
BREGUET (1906). The first Breguet, known as Breguet Gyroplane I. Made a flight in October, 1906, being the first helicopter to leave the ground.
BREGUET IV (1910). On its appearance, this machine was generally laughed at and nicknamed the "Coffee Pot," till in Aug., 1910, it made a world's record by carrying six, and later proved itself superior in stability to anything then existing.
BREGUET. Soc. Anonyme des ateliers d'aviation, Louis Breguet, 16 Boulevard Vauban, Donai (Nord). Capacity: about 200 machines a year. Paris office: 25, Boulevard Jules Sandeau. Schools at La Brayelle, pris Douai, Velisy-Villacoublay, pris Paris.
1913 models. G2 bis. G3 C-U1 C-U2 Aerhydro-
2 or 3- 3-seater 2-seater 2-seater plane tandem
seater biplane biplane. biplane. mono.
biplane 2-seater,
side by side.
Length...feet(m) 33 (10) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75)
Span.....feet(m) 49 (15) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 42 (12.80)
Area...sq.ft(m?) 376 (35) 377(36) 387(36) 387(36) 387(36)
Weight, empty...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 1323(600) 1212(550) 1430(649) 1160(522) 1700(798)
Weight, useful...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 662 (300) 882 (400) 662 (300) 882(400) 662(300)
Motor......h.p. 80 Gnome 100 Gnome 80 Canton 110 Canton 110 Canton
Unne. Unne. Unne.
Speed.........
max. m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 69 (110) 62 (100) 71 (115) 87 (140)
min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 62 (100)
Endurance...hrs. 3? 4 7 7 7
Number built during 1912: A total of 41 sold during 1912 for military purposes.
In each case.--
Construction.--All steel.
Landing chassis.--C consists of three wheels each protected by skids. The two main wheels, placed on either side of the centre of gravity, are fitted with patent "Oleopneumatic" shock absorbers. The steering wheel and the front skid have a spring suspension.
Military machines.--The 1912 sales of these were:--32 to France; 5 British; 3 Italian; 1 Swedish.
Steering.--The patented control system consists of a wheel mounted on a pivoted lever. The backward and forward movement of the entire system operates the elevator: the sideway movement warps the rear edge of the upper wings, and the rotation of the wheel steers the machine. The latter operation also governs the front wheel of the landing chassis, so that when on the ground the machine can be steered like a motor car.
Portability.--The main planes can be folded alongside of the fuselage. The machine can then be towed on any ordinary road, or be housed in places such as farm buildings, stables, &c.
1913 models. G2 bis. G3 C-U1 C-U2 Aerhydro-
2 or 3- 3-seater 2-seater 2-seater plane tandem
seater biplane biplane. biplane. mono.
biplane 2-seater,
side by side.
Length...feet(m) 33 (10) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75)
Span.....feet(m) 49 (15) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 42 (12.80)
Area...sq.ft(m?) 376 (35) 377(36) 387(36) 387(36) 387(36)
Weight, empty...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 1323(600) 1212(550) 1430(649) 1160(522) 1700(798)
Weight, useful...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 662 (300) 882 (400) 662 (300) 882(400) 662(300)
Motor......h.p. 80 Gnome 100 Gnome 80 Canton 110 Canton 110 Canton
Unne. Unne. Unne.
Speed.........
max. m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 69 (110) 62 (100) 71 (115) 87 (140)
min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 62 (100)
Endurance...hrs. 3? 4 7 7 7
Number built during 1912: A total of 41 sold during 1912 for military purposes.
In each case.--
Construction.--All steel.
Landing chassis.--C consists of three wheels each protected by skids. The two main wheels, placed on either side of the centre of gravity, are fitted with patent "Oleopneumatic" shock absorbers. The steering wheel and the front skid have a spring suspension.
Military machines.--The 1912 sales of these were:--32 to France; 5 British; 3 Italian; 1 Swedish.
Steering.--The patented control system consists of a wheel mounted on a pivoted lever. The backward and forward movement of the entire system operates the elevator: the sideway movement warps the rear edge of the upper wings, and the rotation of the wheel steers the machine. The latter operation also governs the front wheel of the landing chassis, so that when on the ground the machine can be steered like a motor car.
Portability.--The main planes can be folded alongside of the fuselage. The machine can then be towed on any ordinary road, or be housed in places such as farm buildings, stables, &c.
BREGUET. Soc. Anonyme des ateliers d'aviation, Louis Breguet, 16 Boulevard Vauban, Donai (Nord). Capacity: about 200 machines a year. Paris office: 25, Boulevard Jules Sandeau. Schools at La Brayelle, pris Douai, Velisy-Villacoublay, pris Paris.
1913 models. G2 bis. G3 C-U1 C-U2 Aerhydro-
2 or 3- 3-seater 2-seater 2-seater plane tandem
seater biplane biplane. biplane. mono.
biplane 2-seater,
side by side.
Length...feet(m) 33 (10) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75)
Span.....feet(m) 49 (15) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 42 (12.80)
Area...sq.ft(m?) 376 (35) 377(36) 387(36) 387(36) 387(36)
Weight, empty...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 1323(600) 1212(550) 1430(649) 1160(522) 1700(798)
Weight, useful...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 662 (300) 882 (400) 662 (300) 882(400) 662(300)
Motor......h.p. 80 Gnome 100 Gnome 80 Canton 110 Canton 110 Canton
Unne. Unne. Unne.
Speed.........
max. m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 69 (110) 62 (100) 71 (115) 87 (140)
min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 62 (100)
Endurance...hrs. 3? 4 7 7 7
Number built during 1912: A total of 41 sold during 1912 for military purposes.
1913 models. G2 bis. G3 C-U1 C-U2 Aerhydro-
2 or 3- 3-seater 2-seater 2-seater plane tandem
seater biplane biplane. biplane. mono.
biplane 2-seater,
side by side.
Length...feet(m) 33 (10) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75) 29 (8.75)
Span.....feet(m) 49 (15) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 45 (13.65) 42 (12.80)
Area...sq.ft(m?) 376 (35) 377(36) 387(36) 387(36) 387(36)
Weight, empty...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 1323(600) 1212(550) 1430(649) 1160(522) 1700(798)
Weight, useful...
.....lbs.(kgs.) 662 (300) 882 (400) 662 (300) 882(400) 662(300)
Motor......h.p. 80 Gnome 100 Gnome 80 Canton 110 Canton 110 Canton
Unne. Unne. Unne.
Speed.........
max. m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 69 (110) 62 (100) 71 (115) 87 (140)
min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 62 (100)
Endurance...hrs. 3? 4 7 7 7
Number built during 1912: A total of 41 sold during 1912 for military purposes.
CAUDRON. Caudron Freres, Hue (Somme). Schools: Crotoy and Juvissy. Capacity, about 100-250 a year.
M2 N. G.D.
Model and Date 1912-13 1912-1 1912-13 1913
mono. mono. mono. mono.
Length.....feet(m.) 20 (6.10) 19? (6) 22 (6.75) 19? (5.80)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.40) 26-1/3(8) 34 (10.30) 27-1/3(8.50)
Area...sq.feet(m.?) 151 (14) 108 (10) 268 (25) 118 (11)
Weight,machine...
........lbs(kgs) 518 (235) 496 (225) 386 (175) 490 (225)
Motor..........h.p. 50 Anzani 50 Anzani Anzani 50 Gnome
or Gnome or Gnome
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 71 (115) 84 (135) 75 (120) 84
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels. Enclosed body.
M2 N. G.D.
Model and Date 1912-13 1912-1 1912-13 1913
mono. mono. mono. mono.
Length.....feet(m.) 20 (6.10) 19? (6) 22 (6.75) 19? (5.80)
Span.......feet(m.) 31 (9.40) 26-1/3(8) 34 (10.30) 27-1/3(8.50)
Area...sq.feet(m.?) 151 (14) 108 (10) 268 (25) 118 (11)
Weight,machine...
........lbs(kgs) 518 (235) 496 (225) 386 (175) 490 (225)
Motor..........h.p. 50 Anzani 50 Anzani Anzani 50 Gnome
or Gnome or Gnome
Speed....m.p.h.(km.) 71 (115) 84 (135) 75 (120) 84
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels. Enclosed body.
CAUDRON. Caudron Frères, Hue (Somme). Schools: Crotoy and Juvissy. Capacity, about 100-250 a year.
Model and date B. E. Monaco type 1913
1912-13 1912-13 1912 hydro-
biplane. biplane. hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...feet(m.) 26? (8) 23? (7.15) 22 (6.75) 32? (10)
Span.....feet(m.) 32? (10) 35-1/3 (10.8) 33 (10.10) 46 (14)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 431 (40) 301 (28) 268 (25) 378 (35)
Weight, machine..
....lbs.(kgs.) 683(310) 640 (295) 772 (350) 882 400)
Motor........h.p. Anzani Gnome Gnome 70 Gnome
or Gnome
S.........m.p.h. 56 (90) 56 (90) 50 (80) 50 (80)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels as well as floats. (Special Caudron patent.)
Model and date B. E. Monaco type 1913
1912-13 1912-13 1912 hydro-
biplane. biplane. hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...feet(m.) 26? (8) 23? (7.15) 22 (6.75) 32? (10)
Span.....feet(m.) 32? (10) 35-1/3 (10.8) 33 (10.10) 46 (14)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 431 (40) 301 (28) 268 (25) 378 (35)
Weight, machine..
....lbs.(kgs.) 683(310) 640 (295) 772 (350) 882 400)
Motor........h.p. Anzani Gnome Gnome 70 Gnome
or Gnome
S.........m.p.h. 56 (90) 56 (90) 50 (80) 50 (80)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels as well as floats. (Special Caudron patent.)
CAUDRON. Caudron Freres, Hue (Somme). Schools: Crotoy and Juvissy. Capacity, about 100-250 a year.
Model and date B. E. Monaco type 1913
1912-13 1912-13 1912 hydro-
biplane. biplane. hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...feet(m.) 26? (8) 23? (7.15) 22 (6.75) 32? (10)
Span.....feet(m.) 32? (10) 35-1/3 (10.8) 33 (10.10) 46 (14)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 431 (40) 301 (28) 268 (25) 378 (35)
Weight, machine..
....lbs.(kgs.) 683(310) 640 (295) 772 (350) 882 400)
Motor........h.p. Anzani Gnome Gnome 70 Gnome
or Gnome
S.........m.p.h. 56 (90) 56 (90) 50 (80) 50 (80)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels as well as floats. (Special Caudron patent.)
Model and date B. E. Monaco type 1913
1912-13 1912-13 1912 hydro-
biplane. biplane. hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...feet(m.) 26? (8) 23? (7.15) 22 (6.75) 32? (10)
Span.....feet(m.) 32? (10) 35-1/3 (10.8) 33 (10.10) 46 (14)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 431 (40) 301 (28) 268 (25) 378 (35)
Weight, machine..
....lbs.(kgs.) 683(310) 640 (295) 772 (350) 882 400)
Motor........h.p. Anzani Gnome Gnome 70 Gnome
or Gnome
S.........m.p.h. 56 (90) 56 (90) 50 (80) 50 (80)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels as well as floats. (Special Caudron patent.)
CAUDRON. Caudron Freres, Hue (Somme). Schools: Crotoy and Juvissy. Capacity, about 100-250 a year.
Model and date B. E. Monaco type 1913
1912-13 1912-13 1912 hydro-
biplane. biplane. hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...feet(m.) 26? (8) 23? (7.15) 22 (6.75) 32? (10)
Span.....feet(m.) 32? (10) 35-1/3 (10.8) 33 (10.10) 46 (14)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 431 (40) 301 (28) 268 (25) 378 (35)
Weight, machine..
....lbs.(kgs.) 683(310) 640 (295) 772 (350) 882 400)
Motor........h.p. Anzani Gnome Gnome 70 Gnome
or Gnome
S.........m.p.h. 56 (90) 56 (90) 50 (80) 50 (80)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels as well as floats. (Special Caudron patent.)
Model and date B. E. Monaco type 1913
1912-13 1912-13 1912 hydro-
biplane. biplane. hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...feet(m.) 26? (8) 23? (7.15) 22 (6.75) 32? (10)
Span.....feet(m.) 32? (10) 35-1/3 (10.8) 33 (10.10) 46 (14)
Area..sq.ft.(m?.) 431 (40) 301 (28) 268 (25) 378 (35)
Weight, machine..
....lbs.(kgs.) 683(310) 640 (295) 772 (350) 882 400)
Motor........h.p. Anzani Gnome Gnome 70 Gnome
or Gnome
S.........m.p.h. 56 (90) 56 (90) 50 (80) 50 (80)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control, warping. Wood construction. On wheels as well as floats. (Special Caudron patent.)
CHAUVIERE (1909-10). Attempt to develop a monoplane with propellers in rear. The idea has been resuscitated for some 1913 military monoplanes.
CLEMENT-BAYARD. Usines Clement-Bayard, 33 quai Michelet, Levallois-Perret (Seine).]
1913. 1913.
Military 3-seater Military single seater
biplane. monoplane.
Length............feet(m) 37 (11.20) 24-2/3 (7.50)
Span, upper.......feet(m) 52 (16) 30 (9.20)
Span, lower.......feet(m) 36 (11) ...
Area...........sq.ft(m?.) 533 (50) 172 (16)
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) 2425 (1100) 1146 (520)
Weight,useful..lbs.(kgs.) 1014 (460) 441 (200)
Motor................h.p. 100 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 53 (85) 75 (120)
Speed, min... m.p.h.(km.) ... ... Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Notes.--Control: lateral, warping.
1913. 1913.
Military 3-seater Military single seater
biplane. monoplane.
Length............feet(m) 37 (11.20) 24-2/3 (7.50)
Span, upper.......feet(m) 52 (16) 30 (9.20)
Span, lower.......feet(m) 36 (11) ...
Area...........sq.ft(m?.) 533 (50) 172 (16)
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) 2425 (1100) 1146 (520)
Weight,useful..lbs.(kgs.) 1014 (460) 441 (200)
Motor................h.p. 100 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 53 (85) 75 (120)
Speed, min... m.p.h.(km.) ... ... Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Notes.--Control: lateral, warping.
CLEMENT-BAYARD. Usines Clement-Bayard, 33 quai Michelet, Levallois-Perret (Seine).]
1913. 1913.
Military 3-seater Military single seater
biplane. monoplane.
Length............feet(m) 37 (11.20) 24-2/3 (7.50)
Span, upper.......feet(m) 52 (16) 30 (9.20)
Span, lower.......feet(m) 36 (11) ...
Area...........sq.ft(m?.) 533 (50) 172 (16)
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) 2425 (1100) 1146 (520)
Weight,useful..lbs.(kgs.) 1014 (460) 441 (200)
Motor................h.p. 100 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 53 (85) 75 (120)
Speed, min... m.p.h.(km.) ... ... Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Notes.--Control: lateral, warping.
1913. 1913.
Military 3-seater Military single seater
biplane. monoplane.
Length............feet(m) 37 (11.20) 24-2/3 (7.50)
Span, upper.......feet(m) 52 (16) 30 (9.20)
Span, lower.......feet(m) 36 (11) ...
Area...........sq.ft(m?.) 533 (50) 172 (16)
Weight,total...lbs.(kgs.) 2425 (1100) 1146 (520)
Weight,useful..lbs.(kgs.) 1014 (460) 441 (200)
Motor................h.p. 100 Gnome 70 Gnome
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 53 (85) 75 (120)
Speed, min... m.p.h.(km.) ... ... Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Notes.--Control: lateral, warping.
D'ARTOIS. Soc. Anonyme des Anciens Chantiers Tellier, Longuenesse, pres St. Omer. Re-established 1912. Capacity: small.
1913 model. 1913
Model and date. "Aero torpille" "Aero torpille "
hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) 24-3/4 (7.50)
Span, upper......feet(m.) 36 (11) 36 (11)
lower......feet(m.) 20 (6) 20 (6)
Area........sq. feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26)
Weight, empty, lbs.(kgs.) 772 (350) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 50 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed........m.p.h. (km.) 56 (90) 84 (135)
Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Single long boat body, canoe-shape.
1913 model. 1913
Model and date. "Aero torpille" "Aero torpille "
hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) 24-3/4 (7.50)
Span, upper......feet(m.) 36 (11) 36 (11)
lower......feet(m.) 20 (6) 20 (6)
Area........sq. feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26)
Weight, empty, lbs.(kgs.) 772 (350) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 50 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed........m.p.h. (km.) 56 (90) 84 (135)
Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Single long boat body, canoe-shape.
D'ARTOIS. Soc. Anonyme des Anciens Chantiers Tellier, Longuenesse, pres St. Omer. Re-established 1912. Capacity: small.
1913 model. 1913
Model and date. "Aero torpille" "Aero torpille "
hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) 24-3/4 (7.50)
Span, upper......feet(m.) 36 (11) 36 (11)
lower......feet(m.) 20 (6) 20 (6)
Area........sq. feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26)
Weight, empty, lbs.(kgs.) 772 (350) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 50 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed........m.p.h. (km.) 56 (90) 84 (135)
Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Single long boat body, canoe-shape.
1913 model. 1913
Model and date. "Aero torpille" "Aero torpille "
hydro-biplane. biplane.
Length...........feet(m.) 23 (7) 24-3/4 (7.50)
Span, upper......feet(m.) 36 (11) 36 (11)
lower......feet(m.) 20 (6) 20 (6)
Area........sq. feet(m?.) 280 (26) 280 (26)
Weight, empty, lbs.(kgs.) 772 (350) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 50 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed........m.p.h. (km.) 56 (90) 84 (135)
Endurance............hrs. ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Notes.--Single long boat body, canoe-shape.
DEPERDUSSIN. Armand Deperdussin, 19 rue des Entrepreneurs, Paris. School: Courey-Betheny (Marne). Established 1910. Capacity: about 150-200 machines a year.
E P T H
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. Monocoque Mono.
school single 2-seater 3-seater 1913. 1913.
mono. mono. mono. mono. mono. 2-seater.
Length,feet(m) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 29(8.80) 19(5.75) ...
Span...feet(m) 29(8.85) 28(8.50) 35(10.65) 41(12.50) 29?(8.95) 36(11)
Area, sq.ft(m?.) ... 162(15) ... 310(28) 97 (9) ...
Weight, total
.lbs.(kgs.) 661(300) 782(355) 1212(550) 2050(930) 882(400) ...
Weight, useful.
.lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor....h.p. 30 Anzani 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 100 Gnome 50 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max.
.....h.(km.) 50 (80) 69 (110) 65 (105) 69 (110) 113(180) 105 (170)
Speed, min...
..m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 81 (130) ...
Endurance,hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 2 5 27 3 2 1
Notes.--Wood construction. Lateral control by warping. Mounted on wheels without skids. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Principal Deperdussin records: 1912 Gordon Bennett (Vedrines) and a number of world records for speed and distance.
Principal pilots include: Busson, Prйvost, Vedrines, Vidart.
E P T H
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. Monocoque Mono.
school single 2-seater 3-seater 1913. 1913.
mono. mono. mono. mono. mono. 2-seater.
Length,feet(m) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 29(8.80) 19(5.75) ...
Span...feet(m) 29(8.85) 28(8.50) 35(10.65) 41(12.50) 29?(8.95) 36(11)
Area, sq.ft(m?.) ... 162(15) ... 310(28) 97 (9) ...
Weight, total
.lbs.(kgs.) 661(300) 782(355) 1212(550) 2050(930) 882(400) ...
Weight, useful.
.lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor....h.p. 30 Anzani 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 100 Gnome 50 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max.
.....h.(km.) 50 (80) 69 (110) 65 (105) 69 (110) 113(180) 105 (170)
Speed, min...
..m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 81 (130) ...
Endurance,hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 2 5 27 3 2 1
Notes.--Wood construction. Lateral control by warping. Mounted on wheels without skids. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Principal Deperdussin records: 1912 Gordon Bennett (Vedrines) and a number of world records for speed and distance.
Principal pilots include: Busson, Prйvost, Vedrines, Vidart.
BRITISH DEPERDUSSINS. British Deperdussin Aeroplane Co., Ltd., 39, Victoria Street. Westminster, London, S.W. School: Hendon.
Chairman: Admiral The Hon. Sir E.R. Freemantle, G.C.B., C.M.G. Managing Directors: Lieut. J.C. Porte, R.N., D. Laurence Santoni. Secretary: N. D. Thompson.
This firm handles the French models of Deperdussins, but has in addition a special hydro-aeroplane of its own, of which one was built in 1912. Details of this special machine are:--Length, 27 feet 10 inches (8.50 m.) Span, 42 feet (12.80 m.) Area, 290 sq. feet (27 m?.) Weight, total, 1,800 lbs. (816 kg.); useful, 1,250 lbs. (566 kg.) Motor, 100 h.p. Anzani. Speed, 67 m.p.h. (110 k.m.) Other models sold by the firm are of French type exactly (see FRANCE).
Chairman: Admiral The Hon. Sir E.R. Freemantle, G.C.B., C.M.G. Managing Directors: Lieut. J.C. Porte, R.N., D. Laurence Santoni. Secretary: N. D. Thompson.
This firm handles the French models of Deperdussins, but has in addition a special hydro-aeroplane of its own, of which one was built in 1912. Details of this special machine are:--Length, 27 feet 10 inches (8.50 m.) Span, 42 feet (12.80 m.) Area, 290 sq. feet (27 m?.) Weight, total, 1,800 lbs. (816 kg.); useful, 1,250 lbs. (566 kg.) Motor, 100 h.p. Anzani. Speed, 67 m.p.h. (110 k.m.) Other models sold by the firm are of French type exactly (see FRANCE).
DEPERDUSSIN. Armand Deperdussin, 19 rue des Entrepreneurs, Paris. School: Courey-Betheny (Marne). Established 1910. Capacity: about 150-200 machines a year.
E P T H
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. Monocoque Mono.
school single 2-seater 3-seater 1913. 1913.
mono. mono. mono. mono. mono. 2-seater.
Length,feet(m) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 29(8.80) 19(5.75) ...
Span...feet(m) 29(8.85) 28(8.50) 35(10.65) 41(12.50) 29?(8.95) 36(11)
Area, sq.ft(m?.) ... 162(15) ... 310(28) 97 (9) ...
Weight, total
.lbs.(kgs.) 661(300) 782(355) 1212(550) 2050(930) 882(400) ...
Weight, useful.
.lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor....h.p. 30 Anzani 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 100 Gnome 50 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max.
.....h.(km.) 50 (80) 69 (110) 65 (105) 69 (110) 113(180) 105 (170)
Speed, min...
..m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 81 (130) ...
Endurance,hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 2 5 27 3 2 1
Notes.--Wood construction. Lateral control by warping. Mounted on wheels without skids. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Principal Deperdussin records: 1912 Gordon Bennett (Vedrines) and a number of world records for speed and distance.
Principal pilots include: Busson, Prevost, Vedrines, Vidart.
E P T H
1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. 1912-13. Monocoque Mono.
school single 2-seater 3-seater 1913. 1913.
mono. mono. mono. mono. mono. 2-seater.
Length,feet(m) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 24(7.30) 29(8.80) 19(5.75) ...
Span...feet(m) 29(8.85) 28(8.50) 35(10.65) 41(12.50) 29?(8.95) 36(11)
Area, sq.ft(m?.) ... 162(15) ... 310(28) 97 (9) ...
Weight, total
.lbs.(kgs.) 661(300) 782(355) 1212(550) 2050(930) 882(400) ...
Weight, useful.
.lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor....h.p. 30 Anzani 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 100 Gnome 50 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed, max.
.....h.(km.) 50 (80) 69 (110) 65 (105) 69 (110) 113(180) 105 (170)
Speed, min...
..m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... 81 (130) ...
Endurance,hrs. ... ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 2 5 27 3 2 1
Notes.--Wood construction. Lateral control by warping. Mounted on wheels without skids. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Principal Deperdussin records: 1912 Gordon Bennett (Vedrines) and a number of world records for speed and distance.
Principal pilots include: Busson, Prevost, Vedrines, Vidart.
DONNET-LEVEQUE.
A 1912. B 1912. C 1912. 1913.
2-seater 2-seater 3-seater 2-seater
hydro- hydro- hydro- hydro-
biplane biplane biplane biplane
Length......feet(m) 26 (7.80) 27 (8.30) 27 (8.30) 34? (10.50)
Span........feet(m) 29? (9) 32? (10) 34? (10.50) 29? (9)
Area....sq.ft.(m?.) 194 (18) 215 (20) 237 (22) 194 (18)
Weight...lbs.(kgs.) 683 (310) 772 (350) 888 (380) 888 (380)
Motor..........h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 75 (120) ... 50 (80)
Endurance......hrs. ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control by warping ailerons. Motor in gap just below upper plane: propeller in rear, direct driven. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Floats.--One large central boat 27 feet (8.20 m.) long--two small ones at each extremity of lower plane.
A 1912. B 1912. C 1912. 1913.
2-seater 2-seater 3-seater 2-seater
hydro- hydro- hydro- hydro-
biplane biplane biplane biplane
Length......feet(m) 26 (7.80) 27 (8.30) 27 (8.30) 34? (10.50)
Span........feet(m) 29? (9) 32? (10) 34? (10.50) 29? (9)
Area....sq.ft.(m?.) 194 (18) 215 (20) 237 (22) 194 (18)
Weight...lbs.(kgs.) 683 (310) 772 (350) 888 (380) 888 (380)
Motor..........h.p. 50 Gnome 70 Gnome 80 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed...m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 75 (120) ... 50 (80)
Endurance......hrs. ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Lateral control by warping ailerons. Motor in gap just below upper plane: propeller in rear, direct driven. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Floats.--One large central boat 27 feet (8.20 m.) long--two small ones at each extremity of lower plane.
MILITARY (1909). The first special military aeroplane ever built. It was specially designed by Capt. Dorand, for what were then held to be the aerial necessities of the French Army. The planes were placed well above the body, giving the pilot a very clear uninterrupted view.
DOUTRE. Soc. Anonyme Doutre, 58, rue Talbot, Paris.
Type. Biplane 3-seater, Biplane 2-seater,
1912-13. 1912-13.
Length.............feet (m.) 40 (12.25) ...
Span, upper........feet (m.) 53 (16.10) ...
lower........feet (m.) 43 (13) ...
Area..........sq. feet (m?.) 533 (50) ...
Weight, machine...lbs.(kgs.) 1323 (600) 1323 (600)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450) 992 (450)
Motor...................h.p. 70 Renault 50 Renault
Speed, max........m.p.h(km.) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Number built during 1912... 1 ?
Notes.--Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie. Both types fitted with the Doutre patent stabiliser, which automatically and instantaneously counteracts troubles due to sudden gusts or partial motor failures. Weight of the 1913 model stabiliser is only 44 lbs. (20 kgs.)
Type. Biplane 3-seater, Biplane 2-seater,
1912-13. 1912-13.
Length.............feet (m.) 40 (12.25) ...
Span, upper........feet (m.) 53 (16.10) ...
lower........feet (m.) 43 (13) ...
Area..........sq. feet (m?.) 533 (50) ...
Weight, machine...lbs.(kgs.) 1323 (600) 1323 (600)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450) 992 (450)
Motor...................h.p. 70 Renault 50 Renault
Speed, max........m.p.h(km.) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Number built during 1912... 1 ?
Notes.--Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie. Both types fitted with the Doutre patent stabiliser, which automatically and instantaneously counteracts troubles due to sudden gusts or partial motor failures. Weight of the 1913 model stabiliser is only 44 lbs. (20 kgs.)
FARMAN. Henry and Maurice Farman, 167, Rue de Silly, Billancourt (Seine) Aerodromes: Buc, pres Versailles and Etampes. Depots: Camp de Chalons--Reims. Established by H. Farman in 1908. M. Farman established works a little later. In 1912 the two brothers combined. The present works were opened in January, 1912, and had an output capacity of at least 300 machines a year in March, 1913.
H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman
Military. Single- 2-seater 2-seater
2 or 3- seater. monoplane. special
seater. Military. hydro-
1912-13. 1913. biplane.
Biplane. Biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 26? (8) 24? (7.35) 24? (7.50) 26 (7.90)
Span......feet(m.) 42? (18.25) 31-1/3 (9.5) 32? (10) 45 (13.70)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 376 (35) 161 (15) 204 (19) 344 (32)
Weight,total...
.. ...lbs. (kgs.) 793 (360) 640 (295) 628 (285) 950 (431)
Weight...
......lbs. (kgs.) 661 (300) 386 (175) ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 70-80 Gnome 70-80 Gnome Designed for 50 Gnome
Gnomes from 40
up to 160 h.p.
Speed, max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 65 (105) 71 (15) ... 52 (100)
Speed, min...
.......m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ...
Endura........hrs. 3 ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman
Military. Single- 2-seater 2-seater
2 or 3- seater. monoplane. special
seater. Military. hydro-
1912-13. 1913. biplane.
Biplane. Biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 26? (8) 24? (7.35) 24? (7.50) 26 (7.90)
Span......feet(m.) 42? (18.25) 31-1/3 (9.5) 32? (10) 45 (13.70)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 376 (35) 161 (15) 204 (19) 344 (32)
Weight,total...
.. ...lbs. (kgs.) 793 (360) 640 (295) 628 (285) 950 (431)
Weight...
......lbs. (kgs.) 661 (300) 386 (175) ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 70-80 Gnome 70-80 Gnome Designed for 50 Gnome
Gnomes from 40
up to 160 h.p.
Speed, max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 65 (105) 71 (15) ... 52 (100)
Speed, min...
.......m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ...
Endura........hrs. 3 ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
FARMAN. Henry and Maurice Farman, 167, Rue de Silly, Billancourt (Seine) Aerodromes: Buc, pres Versailles and Etampes. Depots: Camp de Chalons--Reims. Established by H. Farman in 1908. M. Farman established works a little later. In 1912 the two brothers combined. The present works were opened in January, 1912, and had an output capacity of at least 300 machines a year in March, 1913.
H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman
Military. Single- 2-seater 2-seater
2 or 3- seater. monoplane. special
seater. Military. hydro-
1912-13. 1913. biplane.
Biplane. Biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 26? (8) 24? (7.35) 24? (7.50) 26 (7.90)
Span......feet(m.) 42? (18.25) 31-1/3 (9.5) 32? (10) 45 (13.70)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 376 (35) 161 (15) 204 (19) 344 (32)
Weight,total...
.. ...lbs. (kgs.) 793 (360) 640 (295) 628 (285) 950 (431)
Weight...
......lbs. (kgs.) 661 (300) 386 (175) ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 70-80 Gnome 70-80 Gnome Designed for 50 Gnome
Gnomes from 40
up to 160 h.p.
Speed, max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 65 (105) 71 (15) ... 52 (100)
Speed, min...
.......m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ...
Endura........hrs. 3 ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman. H. Farman
Military. Single- 2-seater 2-seater
2 or 3- seater. monoplane. special
seater. Military. hydro-
1912-13. 1913. biplane.
Biplane. Biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 26? (8) 24? (7.35) 24? (7.50) 26 (7.90)
Span......feet(m.) 42? (18.25) 31-1/3 (9.5) 32? (10) 45 (13.70)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 376 (35) 161 (15) 204 (19) 344 (32)
Weight,total...
.. ...lbs. (kgs.) 793 (360) 640 (295) 628 (285) 950 (431)
Weight...
......lbs. (kgs.) 661 (300) 386 (175) ... ...
Motor.........h.p. 70-80 Gnome 70-80 Gnome Designed for 50 Gnome
Gnomes from 40
up to 160 h.p.
Speed, max...
.......m.p.h.(km) 65 (105) 71 (15) ... 52 (100)
Speed, min...
.......m.p.h.(km) ... ... ... ...
Endura........hrs. 3 ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
H. FARMAN (1908). Farman's first idea of a monoplane. It proved too heavy to fly with the power provided. Was eventually sold to a German officer. Three sets of wings and entirely enclosed body.
GIVAUDIN (1908-09). Built by the Vermorel Co. The first conception of an idea which has since attracted a certain class of inventor in Germany, Italy and the U.S.A.
GOUPY. A.Goupy, 50, Avenue Marceau, Paris. School: Juvissy (Port Aviation). Capacity: about 30 machines a year.
Model and date. 1913 A. 1913 B. 1913.
Staggered Staggered Hydro-staggered
biplane. biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 25 (7.50) 26? (8) 33 (10)
Span......feet(m.) 26? (8) 42? (13) 42 (12.70)
Area....sq.ft.(m?) ... ... 480 (45)
Weight, machine...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 992 (450)
useful...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 661 (300)
Motor........ h.p. 50 Gnome 80 or 100 80 Gnome
Gnome
Speed, max...
......m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 15 (120) 75 (120)
min...
......m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912... ... 12 1
Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Model and date. 1913 A. 1913 B. 1913.
Staggered Staggered Hydro-staggered
biplane. biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 25 (7.50) 26? (8) 33 (10)
Span......feet(m.) 26? (8) 42? (13) 42 (12.70)
Area....sq.ft.(m?) ... ... 480 (45)
Weight, machine...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 992 (450)
useful...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 661 (300)
Motor........ h.p. 50 Gnome 80 or 100 80 Gnome
Gnome
Speed, max...
......m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 15 (120) 75 (120)
min...
......m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912... ... 12 1
Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
GOUPY. A.Goupy, 50, Avenue Marceau, Paris. School: Juvissy (Port Aviation). Capacity: about 30 machines a year.
Model and date. 1913 A. 1913 B. 1913.
Staggered Staggered Hydro-staggered
biplane. biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 25 (7.50) 26? (8) 33 (10)
Span......feet(m.) 26? (8) 42? (13) 42 (12.70)
Area....sq.ft.(m?) ... ... 480 (45)
Weight, machine...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 992 (450)
useful...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 661 (300)
Motor........ h.p. 50 Gnome 80 or 100 80 Gnome
Gnome
Speed, max...
......m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 15 (120) 75 (120)
min...
......m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912... ... 12 1
Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Model and date. 1913 A. 1913 B. 1913.
Staggered Staggered Hydro-staggered
biplane. biplane. biplane.
Length....feet(m.) 25 (7.50) 26? (8) 33 (10)
Span......feet(m.) 26? (8) 42? (13) 42 (12.70)
Area....sq.ft.(m?) ... ... 480 (45)
Weight, machine...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 992 (450)
useful...
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... 661 (300)
Motor........ h.p. 50 Gnome 80 or 100 80 Gnome
Gnome
Speed, max...
......m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 15 (120) 75 (120)
min...
......m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912... ... 12 1
Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
AVIATIK. Autemobil & Aviatik A.G., Mulhausen i.E. Established 1910. Capacity: 100 a year.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
1912. 1912. 1913. 1912-13.
Monoplane. Biplane. Racing Hydro-
biplane. biplane.
Leng......feet(m.) 26? (8) 36 (11) 29? (9) 36 (11)
Spa.......feet(m.) 39 (11.80) 52? (16) 52? (16) 62-1/3 (19)
A.....sq. feet(m?) 258 (24) 517 (48) 517 (48) 597 (56)
Weight,
...total, lbs.(kgs) 1146 (520) 1323 (600) 1234 (560) 1653 (750)
..useful, lbs.(kgs) 661 (30) 882 (400) 882 (400) 661 (300)
[** Text has (k.m.)- should surely be (kgs.)??]
Motor.........h.p. 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus 100 Argus
Speed,
...max. m.p.h.(km.) 68? (110) 56 (90) 62 (100) 52 (80)
...min. m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ...
Endurance.....hrs. 5 6-8 7-8 4-5
Number built
during 1912 6 20 4 3
Remarks.--The monoplanes are constructed under Hanriot license.
HANRIOT. Aeroplanes Hanriot & Cie., 145 rue de Neufchatel, Reims. Paris office: 69 boulevard Berthier, Paris. School: Antibes, Reims.
1913 models D I. D II. D III. D IV. D VII.
Monoplanes. Single 2 or 3- Racer. Steel.
seater. seater.
Length...feet(m.) 23 (7) 26-1/3 (8) 21? (6.65) 23 (7) 23 (7)
Span.....feet(m.) 28-1/3(8.7) 42? (13) 24 (7.3) 28-1/3(8.65) 36(10.95)
Area...sq.ft.(m?) 161 (15) 226 (21) 91 (8.5) 161 (15) 194 (18)
Weight,machine...
...... lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) 937 (425) 661(300) 661 (300) 771 (550)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... 616 (280) ... 396 (180) 364 (165)Motor........h.p. 50 Anzani 100 Gnome 100 Gnome 50 R. 80 Gnome
Peugeot
Speed, max...
......m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 78 (125) 106 (170) 71 (115) 71 (115)
Speed, min...
..... m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--There are also two school types 35 and 45 h.p. Records include 1912 world record for speed with passengers.
None of the above machines represent any very particular divergence from recognised Hanriot practice. D IV is all steel construction, the others wood and steel.
1913 models D I. D II. D III. D IV. D VII.
Monoplanes. Single 2 or 3- Racer. Steel.
seater. seater.
Length...feet(m.) 23 (7) 26-1/3 (8) 21? (6.65) 23 (7) 23 (7)
Span.....feet(m.) 28-1/3(8.7) 42? (13) 24 (7.3) 28-1/3(8.65) 36(10.95)
Area...sq.ft.(m?) 161 (15) 226 (21) 91 (8.5) 161 (15) 194 (18)
Weight,machine...
...... lbs.(kgs.) 661 (300) 937 (425) 661(300) 661 (300) 771 (550)
Weight, useful...
.......lbs.(kgs.) ... 616 (280) ... 396 (180) 364 (165)Motor........h.p. 50 Anzani 100 Gnome 100 Gnome 50 R. 80 Gnome
Peugeot
Speed, max...
......m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110) 78 (125) 106 (170) 71 (115) 71 (115)
Speed, min...
..... m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ... ... ...
Endurance...hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--There are also two school types 35 and 45 h.p. Records include 1912 world record for speed with passengers.
None of the above machines represent any very particular divergence from recognised Hanriot practice. D IV is all steel construction, the others wood and steel.
PISCHOFF-KOECHLIN (1906 or earlier). Dates from the days when a box-kite was the elementary idea in design, and the accepted position of the aviator lying prone.
FARMAN. Henry and Maurice Farman, 167, Rue de Silly, Billancourt (Seine) Aerodromes: Buc, pres Versailles and Etampes. Depots: Camp de Chalons--Reims. Established by H. Farman in 1908. M. Farman established works a little later. In 1912 the two brothers combined. The present works were opened in January, 1912, and had an output capacity of at least 300 machines a year in March, 1913.
M. Farman M. Farman M. Farman
Military biplane. Big military Staggered
biplane. biplane.
Length..........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12) 46 (14) 39 (11.90)
Span............feet (m.) 50-3/4 (15.50) 65-3/4 (20) 36 (11)
Area.....,...sq. ft. (m?) 646 (60) 861 (80) 323 (30)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1102 (500) 1433 (650) 882 (400)
Weight, useful,lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 882 (400) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 70 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 44 (70) 69 110)
Speed, min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance............hrs. ... ... ...
Number built during 1912. ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Latest Hydro.--In March, 1913, a new hydro was produced experimentally. There is a boat body, without steps, carrying the motor which is chain connected with the propeller. Machine is fitted with wheels and skids as well.
M. Farman M. Farman M. Farman
Military biplane. Big military Staggered
biplane. biplane.
Length..........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12) 46 (14) 39 (11.90)
Span............feet (m.) 50-3/4 (15.50) 65-3/4 (20) 36 (11)
Area.....,...sq. ft. (m?) 646 (60) 861 (80) 323 (30)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1102 (500) 1433 (650) 882 (400)
Weight, useful,lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 882 (400) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 70 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 44 (70) 69 110)
Speed, min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance............hrs. ... ... ...
Number built during 1912. ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Latest Hydro.--In March, 1913, a new hydro was produced experimentally. There is a boat body, without steps, carrying the motor which is chain connected with the propeller. Machine is fitted with wheels and skids as well.
FARMAN. Henry and Maurice Farman, 167, Rue de Silly, Billancourt (Seine) Aerodromes: Buc, pres Versailles and Etampes. Depots: Camp de Chalons--Reims. Established by H. Farman in 1908. M. Farman established works a little later. In 1912 the two brothers combined. The present works were opened in January, 1912, and had an output capacity of at least 300 machines a year in March, 1913.
M. Farman M. Farman M. Farman
Military biplane. Big military Staggered
biplane. biplane.
Length..........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12) 46 (14) 39 (11.90)
Span............feet (m.) 50-3/4 (15.50) 65-3/4 (20) 36 (11)
Area.....,...sq. ft. (m?) 646 (60) 861 (80) 323 (30)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1102 (500) 1433 (650) 882 (400)
Weight, useful,lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 882 (400) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 70 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 44 (70) 69 110)
Speed, min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance............hrs. ... ... ...
Number built during 1912. ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Latest Hydro.--In March, 1913, a new hydro was produced experimentally. There is a boat body, without steps, carrying the motor which is chain connected with the propeller. Machine is fitted with wheels and skids as well.
M. Farman M. Farman M. Farman
Military biplane. Big military Staggered
biplane. biplane.
Length..........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12) 46 (14) 39 (11.90)
Span............feet (m.) 50-3/4 (15.50) 65-3/4 (20) 36 (11)
Area.....,...sq. ft. (m?) 646 (60) 861 (80) 323 (30)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1102 (500) 1433 (650) 882 (400)
Weight, useful,lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 882 (400) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 70 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 44 (70) 69 110)
Speed, min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance............hrs. ... ... ...
Number built during 1912. ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Latest Hydro.--In March, 1913, a new hydro was produced experimentally. There is a boat body, without steps, carrying the motor which is chain connected with the propeller. Machine is fitted with wheels and skids as well.
FARMAN. Henry and Maurice Farman, 167, Rue de Silly, Billancourt (Seine) Aerodromes: Buc, pres Versailles and Etampes. Depots: Camp de Chalons--Reims. Established by H. Farman in 1908. M. Farman established works a little later. In 1912 the two brothers combined. The present works were opened in January, 1912, and had an output capacity of at least 300 machines a year in March, 1913.
M. Farman M. Farman M. Farman
Military biplane. Big military Staggered
biplane. biplane.
Length..........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12) 46 (14) 39 (11.90)
Span............feet (m.) 50-3/4 (15.50) 65-3/4 (20) 36 (11)
Area.....,...sq. ft. (m?) 646 (60) 861 (80) 323 (30)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1102 (500) 1433 (650) 882 (400)
Weight, useful,lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 882 (400) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 70 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 44 (70) 69 110)
Speed, min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance............hrs. ... ... ...
Number built during 1912. ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Latest Hydro.--In March, 1913, a new hydro was produced experimentally. There is a boat body, without steps, carrying the motor which is chain connected with the propeller. Machine is fitted with wheels and skids as well.
M. Farman M. Farman M. Farman
Military biplane. Big military Staggered
biplane. biplane.
Length..........feet (m.) 39-1/3 (12) 46 (14) 39 (11.90)
Span............feet (m.) 50-3/4 (15.50) 65-3/4 (20) 36 (11)
Area.....,...sq. ft. (m?) 646 (60) 861 (80) 323 (30)
Weight, total, lbs.(kgs.) 1102 (500) 1433 (650) 882 (400)
Weight, useful,lbs.(kgs.) 617 (280) 882 (400) 551 (250)
Motor................h.p. 70 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed, max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 44 (70) 69 110)
Speed, min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Endurance............hrs. ... ... ...
Number built during 1912. ... ... ...
Remarks.--The whole of the above can easily be converted into hydro-avions --two long narrow floats without steps. H. Farmans are of wood and steel construction; M. Farman, wood. In all 1913 biplanes the ailerons are inter-connected. All 1913 machines designed to carry one or in some cases two mitrailleuse, and special attention is paid to facility for taking down for transport and re-assembling. The 1911-12 H. Farmans had elevators forward, were a good deal longer, and had more surface than 1913 models. Ailerons not inter-connected. The M. Farmans generally as now, except that all planes, etc., had rounded edges. On September 11th, 1912, Foury, in an M. Farman military, made world's endurance record to date, 13 hrs. 22 min., covering 631 miles (1,017 km.) All models of this type, also the "big military," are fitted with the Doutre stabiliser. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
Latest Hydro.--In March, 1913, a new hydro was produced experimentally. There is a boat body, without steps, carrying the motor which is chain connected with the propeller. Machine is fitted with wheels and skids as well.
MORANE-SAULNIER. Soc. de constructions aйronautiques, Morane-Saulnier. 206 Boulevard Pereire. Capital: 1,500,000 francs. School: Villacoublay. Output capacity: about 50 machines a year.
Military, 1913. 2 places.
Tandem.
Length ... ... feet (m.) 21 6.38 21 6.38
Span ... ... feet (m.) 30-1/5 9.20 33? 10.20
Surface ... .. sq. feet (m?.) 151 14 172 16
Weight ... (total ...lbs. (kgs.) 595 270 617 280
(useful ...lbs. (kgs.) ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 50 h.p. 80 h.p.
Speed ... ... m.p.h. (km.) 75 120 75 120
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
In each case body is of rectangular section, wood, mounted on wheels only, except for the military type which has skids also. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
In all there is a rear elevator and a Chauviere tractor.
Note.--Flown in the European Circuit, 1911, by Vedrines, Gajet, Lesire, Morisson, Verept, Frey, Garnier and Dalgier.
Military, 1913. 2 places.
Tandem.
Length ... ... feet (m.) 21 6.38 21 6.38
Span ... ... feet (m.) 30-1/5 9.20 33? 10.20
Surface ... .. sq. feet (m?.) 151 14 172 16
Weight ... (total ...lbs. (kgs.) 595 270 617 280
(useful ...lbs. (kgs.) ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 50 h.p. 80 h.p.
Speed ... ... m.p.h. (km.) 75 120 75 120
Number built during 1912 ... ... ...
In each case body is of rectangular section, wood, mounted on wheels only, except for the military type which has skids also. Fabric: "Aviator" Ramie.
In all there is a rear elevator and a Chauviere tractor.
Note.--Flown in the European Circuit, 1911, by Vedrines, Gajet, Lesire, Morisson, Verept, Frey, Garnier and Dalgier.
MOREAU. Moreau freres, Combs-la-Ville.
1913.
Model and date. 2-seater.
Length..............feet (m) 31 (9.50)
Span................feet (m) 39-1/3 (12)
Area..........sq. feet (m?.) 258 (24)
Weight, machine...lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor...................h.p. 70 Gnome
Speed......max. m.p.h. (km.) 62 (100)
Number built during 191.... 2
Notes.--Fitted with a special stabilising device.
1913.
Model and date. 2-seater.
Length..............feet (m) 31 (9.50)
Span................feet (m) 39-1/3 (12)
Area..........sq. feet (m?.) 258 (24)
Weight, machine...lbs.(kgs.) 992 (450)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor...................h.p. 70 Gnome
Speed......max. m.p.h. (km.) 62 (100)
Number built during 191.... 2
Notes.--Fitted with a special stabilising device.
NIEUPORT. Etablissements Nieuport, 9 rue de Seine, Suresnes (Seine). Established 1910 by the late Edouard Nieuport. Approximate capacity of works: about 100 machines a year. Chief designer during 1911 was Pagny, who has now joined the Hanriot firm.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
NIEUPORT. Etablissements Nieuport, 9 rue de Seine, Suresnes (Seine). Established 1910 by the late Edouard Nieuport. Approximate capacity of works: about 100 machines a year. Chief designer during 1911 was Pagny, who has now joined the Hanriot firm.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
NIEUPORT. Etablissements Nieuport, 9 rue de Seine, Suresnes (Seine). Established 1910 by the late Edouard Nieuport. Approximate capacity of works: about 100 machines a year. Chief designer during 1911 was Pagny, who has now joined the Hanriot firm.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
NIEUPORT. Etablissements Nieuport, 9 rue de Seine, Suresnes (Seine). Established 1910 by the late Edouard Nieuport. Approximate capacity of works: about 100 machines a year. Chief designer during 1911 was Pagny, who has now joined the Hanriot firm.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
Model and date. II N. II G. IV G. 1912-13. IV M, 1912-13. 1913. 1913. 1913. 1913.
Monoplanes. 1912. 1912. 2-seater. 3-seater. 2-seater. 1-seater. 1-seater. Hydro 3-seater.
Length........ feet(m.) 23-2/3 (7.20) 23-2/3 (7.20) 25-2/3 (7.80) 25-2/3 (7.80) 26-1/4 (8) 21-3/4 (6.60) 23 (7) 29 (8.80)
Span ........ feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.65) 28-1/3 (8.65) 36 (10.9) 39-1/3 (12.10) 36 (11) 28-1/3 (8.70) 27-2/3 (8.40) 40 (12.20)
Area ......sq.feet(m?.) ... ... ... ... 231 (21-1/2) 140 (13) 156 (14-1/2) 242 (22-1/2)
Weight, machine lbs. (kgs.) 529 (240) 683 (310) 771 (350) 1058 (480) 771 (350) 573 (260) 573 (260) 1230 (558)
Weight, useful lbs. (kgs.) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Motor ... ... ... h.p. 30 Nieuport Gnome Gnome Gnome Gnome 50 Gnome 30 Nieuport 100 Gnome
Speed, max. m.p.h. (km.) 75 (120) 87 (140) 72 (117) 72 (117) 69 (110) 78 (125) 69 (110) 72 (117)
Speed, min. m.p.h. (km.) ... 75 (120) 69 (110) ... ... ... ... ...
Number built during 1912... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Notes.--Early types had a Hanriot style landing carriage; the 1913 models revert to a Bleriot type. Warping wings. Fuselage entirely enclosed, rectilineal with rounded nose.
PISCHOFF-KOECHLIN (1908). Very early example of a tractor biplane. The extra span of the upper plane is also of interest. The machine had twin mono-elevators aft and also twin rudders.
The Pischoff I biplane of 1907, though not quite a flyer, set the style of future biplanes with its clean configuration, uncluttered by forward control areas or box-kite cellules, its Chauviere Integrate tractor propeller making it what is now regarded as the first in Europe of a modern design. The tail unit was a Cayley-type cruciform union of tailplane, fin, elevator and rudder. There were no ailerons, no wingwarping, and consequently no pilot-operated lateral control. The Pischoff I introduced the famous Anzani engine into aeronautics.
The Pischoff I biplane of 1907, though not quite a flyer, set the style of future biplanes with its clean configuration, uncluttered by forward control areas or box-kite cellules, its Chauviere Integrate tractor propeller making it what is now regarded as the first in Europe of a modern design. The tail unit was a Cayley-type cruciform union of tailplane, fin, elevator and rudder. There were no ailerons, no wingwarping, and consequently no pilot-operated lateral control. The Pischoff I introduced the famous Anzani engine into aeronautics.
1907 De Pischoff tractor biplane
Country of origin: France Designed by Alfred de Pischoff Constructor: L.Chauviere
Span: 32'10"
Country of origin: France Designed by Alfred de Pischoff Constructor: L.Chauviere
Span: 32'10"
TUBAVION. Ponche & Primaud, Long.
Model and date. Monoplane.
1913
Length........feet (m.) 29 (8.85)
Span..........feet (m.) 29? (9)
Area........sq.ft.(m?.) 194 (18)
Weight
machine....lbs.(kgs.) 772 (350)
useful.....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor..............h.p. 70 Gnome
Speed...max. m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105)
Number built during 1912 1
Notes.--Tubular steel construction. Landing: wheels and 2 very long skids. Propeller: amidships.
Model and date. Monoplane.
1913
Length........feet (m.) 29 (8.85)
Span..........feet (m.) 29? (9)
Area........sq.ft.(m?.) 194 (18)
Weight
machine....lbs.(kgs.) 772 (350)
useful.....lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor..............h.p. 70 Gnome
Speed...max. m.p.h.(km.) 65 (105)
Number built during 1912 1
Notes.--Tubular steel construction. Landing: wheels and 2 very long skids. Propeller: amidships.
R.E.P. (1908). Early example of enclosed stream line body. Apparently the first machine in which steel construction appeared.
R.E.P. Robert Esnault-Pelterie, Billancourt. School: Bue. One of the earliest established French firms. The first to go in for steel construction. Reported to have amalgamated with Breguet in 1912, but this fell through.
Model. 1912 1912 1912 1913. 1913.
Steel 1-seater. 2-seater. Military. 2-seater. Hydro-mono.
monoplanes. 3-seater. 2-seater
Length,feet(m.) 25-1/3(7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 23 (7) 25 (7.5)
Span,feet(m.) 35 (10.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 36 (11) 38?(11.6)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) 215 (20) 237 (22) 323 (30) 237 (22) 323 (20)
Weight, machine
lbs.(kgs.) 882 (400) 661 (300) 882 (400) 595 (270) ...
Weight, useful,
lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ...
Motor, make
and h.p. 60 Rep. 66 Rep. 90 Rep. 95 Rep. 80 Rep.
Speed,
max. mph.(km.) 69 (110) 69 (110) 69 (110) 78 (125) 78 (125)
Speed,
min. mph.(km.) ... ... ... 62 (100) 62 (100)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks:--Steel construction. Pentagonal and triangular body. Mounted on wheels and skids. The hydro is on one very large central float.
Model. 1912 1912 1912 1913. 1913.
Steel 1-seater. 2-seater. Military. 2-seater. Hydro-mono.
monoplanes. 3-seater. 2-seater
Length,feet(m.) 25-1/3(7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 23 (7) 25 (7.5)
Span,feet(m.) 35 (10.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 36 (11) 38?(11.6)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) 215 (20) 237 (22) 323 (30) 237 (22) 323 (20)
Weight, machine
lbs.(kgs.) 882 (400) 661 (300) 882 (400) 595 (270) ...
Weight, useful,
lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ...
Motor, make
and h.p. 60 Rep. 66 Rep. 90 Rep. 95 Rep. 80 Rep.
Speed,
max. mph.(km.) 69 (110) 69 (110) 69 (110) 78 (125) 78 (125)
Speed,
min. mph.(km.) ... ... ... 62 (100) 62 (100)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks:--Steel construction. Pentagonal and triangular body. Mounted on wheels and skids. The hydro is on one very large central float.
R.E.P. Robert Esnault-Pelterie, Billancourt. School: Bue. One of the earliest established French firms. The first to go in for steel construction. Reported to have amalgamated with Breguet in 1912, but this fell through.
Model. 1912 1912 1912 1913. 1913.
Steel 1-seater. 2-seater. Military. 2-seater. Hydro-mono.
monoplanes. 3-seater. 2-seater
Length,feet(m.) 25-1/3(7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 23 (7) 25 (7.5)
Span,feet(m.) 35 (10.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 36 (11) 38?(11.6)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) 215 (20) 237 (22) 323 (30) 237 (22) 323 (20)
Weight, machine
lbs.(kgs.) 882 (400) 661 (300) 882 (400) 595 (270) ...
Weight, useful,
lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ...
Motor, make
and h.p. 60 Rep. 66 Rep. 90 Rep. 95 Rep. 80 Rep.
Speed,
max. mph.(km.) 69 (110) 69 (110) 69 (110) 78 (125) 78 (125)
Speed,
min. mph.(km.) ... ... ... 62 (100) 62 (100)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks:--Steel construction. Pentagonal and triangular body. Mounted on wheels and skids. The hydro is on one very large central float.
Model. 1912 1912 1912 1913. 1913.
Steel 1-seater. 2-seater. Military. 2-seater. Hydro-mono.
monoplanes. 3-seater. 2-seater
Length,feet(m.) 25-1/3(7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 25-1/3 (7.7) 23 (7) 25 (7.5)
Span,feet(m.) 35 (10.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 38-1/3(11.7) 36 (11) 38?(11.6)
Area,sq.ft.(m?.) 215 (20) 237 (22) 323 (30) 237 (22) 323 (20)
Weight, machine
lbs.(kgs.) 882 (400) 661 (300) 882 (400) 595 (270) ...
Weight, useful,
lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ...
Motor, make
and h.p. 60 Rep. 66 Rep. 90 Rep. 95 Rep. 80 Rep.
Speed,
max. mph.(km.) 69 (110) 69 (110) 69 (110) 78 (125) 78 (125)
Speed,
min. mph.(km.) ... ... ... 62 (100) 62 (100)
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ... ... ...
Remarks:--Steel construction. Pentagonal and triangular body. Mounted on wheels and skids. The hydro is on one very large central float.
SANCHEZ BESA. 2 avenue de Villiers, Paris.
Model and date. 1912 1912 1913
Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane.
(amphibious)
Length...........feet (m.) 34 (10.40) ... 32-3/4 (10)
Span.............feet (m.) 54 (16.40) 55-3/4 (17) 54-3/4 (16.60)
Area........sq. feet (m?.) 646 (60) ... 646 (60)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1984 (900) ... 1102 (500)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor.................h.p. 100 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed,max......m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ... 50 (80)
Endurance.............hrs. 5 5 6
Number built during 1912 3 1 1
Notes.--Wood and steel construction.
Controls.--Ailerons and rear elevators. Floats: The first has two and the second three floats. The 1913 model has a single boat body mounted on wheels.
Model and date. 1912 1912 1913
Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane.
(amphibious)
Length...........feet (m.) 34 (10.40) ... 32-3/4 (10)
Span.............feet (m.) 54 (16.40) 55-3/4 (17) 54-3/4 (16.60)
Area........sq. feet (m?.) 646 (60) ... 646 (60)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1984 (900) ... 1102 (500)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor.................h.p. 100 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed,max......m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ... 50 (80)
Endurance.............hrs. 5 5 6
Number built during 1912 3 1 1
Notes.--Wood and steel construction.
Controls.--Ailerons and rear elevators. Floats: The first has two and the second three floats. The 1913 model has a single boat body mounted on wheels.
SANCHEZ BESA. 2 avenue de Villiers, Paris.
Model and date. 1912 1912 1913
Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane.
(amphibious)
Length...........feet (m.) 34 (10.40) ... 32-3/4 (10)
Span.............feet (m.) 54 (16.40) 55-3/4 (17) 54-3/4 (16.60)
Area........sq. feet (m?.) 646 (60) ... 646 (60)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1984 (900) ... 1102 (500)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor.................h.p. 100 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed,max......m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ... 50 (80)
Endurance.............hrs. 5 5 6
Number built during 1912 3 1 1
Notes.--Wood and steel construction.
Controls.--Ailerons and rear elevators. Floats: The first has two and the second three floats. The 1913 model has a single boat body mounted on wheels.
Model and date. 1912 1912 1913
Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane. Hydro-biplane.
(amphibious)
Length...........feet (m.) 34 (10.40) ... 32-3/4 (10)
Span.............feet (m.) 54 (16.40) 55-3/4 (17) 54-3/4 (16.60)
Area........sq. feet (m?.) 646 (60) ... 646 (60)
Weight, total...lbs.(kgs.) 1984 (900) ... 1102 (500)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor.................h.p. 100 Renault 70 Renault 70 Renault
Speed,max......m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ... 50 (80)
Endurance.............hrs. 5 5 6
Number built during 1912 3 1 1
Notes.--Wood and steel construction.
Controls.--Ailerons and rear elevators. Floats: The first has two and the second three floats. The 1913 model has a single boat body mounted on wheels.
1906 Santos-Dumont 14-BIS - made first powered flight in Europe
Country of origin: France/Brazil. Designer: Alberto Santos-Dumont, Brazilian living in France.
Span: 38'9", Length: 31'10" Weight: 661 lbs
Country of origin: France/Brazil. Designer: Alberto Santos-Dumont, Brazilian living in France.
Span: 38'9", Length: 31'10" Weight: 661 lbs
SANTOS-DUMONT XIX. This little machine, surface only 9 m2. made an extraordinary sensation in France in 1909. It flew at the then incredible speed of 65 m.p.h. (100 k.p.h.) Santos-Dumont presented all rights to the world soon afterwards, and a large number were built before it was realised that only an extremely light weight pilot could fly in one. Few of the copies ever left the ground.
SAVARY. Soc. anonyme des aeroplanes. Robert Savary, 31 rue Dunois, Paris. School: Chartres. Output capacity. 100 to 150 machines a year.
Model and date. 1912. 1912. 1913.
Biplane. Military Biplane.
(3-seater.)
Length..........feet(m.) 36 (11) 33 (10.15) 38? (11.70)
Span, upper.....feet(m.) 46 (14) 49 (14.90) 9? (15)
lower.....feet(m.) 33 (10) 37 (11.20) 33 (10)
Area.......sq. feet(m?.) 510 (48) 533 (50) 550 (52)
Weight, machine...
.............lbs.(kgs.) 1132 (600) ... 1132 (600)
Weight,useful...
.............lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...............h.p. various 0 Labor 75 Renault
(Gnome or Labor)
Speed,max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ... 59 (96)
min....m.p.h.(km.) 50 (80) ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... 47 ...
Notes.--Wood and steel construction. Control: ailerons and rear elevator. Landing gear: wheels and skids. Special features: There are 4 rudders in the gap, and 2 tractors, chain driven. Aeroplatte fabric.
Model and date. 1912. 1912. 1913.
Biplane. Military Biplane.
(3-seater.)
Length..........feet(m.) 36 (11) 33 (10.15) 38? (11.70)
Span, upper.....feet(m.) 46 (14) 49 (14.90) 9? (15)
lower.....feet(m.) 33 (10) 37 (11.20) 33 (10)
Area.......sq. feet(m?.) 510 (48) 533 (50) 550 (52)
Weight, machine...
.............lbs.(kgs.) 1132 (600) ... 1132 (600)
Weight,useful...
.............lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...............h.p. various 0 Labor 75 Renault
(Gnome or Labor)
Speed,max....m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) ... 59 (96)
min....m.p.h.(km.) 50 (80) ... ...
Number built during 1912 ... 47 ...
Notes.--Wood and steel construction. Control: ailerons and rear elevator. Landing gear: wheels and skids. Special features: There are 4 rudders in the gap, and 2 tractors, chain driven. Aeroplatte fabric.
SOMMER. Ateliers Roger Sommer, Mouzon, Ardennes. Flying grounds: Douzy, Mourmelon, Vidamme.
Monoplanes.
Model and date. E 1912. 1913.
Length ...feet(m.) 22 (6.70) 23 (7)
Span ...feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.70) 26? (8)
Area sq.feet(m?.) 172 (16) 172 (16)
Weight, machine.....
..........lbs.(kgs.) 595 (270) 617 (280)
Weight, useful......
..........lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 50 Anzani or 50 Gnome
Gnome
Speed, max..........
.........m.p.h.(km.) 84 (135) 84 (135)
Speed, min..........
.........m.p.h.(km.) 67 (108) 65 (105)
Endurance.......hrs. 4 4
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Wood and steel construction. Landing: carriage wheels. Control: warping and rear elevator. Rectangular body.
Monoplanes.
Model and date. E 1912. 1913.
Length ...feet(m.) 22 (6.70) 23 (7)
Span ...feet(m.) 28-1/3 (8.70) 26? (8)
Area sq.feet(m?.) 172 (16) 172 (16)
Weight, machine.....
..........lbs.(kgs.) 595 (270) 617 (280)
Weight, useful......
..........lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 50 Anzani or 50 Gnome
Gnome
Speed, max..........
.........m.p.h.(km.) 84 (135) 84 (135)
Speed, min..........
.........m.p.h.(km.) 67 (108) 65 (105)
Endurance.......hrs. 4 4
Number built during 1912 ... ...
Wood and steel construction. Landing: carriage wheels. Control: warping and rear elevator. Rectangular body.
1912 Sommer monoplane
Country of Origin: France Designed and built by Roger Sommer
2 seater Span: 37'9" Length: 29'6" Weight: 900 lb
1 seater Span: 34'6"
Country of Origin: France Designed and built by Roger Sommer
2 seater Span: 37'9" Length: 29'6" Weight: 900 lb
1 seater Span: 34'6"
SOMMER. Ateliers Roger Sommer, Mouzon, Ardennes. Flying grounds: Douzy, Mourmelon, Vidamme.
Biplanes.
Model and date. K 1912 R 1912 S 1912 L 1912 R3 1913
Length....feet(m.) 39? (12) 36 (11) 31 (9.50) 29? (9) 38-2/3 (11.7)Span......feet(m.) 39 (12) 51 (15.50) 42 (12.80) 39? (12) 46 (14)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 215 (20) 533 (50) 350 (32) ... 575 (54)
Weight, machine
......lbs.(kgs.) 617(280) 992(450) 597 (275) 639(290) 882 (400)
Weight, useful....
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ...
Motor...h.p. Various Various Various Various 70 Renault
Speed, max....
.......m.p.h.(km.) 61 (98) 50 (80) 57 (92) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Speed, min........
.......m.p.h.(km.) 53 (85) ... 53 (84) ... ...
Endurance....hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912..... ... ... ... ... ...
Wood and steel construction. Landing: wheels and skids.
Control:ailerons and front rear elevator.
Biplanes.
Model and date. K 1912 R 1912 S 1912 L 1912 R3 1913
Length....feet(m.) 39? (12) 36 (11) 31 (9.50) 29? (9) 38-2/3 (11.7)Span......feet(m.) 39 (12) 51 (15.50) 42 (12.80) 39? (12) 46 (14)
Area...sq.ft.(m?.) 215 (20) 533 (50) 350 (32) ... 575 (54)
Weight, machine
......lbs.(kgs.) 617(280) 992(450) 597 (275) 639(290) 882 (400)
Weight, useful....
........lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ... ... ...
Motor...h.p. Various Various Various Various 70 Renault
Speed, max....
.......m.p.h.(km.) 61 (98) 50 (80) 57 (92) 56 (90) 56 (90)
Speed, min........
.......m.p.h.(km.) 53 (85) ... 53 (84) ... ...
Endurance....hrs. ... ... ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912..... ... ... ... ... ...
Wood and steel construction. Landing: wheels and skids.
Control:ailerons and front rear elevator.
TRAIN. E. Train, Buoy, Camp de Chalons (Marne).
Model and date. 1-seater 2-seater Hydro-mono.
Monoplanes.
Length.....feet (m.) 26? (8) 26 (8) 26 (8)
Span.......feet (m.) 30? (9.30) 35 (10.66) 42? (12.94)
Area.....sq.ft.(m?.) 172 (16) 215 (20) ...
Weight,
machine, lbs.(kgs.) 573 (200) 617 (280) ...
useful, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 30/60 Anzani 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed
max.....m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95) 65 (105) ...
min.....m.p.h.(km.) 47 (75) ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Notes.--Steel construction. Landing: carriage wheels and skids. Control: warping and rear elevator. The hydro has one very large float which extends a considerable distance ahead of the tractor.
Model and date. 1-seater 2-seater Hydro-mono.
Monoplanes.
Length.....feet (m.) 26? (8) 26 (8) 26 (8)
Span.......feet (m.) 30? (9.30) 35 (10.66) 42? (12.94)
Area.....sq.ft.(m?.) 172 (16) 215 (20) ...
Weight,
machine, lbs.(kgs.) 573 (200) 617 (280) ...
useful, lbs.(kgs.) ... ... ...
Motor...........h.p. 30/60 Anzani 70 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed
max.....m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95) 65 (105) ...
min.....m.p.h.(km.) 47 (75) ... ...
Number built
during 1912 ... ... ...
Notes.--Steel construction. Landing: carriage wheels and skids. Control: warping and rear elevator. The hydro has one very large float which extends a considerable distance ahead of the tractor.
VINET. Gaston Vinet, 41-47 quai de Seine, Courbevoie: also 2-8 rue Larnac. Established for automobile work, 1893. Aeroplane output capacity: small.
Model and date. Type D 1913.
1912 mono. Mono.
Length..............feet(m.) 21-1/2 (6.60) 21 (6.40)
Span................feet(m.) 28-1/2 (8.60) 28 (8.50)
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) 162 (15) 162 (15)
Weight, machine...lbs.(kgs.) 550 (250) 440 (200)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...................h.p. 50 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed,max........m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 60 (95)
Number built during 1912.... 6 ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Landing wheels and skids. Control: warping and rear elevator. Rectangular body. The two types are practically identical.
Model and date. Type D 1913.
1912 mono. Mono.
Length..............feet(m.) 21-1/2 (6.60) 21 (6.40)
Span................feet(m.) 28-1/2 (8.60) 28 (8.50)
Area...........sq. feet(m?.) 162 (15) 162 (15)
Weight, machine...lbs.(kgs.) 550 (250) 440 (200)
useful....lbs.(kgs.) ... ...
Motor...................h.p. 50 Gnome 50 Gnome
Speed,max........m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90) 60 (95)
Number built during 1912.... 6 ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Landing wheels and skids. Control: warping and rear elevator. Rectangular body. The two types are practically identical.
H. FARMAN (1907). This famous machine is the first Voisin, and the one on which H. Farman taught himself to fly. It was the first machine to make a turn in the air. Won the Deutsh-Archdeacon Grand Prix, 13th January, 1908, with a flight of 1 minute, 28 seconds. The extra third plane was added later. An Austrian Syndicate subsequently bought the machine.
VOISIN. Voisin Aeroplanes, Boulevard Gambetta, Issy le Molineux, (Seine). School: Mourmelon. Capital 1,000,000 francs. The oldest aeroplane firm in the world, founded by the Brothers Voisin in 1905. (See past editions).
Latest models are:
Military Military
Model and date. biplane. Hydro-biplane. biplane.
Model 1912. Model 1912. Model 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 37? (11.50) 36 (11) 32? (10)
Span........feet(m.) 55? (17) 43? (13.50) 45-1/3 (13.80)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 387 (36) 376 (35) 398 (37)
Weight,
total....lbs.(kgs) 1367 (620) 1212 (550) 1102 (500)
useful...lbs.(kgs) 772 (350) 661 (300) 794 (360)
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 100 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 62 (100) 65 (105)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 47 8 ...
Latest models are:
Military Military
Model and date. biplane. Hydro-biplane. biplane.
Model 1912. Model 1912. Model 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 37? (11.50) 36 (11) 32? (10)
Span........feet(m.) 55? (17) 43? (13.50) 45-1/3 (13.80)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 387 (36) 376 (35) 398 (37)
Weight,
total....lbs.(kgs) 1367 (620) 1212 (550) 1102 (500)
useful...lbs.(kgs) 772 (350) 661 (300) 794 (360)
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 100 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 62 (100) 65 (105)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 47 8 ...
VOISIN. Voisin Aeroplanes, Boulevard Gambetta, Issy le Molineux, (Seine). School: Mourmelon. Capital 1,000,000 francs. The oldest aeroplane firm in the world, founded by the Brothers Voisin in 1905. (See past editions).
Latest models are:
Military Military
Model and date. biplane. Hydro-biplane. biplane.
Model 1912. Model 1912. Model 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 37? (11.50) 36 (11) 32? (10)
Span........feet(m.) 55? (17) 43? (13.50) 45-1/3 (13.80)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 387 (36) 376 (35) 398 (37)
Weight,
total....lbs.(kgs) 1367 (620) 1212 (550) 1102 (500)
useful...lbs.(kgs) 772 (350) 661 (300) 794 (360)
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 100 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 62 (100) 65 (105)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 47 8 ...
Latest models are:
Military Military
Model and date. biplane. Hydro-biplane. biplane.
Model 1912. Model 1912. Model 1913.
Length......feet(m.) 37? (11.50) 36 (11) 32? (10)
Span........feet(m.) 55? (17) 43? (13.50) 45-1/3 (13.80)
Area....sq.feet(m?.) 387 (36) 376 (35) 398 (37)
Weight,
total....lbs.(kgs) 1367 (620) 1212 (550) 1102 (500)
useful...lbs.(kgs) 772 (350) 661 (300) 794 (360)
Motor..........h.p. 70 Renault 100 Gnome 80 Gnome
Speed,
max....m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100) 62 (100) 65 (105)
min....m.p.h.(km.) ... ... ...
Number built
during 1912 47 8 ...
WITZIG-LIORE-DUTILLUEL (1908-09). First or one of the first appearances of the idea of a series of staggered planes, with which Sellers has ever since experimented in the U.S.A.
ZODIAC. Societe Zodiac, 10 route du Havre, Puteaux pres Paris (Seine). Aero park: St. Cyr l'Ecole pres Versailles. Established 1896. Capital 850,000 francs.
Model and date. S2.
1913.
Length.................feet(m.) 38-3/4 (11.75)
Span, upper............feet(m.) 49 (15)
lower............feet(m.) 36 (11)
Area..............sq. feet(m?.) 350 (32)
Weight, machine......lbs.(kgs.) 1010 (460)
useful.......lbs.(kgs.) 551 (250)
Motor......................h.p. 50 Gnome
Speed, max..........m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95)
Number built during 1912 ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Control: Ailerons and 1 rear elevator. Upper planes staggered 30 in advance of lower. Quadrilateral fuselage. Piloted passenger side by side. Landing carriage: 2 wheels and 1 skid. Aeroplatte fabric.
The 1912 model was practically the same.
Model and date. S2.
1913.
Length.................feet(m.) 38-3/4 (11.75)
Span, upper............feet(m.) 49 (15)
lower............feet(m.) 36 (11)
Area..............sq. feet(m?.) 350 (32)
Weight, machine......lbs.(kgs.) 1010 (460)
useful.......lbs.(kgs.) 551 (250)
Motor......................h.p. 50 Gnome
Speed, max..........m.p.h.(km.) 59 (95)
Number built during 1912 ...
Notes.--Wood construction. Control: Ailerons and 1 rear elevator. Upper planes staggered 30 in advance of lower. Quadrilateral fuselage. Piloted passenger side by side. Landing carriage: 2 wheels and 1 skid. Aeroplatte fabric.
The 1912 model was practically the same.
1909 Dufaux tractor biplane - many flight during 1909 and in 1910. Armand Dufaux flew almost 50 miles in 1 hr 18 mins over water the length of Lake Geneva (almost double the distance over water than Bleriot during his channel crossing)
Country of origin: Switzerland Designed and built by Armand & Henri Dufaux
Country of origin: Switzerland Designed and built by Armand & Henri Dufaux
1911 Dufaux-5 biplane
Country of Origin: Switzerland Designed and built by Dufaux brothers
Span: 27'3" Length: 30'6" Weight: 1224 lbs Speed: 52 mph
Country of Origin: Switzerland Designed and built by Dufaux brothers
Span: 27'3" Length: 30'6" Weight: 1224 lbs Speed: 52 mph
GRANDJEAN.
Model and date. Hydro-monoplane.
1911-12.
Length.......feet(m.) 33 (10)
Span.........feet(m.) 33 (10)
Area....sq. feet(m?.) 191 (18)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 750 (340)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 310 (140)
Motor............h.p. 50 Oerlikon
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 62 (100)
min...m.p.h.(km.) 56 (90)
Number Built during 1912 2
1912 Grandjean Hydravion monoplane
Country of Origin: Switzerland Designed and built by Rene Grandjean
Span: 29'6" Length: 27'11"
Country of Origin: Switzerland Designed and built by Rene Grandjean
Span: 29'6" Length: 27'11"
TADDEOLI.
Model and date. Monoplane.
1911-1912.
Length.......feet(m.) 19? (6)
Span.........feet(m.) 29? (9)
Area....sq. feet(m?.) 151 (14)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 880 (400)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) 330 (150)
Motor............h.p. 50 Gnome
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) 69 (110)
min...m.p.h.(km.) ...
Number Built during 1912 1
1911 Taddeoli monoplane - he lost a wheel on take off in Berne!
Country of Origin: Italy? Designed and built by Taddeoli
Country of Origin: Italy? Designed and built by Taddeoli
WETTERWALD.
Model and date. Monoplane.
1911-1912.
Length.......feet(m.) 24? (7.50)
Span.........feet(m.) 33 (10)
Area....sq. feet(m?.) 215 (20)
Weight,
total...lbs.(kgs.) 705 (320)
useful..lbs.(kgs.) ...
Motor............h.p. 40 E.N.V.
Speed,
max...m.p.h.(km.) ...
min...m.p.h.(km.) ...
Number Built during 1912 1
SWEDISH AEROPLANES. Nyrop. Naval monoplane. Bleriot 2-seater. Built in Sweden by Nyrop, 1911. Motor, 50 h.p. Gnome.