Описание
Страна: Германия
Год: 1914
M.Dusing Germania Flugzeugwerke and its Aircraft (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 41)
Germania Taube (Observation Aircraft/Trainer)
Despite innovative elements, such as the wooden band tube technology, Egwin Leiber's early designs did not have any significant success. Neither the already mentioned Taube with a 50 hp four-cylinder Argus engine (1912) nor the other Tauben (doves) with a 100 hp six-cylinder Argus engine, a few of which were still delivered to the army or navy in 1914/1915, resulted in a viable series production. All Taube fanciers used tape tube technology, with the wings having the traditional Zanonia shape.
The exact number of Germania A.I Tauben delivered is not known. S 18 was a naval landplane that was likely a Germania A.I (noted as a Rahtjen).
Germania A.I Taube Specifications
Engine: 100 hp Argus
Wing: Span 14.0 m
General: Length 10.2 m
Height 3.2 m
Wing Area 30 m1
Empty weight 690 kg
Max Take-off weight 1062 kg
Max. Speed 96 km/h
Max. Operating Range 385 km
Описание:
- M.Dusing Germania Flugzeugwerke and its Aircraft (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 41)
- M.Dusing German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 84)
Фотографии
-
M.Dusing - Germania Flugzeugwerke and Its Aircraft /Centennial Perspective/ (41)
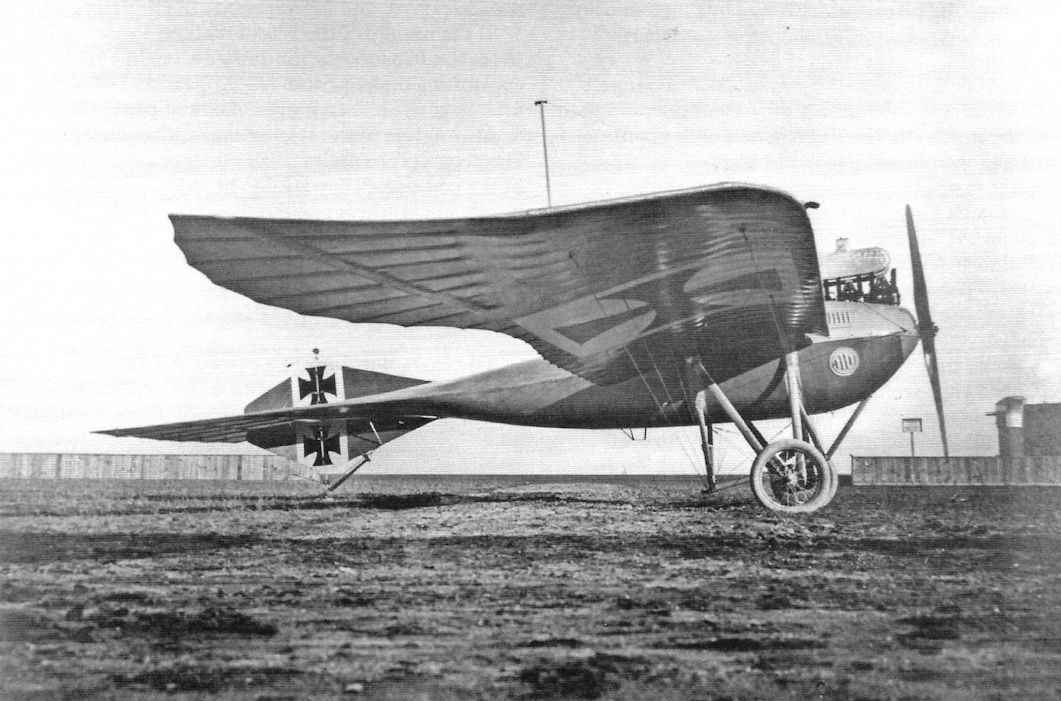
Germania Taube (1914) with 6 cylinder Argus engine and Wolff propeller.
Military Germania-Taube with "Eisernem Kreuz" (Iron Cross). A pilot and observer comprised the crew. -
M.Dusing - Germania Flugzeugwerke and Its Aircraft /Centennial Perspective/ (41)
Germania-Taube with radiator located directly above the engine (100 hp Argus).
-
M.Dusing - Germania Flugzeugwerke and Its Aircraft /Centennial Perspective/ (41)
Fhe first Germania-Tauben, production line in Leipzig-Mockau. In front and in the back are Lawrenz-Tauben in production (100 hp 4-cyl. Argus).
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Lawrenz Taube - Германия - 1913
-
M.Dusing - Germania Flugzeugwerke and Its Aircraft /Centennial Perspective/ (41)
Final assembly of Germania-Taube. In front is a Lawrenz-Tauben (100 hp 4-cyl. Argus).
Six-cylinder Argus As.I and Wolff propellers have been used.Другие самолёты на фотографии: Lawrenz Taube - Германия - 1913
-
M.Dusing - Germania Flugzeugwerke and Its Aircraft /Centennial Perspective/ (41)
Production hall, left side - Tauben, right side - B-type aeroplane.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Germania B.I - Германия - 1915





