Описание
Страна: Германия
Год: 1917
Fighter
O.Thetford, P.Gray German Aircraft of the First World War (Putnam)
L.T.G. SD 1
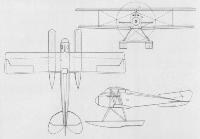
Six of these single-seat seaplanes (Seejagdeinsitzer) with some variation of the tail surfaces were constructed by the Luft Torpedo Gesellschaft, Johannisthal, known initially as L.T.G. and whose official abbreviation was "Torp". The aircraft were ordered on 8th February 1917 and delivery completed by 8th March 1918. Marine numbers 1299-1301 and 1518-1520 were allocated. No. 1299 was used solely as an experimental machine and carried out load tests. The engine generally credited to this aircraft is 150 h.p. Benz Bz III, but from photographs it is obvious, from the hand of the airscrew, that some sort of geared motor was installed. Span, 10.0 m. (32 ft. 9 3/4 in.). Length, 9.0 m. (29 ft. 6 3/8 in.). Height, 3.55 m. (11 ft. 7 3/4 in.). Weights: Empty, 895 kg. (1,969 lb.). Loaded, 1,165 kg. (2,563 lb.).
Описание:
- O.Thetford, P.Gray German Aircraft of the First World War (Putnam)
- W.Green, G.Swanborough The Complete Book of Fighters
- J.Herris German Seaplane Fighters of WWI (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 2)
- J.Herris German Seaplanes of WWI (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 15)
- M.Dusing German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 84)
Фотографии
-
J.Herris - German Seaplanes of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (15)
FD 1 Marine #1299
-
J.Herris - German Seaplanes of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (15)
FD 1 Marine #1518
-
J.Herris - German Seaplane Fighters of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (2)
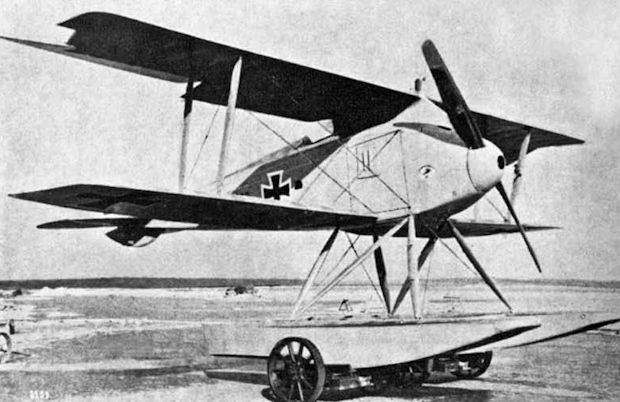
Marine number 1299 was the first prototype of the FD 1 floatplane fighter. Power was provided by a 150 hp Benz Bz.III engine driving the propeller through a Loeb reduction gear, accounting for the propeller rotating in opposite direction to that of the engine.
Three FD1 prototypes, Marine #1299-1301, were ordered. Marine #1299 shown here was destroyed during static load testing. Problems noted during testing resulted in an order for three redesigned versions, at least two of which were delivered to the SVK, but no production resulted. -
J.Herris - German Seaplanes of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (15)
Marine number 1299, the first prototype of the LTG FD 1 single-seat floatplane fighter, was later destroyed during structural testing. The 150 hp Benz Bz.III engine drove the propeller through a reduction gear. Flight testing revealed poor maneuverability and mediocre performance. The man holding the tail has been partially edited out of the photo.
-
J.Herris - German Seaplanes of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (15)
Marine number 1518 was the first aircraft of the redesigned FD 1 fighter batch. The vertical tail surfaces were considerably enlarged compared to the first three prototypes. In addition, the lower wing was modified and the interplane struts were now almost parallel.
FD1 Marine Number 1518 was the first of three of the re-designed, strengthened FD1 fighters ordered; the vertical tail was greatly enlarged compared to the first version. It was delivered to the SVK in July 1918 together with Marine #1519. Testing was incomplete when the war ended. It is difficult to understand why an experimental single-seat floatplane fighter was being tested this late in the war after the great success of the Brandenburg two-seat floatplane fighters. Perhaps this aircraft was tested more to evaluate its technology than as a potential production aircraft. -
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 /Centennial Perspective/ (84)
The LTG FD1 Marine Number 1518 was the first of three revised prototype floatplane fighters. The vertical tail surfaces were greatly enlarged to improve stability. By the time this aircraft appeared, the Brandenburg W.12 had proved the operational superiority of the two-seat floatplane fighter and the single-seat floatplane fighter was obsolete.
-
J.Herris - German Seaplanes of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (15)
FD 1 Marine Number 1518 was the first of three of the re-designed, strengthened FD 1 fighters ordered; the vertical tail was greatly enlarged compared to the first version. Testing was incomplete when the war ended. It is difficult to understand why an experimental single-seat floatplane fighter was being tested this late in the war after the great success of the Brandenburg two-seat floatplane fighters.
-
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 /Centennial Perspective/ (84)
Torp SD1 Marine number 1518 with new fin design to improve stability and maneuverability.
-
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 /Centennial Perspective/ (84)
Undocumented single-seater photographed in the LTG factory. This may have been a landplane development of the SD1 or a type developed in parallel. While the size of the vertical tail surfaces did not need to be as large as the floatplanes, it still looks too small for good stability.
-
J.Herris - German Seaplanes of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (15)
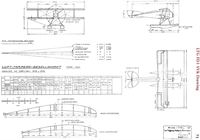
LTG FD1 SVK Drawing