Описание
Страна: Германия
Год: 1918
Варианты
- Gotha - WD.7 - 1916 - Германия
- Gotha - WD.11 - 1917 - Германия
- Gotha - WD.14/WD.20 - 1917 - Германия
- Gotha - WD.22 - 1918 - Германия
- Gotha - WD.27 - 1918 - Германия
- O.Thetford, P.Gray German Aircraft of the First World War (Putnam)
- J.Herris Gotha Aircraft of WWI (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 6)
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
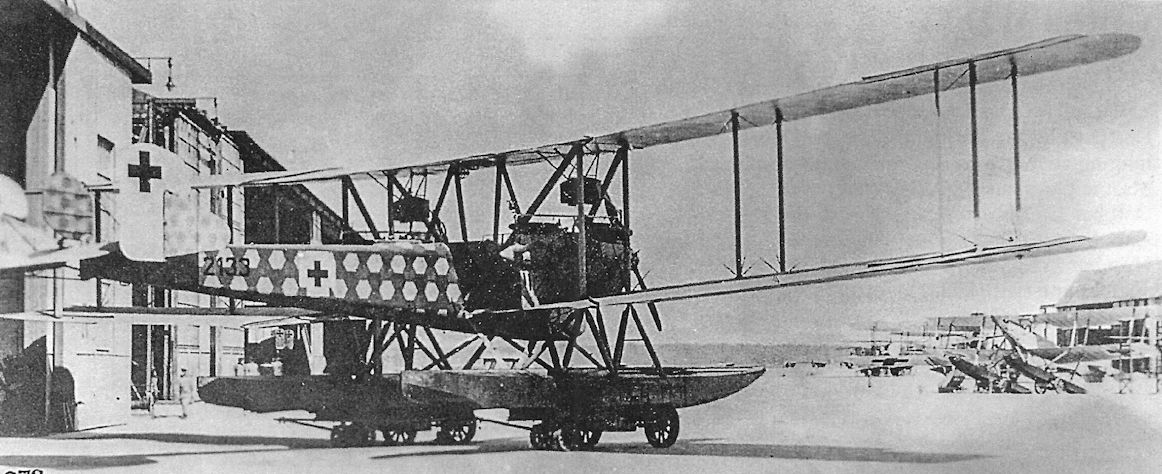
The first WD22, Marine Number 2133, photographed at the SVK on 3 July 1918 in its original form.The tractor engines were 160 hp Mercedes D.III engines and the pushers were 100 hp Mercedes D.I engines.
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
The first of two prototype WD22 seaplanes, Marine Number 2133, in its original form.
The Gotha WD 22 powered by a pair of 200 hp Benz Bz.IV engines, was one of the later, more powerful torpedo bomber designs. When actual torpedo operations gave disappointing results and the aircraft too vulnerable during their attacks, torpedo operations were abandoned and the aircraft were reassigned to long-range reconnaissance and bombing. To extend their reconnaissance range, jettisonable fuel tanks were carried in the torpedo slings. -
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 /Centennial Perspective/ (84)
The massive WD22 would seem to deserve four 260 hp Mercedes D.IVa engines of the type used in the Gotha G.IV and G.V instead of the smaller, less powerful engines fitted. That less powerful engines were installed was likely a result of the Royal Navy's Distant Blockade that was strangling German access to resources.
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
The first WD22, Marine Number 2133, photographed at the SVK. Like the Gotha G.IV and G.V bombers and the preceding WD20 long-range reconnaissance seaplane, the WD22 was very tail heavy, a fault that seriously reduced longitudinal stability and therefore greatly compromised flight safety. There was no rationale for this in a seaplane.
O.Thetford, P.Gray German Aircraft of the First World War (Putnam)
Gotha WD 22
To pursue investigation into long-range reconnaissance and patrol duties, two Gotha WD 22s were built during 1918, Nos. 2133 and 2134. They were powered by four engines tandem mounted in twin nacelles; the forward engines driving tractor airscrews were 160 h.p. Mercedes D IIIs, and the rear engines driving pusher airscrews were 100 h.p. Mercedes D I. They were generally similar to the WD 14s. Span, 26.0 m. (85 ft. 3 3/4 in.) Length, 14.4 m. (47 ft. 3 in.). Area, 147 sq.m. (1,588 sq.ft.). Weights. Empty, 3,800 kg. (8,360 lb.). Loaded, 5,170 kg. (11,374 lb.). Speed. 131 km.hr. (82.19 m.p.h.). Armament, manually operated Parabellum machine-guns fore and aft.
Описание:




