Описание
Страна: Германия
Год: 1916
Варианты
- Gotha - G.I (Gotha-Ursinus) - 1915 - Германия
- Gotha - WD.4 / U.W.D. - 1916 - Германия
- O.Thetford, P.Gray German Aircraft of the First World War (Putnam)
- J.Herris Gotha Aircraft of WWI (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 6)
- M.Dusing German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 (A Centennial Perspective on Great War Airplanes 84)
-
O.Thetford, P.Gray - German Aircraft of the First World War /Putnam/
Gotha Ursinus U.W.D.
-
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919 /Jane's/
The Ursinus GUH G.I. Hydro-Aeroplane at rest.
-
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 /Centennial Perspective/ (84)
Gotha WD4 (UWD), Ursinus-Wasser-DD (1916)
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
The Gotha UWD attracted a crowd during its sea trials in February 1916. So many people rode in it that it was nicknamed the "Trojan Horse".
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
The Gotha UWD resting on a beaching dolly before the bomb-dropping fairing was added.
-
H.Cowin - Aviation Pioneers /Osprey/
The Naval Air Service's sole Gotha WD-4, 120. This three seat bomber owed much to the earlier Gotha G I built for the Army. First flown on 26 January 1916, the WD-4 typifies the seemingly haphazard procurement policy of the navy towards the purchase of aeroplanes for most of the war. Instead of buying a few types of aircraft and engines to meet their mission requirements, the navy bought a large variety of aeroplanes and engines in often very small quantities, making the maintenance crews' and supply people's lives a nightmare. Few performance details survive for the WD-4 other than that it had two 160hp Mercedes D III, giving it atop level speed of 85.5mph. Used spasmodically during 1916, the Zeebrugge-based WD-4, accompanied by five other seaplanes, was reported to have raided several ports in the south east of England, on 19 March 1916, ranging from Dover to Margate.
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
The Gotha UWD in flight displays its distinctive lines and the clear field of fire for its gunners, especially the nose gunner. The second gunner sat in the middle with the pilot aft as a result of its 'battle-plane' heritage from the Gotha G.I.
Only one Gotha Ursinus seaplane was used by the Navy, being allocated number 120. It is shown on 19 March 1916 on one of its operational flights, when in company with five other seaplanes from Zeebrugge it dropped bombs on Dover, Deal, Ramsgate and Margate, causing 14 fatalities among the civilian population. -
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
The Gotha UWD shows more of its distinctive profile in this dramatic image. Interestingly, the Iron Cross national insignia was painted on a white background on the tops and undersides of both wings and both sides of the rudders. The protrusion below the nose was a fairing for dropping bombs added after the UWD was built.
-
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 2 /Centennial Perspective/ (85)
The Gotha UWD at the factory prior to shipment to the SVK at Warnemunde on 30 December 1915.
The Gotha UWD (WD4, Navy No.120) was also equipped with Integral propellers in 1916. -
M.Dusing - German Aviation Industry in WWI. Volume 1 /Centennial Perspective/ (84)
Cover of the magazine "Motor", issue Jan./Feb. 1918.
-
J.Herris - Gotha Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (6)
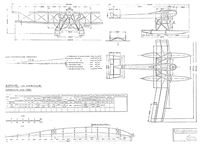
The SVK drawing of the UWD.
O.Thetford, P.Gray German Aircraft of the First World War (Putnam)
Gotha Ursinus G.U.H. G I and U.W.D.
This unique aeroplane, to the design of Oskar Ursinus (editor of Flugsport), was built by Gothaer Waggonfabrik A.G., in both land and seaplane versions. The landplane first flew on 27th July 1915 and the seaplane early in 1916. Several of the former version were constructed and designated G I. A crew of three was carried, and the gunner in the front cockpit had an unparalleled field of fire. The idea of raising the fuselage was to enable the engines to be placed as close together as possible - airscrew tips almost touching - in order to retain a good degree of control in asymmetric flight should failure of either engine occur. In both types "handed" airscrews were employed.
Only a single seaplane (No. 120) was built, and was ultimately used as a school machine for torpedo crews.
Engines, two 160 h.p. Mercedes D III. Span, 20.3 m. (66 ft. 7 1/4 in.). Length, 14.2 m. (46 ft. 7 1/8 in.). Area, 82 sq.m. (885.6 sq.ft.). Weights: Empty, 1,940 kg. (4,268 lb.). Loaded, 2,830 kg. (6,849 lb.). Speed 138 km.hr. (86.125 m.p.h.). Climb, 1,000 m. (3,280 ft.) in 8 min. (U.W.D Seaplane data.)
Armament, two Parabellum machine-guns, both types.
Описание: