C.Barnes Short Aircraft since 1900 (Putnam)
Short Seaplanes (1914-16): Admiralty Types 166, 827 and 830
<...>
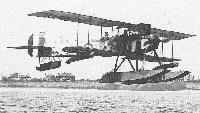
The smaller seaplanes, at first known at Eastchurch as Short Type C, were more numerous than Type 166 and went farther afield. Originally they had constant-chord ailerons and a span of 52 ft 4 in, but both the span and the aileron area were increased before they were flown. They were the first to be built at Rochester seaplane works when production there began in April 1914. Salmson engines were scarce at that date, and the first eight out of Rochester had to be completed with 100 hp Gnome-Monosoupapes; somewhat misleadingly, the Admiralty called them Improved Type 74, but they were identical in design to the Salmson seaplanes except for the deeply cowled overhung engine mounting and a much smaller fixed fin. These eight (811 - 818) were all assigned to Empress, Engadine and Riviera, and 811, 814 and 815 took part in the Cuxhaven raid, flown by Edmonds, Gaskell Blackburn and Oliver respectively. 135 hp Salmsons were available for the next six off the Rochester line, and the old S.41 was rebuilt to the same standard to serve as a development prototype, still with its original serial No. 70; finally, it saw active service with No. 2 Wing, R.N.A.S., as a landplane at Imbros in 1915. Meanwhile a promising new alternative engine had come into production - the 150 hp Sunbeam V-8 water-cooled engine, later named Nubian. Its makers, John Marston & Sons Ltd of Wolverhampton, were originally bicycle manufacturers, who added motor-cars to their products early in the 20th century and soon earned a name for quality; in 1909 they engaged as chief engineer Louis Coatalen, who designed a 3-litre Sunbeam racing car which won the Coupe des Voiturettes at Dieppe in 1912. Combining two banks of the racing car engine to make a V-8 aero-engine, Coatalen installed it in a Maurice Farman, which was flown for long periods at Brooklands by Jack Alcock during the summer of 1913. Having demonstrated its reliability, it was adopted by the Admiralty, together with a V-12 development of 225 hp, for both seaplanes and airships.
The smaller Short seaplane was readily modified to take the Sunbeam engine, and its performance was enhanced by an extra 15 hp for the same installed weight as the Salmson. After the early difficulties with the radiator on the 1913 Circuit of Britain seaplane, Horace Short had decided that only a robust unit of rectangular formation would stand up to severe vibration, so he based his design on marine condenser practice, with vertical spiral tubes assembled into flat elements arranged in four rows edge-on to the slipstream and to the pilot’s line of sight. This highly individual design remained a constant feature of Short seaplanes for several years, and has sometimes been disparaged as clumsy and unsightly, but in fact it was efficient and reliable, did not seriously interfere with the pilot’s vision and helped to keep the crew warm in winter; being located above the engine, its circulation was assisted by the natural thermosiphon effect, so that engine cooling was not wholly dependent on water-pump efficiency; in a hot climate, if (as it frequently did) the water boiled away, the cylinders remained immersed for as long as possible, and forced landings were more often averted. Introduced on 135 and 136, this block radiator was a standard unit for either the 135 hp Salmson or the 150 hp Sunbeam in one size, or for the 200 hp Salmson and 225 hp Sunbeam in a larger size. So of the remainder of the first production batch at Rochester, six (819-821 and 828-830) were built with Salmsons and were called Type 830, while 822-822 had Sunbeams and were called Type 827; 827 itself, however, was tested with both engines in turn at Rochester. Since the engine weight was less than in the 200 hp seaplane, the observer was moved forward to a point above the c.g., which also made ballast unnecessary for solo flying; the cockpit under the centre-section required a longer fuselage bay than the wing-spar pitch, so the rear struts had to be raked instead of vertical; all the wing struts were of oval-section steel tube without additional fairings and the ailerons were inversely tapered with straight trailing edges. Only one other batch of Type 830 was built, comprising 1335-1346, which followed 161-166 at Eastchurch; after war began all these seaplanes were camouflaged before being taken by road to Queenborough Pier, where they were lowered into the water by crane for flight test; this pier, built for the Queenborough-Flushing railway steamers, was commandeered by the Admiralty to avoid having to take seaplanes to Sheerness for launching.
After satisfactory trials with 824 and 826 from H.M.S. Campania in June 1915, Type 827 was adopted for wider production, 30 (3063-3072/3093-3112) being built at Rochester, while 72 were subcontracted, 20 each to the Brush Electrical Engineering Co Ltd, Loughborough; Parnall & Sons Ltd, Bristol, and the Sunbeam Motor Car Co Ltd, Wolverhampton; also 12 to the Fairey Aviation Co Ltd, Hayes, Middlesex, a new aircraft company set up in 1915 by C. R. Fairey, who had been Short Brothers’ works manager and assistant designer at Eastchurch, after previously working there for the Blair Atholl Syndicate. These arrangements resulted from the vastly increased demand for seaplanes after war began, far beyond the combined resources of Eastchurch and Rochester, to meet which a number of Admiralty contractors without aircraft experience were asked to undertake seaplane manufacture under Short Brothers’ supervision, for which they were entitled to claim an agreed royalty after the war was over. Type 827 was the standard equipment from 1915 onwards of many R.N.A.S. coastal stations, including Grain, Calshot, Dundee, Killingholme and Great Yarmouth, for both patrol duties and training; 3063, 3064, 3106 and 3107, allotted to Grain in April 1916, were still there in the Nore Patrol Flight in April 1918. On 25 April, 1916, Yarmouth, Lowestoft and Southwold were shelled by battleships of the German High Seas Fleet, which in turn were bombed by R.N.A.S. seaplanes, including 3108 flown by Flt Sub-Lts Hall and Evans from Great Yarmouth. Three 827s were sent to Mombasa on the armed liner Laconia in July 1915 to help the monitors Severn and Mersey to destroy the Konigsberg in the Rufiji delta, but arrived too late to participate in the final action and were sent on in August to Mesopotamia; there they proved unable to take-off from the Shatt al Arab at Basra because of the heat and limited clear fairway; two were converted into landplanes and pressed into service as bombers against the Turkish advance on Kut-al-Amara in December 1915. Four more 827s equipped No. 8 Squadron R.N.A.S. when it arrived at Zanzibar on the Laconia in March 1916 and were flown from Chukwani Bay, their limited range being later increased by carrying one on board each of the three ships in the area, Laconia, Himalaya and Manica. They spotted for the guns of the monitor Severn at Lindi and reconnoitred enemy positions to assist British landings. Finally, these four (Short-built 3093-3095 and Parnall-built 8219) were handed over in March 1916 to the Belgian volunteer force opposing the Germans on Lake Tanganyika. Shipped in crates from Zanzibar to Matadi, they were transported up the Congo and overland to Lukuga (Albertville) and finally reerected on the shore of Lake Tongwe at Mtoa, whence the first seaplane was flown on 14 May, 1916; this feat was a tribute to both the endurance of the party and the relative ease of assembly of the seaplane with only the crudest of skill and facilities. In spite of their marginal performance in that climate, two of the seaplanes bombed the German lake cruiser Graf von Goetzen in harbour at Kigoma on 23 July, and three days later the town surrendered. Two more 827s, 3097 and 8218 were sent to Zanzibar as replacements for use on Manica and were supplemented by Sunbeam-built 8641-2 shipped from Grain on 29 May, 1916; 8641 was still on Manica in February 1917. Other 827s served in the Mediterranean, at Otranto and on Ben-my-Chree', Parnall-built 8251 was sent to Grain for gunnery trials as late as April 1918, no doubt for use as a target, but in October 1918 three survived at home stations and one at Otranto. They were flown also as dual-control trainers at Windermere, and at least one of these had small boat-built wing-tip floats in place of the usual air-bags.
Single examples of both Type 827 and Type 830 were modified by R.N.A.S. stations for their own purposes. On one of the latter, whose identity has not been ascertained, the wings were modified to a constant-chord plan-form, with stiff trailing edges, parallel ailerons and elliptical wing-tips; this may have been connected with experiments on new aerofoil sections by the Admiralty Board of Invention and Research. The 827, Brush-built 8237, was more drastically altered at Calshot in 1917 and was flown with equal-span constant-chord three-bay wings, with strut-linked ailerons and wing-tip floats mounted directly on the lower surface; these features were typical of Howard T. Wright’s designs for J. Samuel White & Co of Cowes, and may have been suggested as a means of combining the best Short and Wight design features in one seaplane. The purpose of this modification seems to have been to adapt Type 827 as a trainer reproducing the handling characteristics of the Short 184.
Type 827 - Span 53 ft 11 in (16-4 m); length 35 ft 3 in (10 75 m); area 506 sq ft (47 m2); empty weight 2,700 lb (1,225 kg); all-up weight 3,400 lb (1,542 kg); max speed 62 mph (100 km/h); duration 3-5 hr.
Type 830 - Dimensions and area as for Type 827; empty weight 2,624 lb (1,192 kg); all-up weight 3,324 lb (1,510 kg); max speed 70 mph (113 km/h); duration 3-5 hr.
Ten later Salmson-engined Short seaplanes, S.301-310 (9781-9790), were built at Rochester in 1916, primarily for training duties at Calshot. They were a hybrid design, with the wide-span wings and long fuselage of Type 166, and the straight-edged ailerons and forward observer’s position of Type 830. The power plant was a 140 hp single-row Dudbridge-built Salmson and the top centre-section was left open to afford easy access for slinging; the seaplane was unarmed, but carried a rack for practice bombs. The long fuselage enhanced its appearance and doubtless improved its flying qualities, but by the time this variant appeared, the earlier Short seaplanes had been almost superseded by the larger and sturdier Type 184 with 225 hp Sunbeam, which became the best-known and most numerous of all the seaplanes of the First World War.
S.301-310 - as for Type 830 except length 40 ft 7 in (12 3 m).
Показать полностью
K.Wixey Parnall Aircraft Since 1914 (Putnam)
Parnall and Sons Limited
Aircraft Built under Contract 1914-1918
Short 827
Having become established as sub-contractors to build naval aeroplanes for the Admiralty, Parnall undertook the construction of two types of machine designed by Short Brothers. The first of these was the Short Seaplane Admiralty Type 827, of which twenty were ordered from Parnall in two batches of twelve and eight respectively.
The Short 827 was a single-engined, two-seat twin-float seaplane designed for naval reconnaissance and bombing duties, and was identical to its contemporary, the Short 830, except for the powerplant installation. The Short 827 was powered by a 150 hp Sunbeam Nubian water-cooled vee-type engme, whereas the Short 830 was fitted with the 135 hp Salmson radial.
In the event the Type 827 predominated, the Nubian being more or less standardised for the type with the result that comparatively few Type 830s were built. Indeed while the parent firm produced only nineteen Type 830s, the Type 827 of which more than 100 were ordered, was sub-contracted to four other companies, Short Brothers producing forty-eight.
The Type 827 was a two-bay biplane with steel-tube interplane struts and wire bracing, and the extended upper wings, which included inversely tapered ailerons, were cable-braced. Both sets of wings folded rearward to facilitate stowage. A rather large radiator was mounted above the Sunbeam Nubian engine forward of the wings. Provision was made for the carrying of a .303-in Lewis machine-gun for the observer's use, and small bombs could be carried on racks beneath the fuselage.
After the Short Type 827 began to appear in 1915, it remained in service until the Armistice, and was employed both at home and overseas. Those used in home waters flew patrol duties over the English Channel, and especially the North Sea. They were based at the RNAS coastal air stations at Calshot, Dundee, Killingholme, the Isle of Grain and Great Yarmouth. In fact it was one of the Great Yarmouth based Short Type 827s, which, at 04.05 on 25 April, 1916, bombed the German warships that had begun bombarding Lowestoft.
Short Type 827s also operated from the seaplane carriers Ben-my-Chree, Manica and Raven II, while the armed merchant ships Laconia and Himalaya operated one Short Type 827 each. During March 1916, four Short 827s, in company with four French Voisin pusher biplanes were shipped to Zanzibar for service in East Africa, where they eventually became No.8 Naval Squadron.
Four other Short Type 827s were handed over to the Belgian forces in East Africa, and in 1917, a further four went to the Mediterranean area, where they operated from a base at Otranto.
Parnall's first order for Short 827s was for twelve machines (8218-8229) one of which served with No.8 Naval Squadron in East Africa. This aircraft was one of four later handed over to the Belgian forces. Four other 827s from this batch were fitted with dual controls.
An extension of the original contract for twelve Short 827s was undertaken by Parnall's, and involved the construction of a further eight.
Short 827
Two-seat reconnaissance and bomber seaplane. 150 hp Sunbeam Nubian eight-cylinder vee water-cooled engine.
Span 53 ft 11 in upper, 40 ft lower; length 35 ft 3 in; height 13 ft 6 in; wing area 506 sq ft.
Loaded weight 3,400 lb.
Maximum speed 61 mph at 2,000 ft.
Provision for one .303-in Lewis machine-gun and bombs.
Production (Parnall only)
Twenty confirmed
Показать полностью
F.Manson British Bomber Since 1914 (Putnam)
Short Admiralty Types 827 & 830
As early as 1912 both the War Office and Admiralty had expressed concern that no British engine manufacturer was yet working on an engine which promised high power with reliability. During the following year Louis Coatalen at the Sunbeam Motor Car Company was commissioned by the Admiralty to start on an adaptation o f his successful 3-litre racing car engine, producing a V-8 of 150hp (later named the Nubian) and a V-12 of 225hp. The first examples of these engines, roughly equivalent in power and weight to the Salmson nine- and fourteen-cylinder water-cooled radials (which were being purchased in small numbers from France), were not ready by the outbreak of war. In anticipation of deliveries, however, the Admiralty had during the early summer of 1914 ordered twelve new seaplanes from Short Bros similar in most respects to the Type 166; six of them (Nos 819-821 and 828-830), referred to as Admiralty Type 830, were powered by the 135hp Salmson, while Nos 822-827, the Type 827, featured the 150hp Sunbeam Nubian.
By the time these seaplanes were being completed at the end of 1914, the Admiralty was beginning to express a preference for bombs, and neither the Type 827 nor 830 had provision to carry torpedoes. Moreover, despite its slightly inferior performance, it was the Type 827, with its indigenous Sunbeam engine, that was selected for the greater production, sub-contracts being placed with Brush Electrical Engineering, Parnall and Sunbeam for a total of 72 aircraft, in addition to 30 further examples from Shorts, which switched production from Eastchurch to Rochester.
Following shipboard trials by Nos 824 and 826 with HMS Campania in June 1915, Type 827s began delivery to the RNAS Stations at Calshot, Dundee, Grain, Great Yarmouth and Killingholme, being equipped to carry a pair of 112 lb bombs for coastal patrol duties.
When Lowestoft and Southwold were shelled by warships of the German High Seas Fleet in April 1916, a Short 827 was among the British seaplanes which attacked the enemy ships with bombs.
Three Short 827s were shipped to East Africa to spot for British naval guns operating against the German warship Konigsberg trapped in the Rufiji delta, but arrived too late to take part; they were therefore sent on to Mesopotamia where two of them, converted as landplanes with wheel undercarriages, flew bombing attacks on the Turkish forces advancing on Kut in December 1915.
Another epic involved the use of four Short 827s, Nos 3093-3095 and 8219, which were handed over to Belgian volunteers who, in March 1916, were opposing German colonial forces on Lake Tanganyika. Dismantled and transported overland to Lake Tongwe, they were assembled and flown in May, and two months later bombed the German lake cruiser Graf von Goetzen in port at Kigoma, leading to the surrender of the town three days later.
At home, Short 827s remained in service until late in 1918.
Type: Single-engine, two-seat, two-bay biplane, twin-float reconnaissance bomber seaplane.
Manufacturers: Short Brothers, Rochester, Kent; The Brush Electrical Engineering Co Ltd, Loughborough; The Fairey Aviation Co Ltd, Hayes, Middlesex; Parnall & Sons Ltd, Eastville, Bristol; The Sunbeam Motor Car Co Ltd, Wolverhampton.
Powerplant; Type 830. One 135hp Salmson water-cooled radial engine. Type 827. One 150hp Sunbeam (later Nubian) eight-cylinder water-cooled in-line engine.
Dimensions: Span, 53ft 11in; length, 35ft 3in; height, 13ft 3in; wing area, 506 sq ft.
Weights: Type 830. Tare, 2,624 lb; all-up, 3,324 lb; Type 827. Tare, 2,700 lb; all-up, 3,400 lb.
Performance: Sunbeam. Max speed, 61 mph. Salmson. Max speed, 70 mph; climb to 2,000ft, 10 min 25 sec; endurance, 3 1/2 hr.
Armament: Provision to mount one Lewis gun on rear cockpit. Bomb load of two 112 lb or four 65 lb bombs carried on underwing racks.
Prototypes and Production: The Type 830 (Salmson) appeared before the Type 827 (Sunbeam), the first 830s being flown and delivered to the RNAS at the end of 1914. Production of the Type 830 was 19 aircraft, all built by Short Bros (Nos. 819-821, 827*-830 and 1335-1346). Total of 827s' was 107 aircraft: Short, 35 (Nos 822-826, 3063-3072 and 3093-3112); Brush, 20 (Nos 3221-3332 and 8230-8237); Parnall, 20 (Nos 8218-8229 and 8250-8257); Sunbeam, 20 (Nos 8630-8649); Fairey, 12 (Nos 8550-8561).
Summary of Service: Short 827s and 830s served on patrol and bombing duties at RNAS Stations Calshot, Dundee, Grain, Great Yarmouth and Killingholme; others were shipped to East Africa with HM Armed Liner Laconia, and operated from Laconia. Himalaya and Manica, flying with No 8 Squadron, RNAS; Short 827s operated in the Mediterranean at Otranto, Italy, and from HM Seaplane Carrier Ben-my-Chree.
* No 827 was test flown with both Sunbeam and Salmson engines; therefore it was at one time a Type 827.
Показать полностью
P.Lewis British Bomber since 1914 (Putnam)
During mid-1914 an initial order for twelve floatplanes of a new design was placed with Short Brothers, half of which were to be powered by the 135 h.p. Salmson, while the other half were to receive the more powerful water-cooled eight-cylinder vee 150 h.p. Sunbeam Nubian. The Admiralty designations applied were Type 827 to the Nubian version and Type 830 to the Salmson model. There was basically little difference in the Types 827 and 830 from the Type 166, one of the main alterations being a reduction in span to 53 ft. 11 in. The compound taper of the 166’s ailerons was abandoned in favour of straight taper on the 827 and 830, while the newly-adopted kingpost-and-wire bracing of the overhanging upper wingtips was embodied once again. The two-bay wings incorporated folding as a standard feature, but no provision was made for a torpedo as a missile. Underneath the fuselage, however, bomb-racks were installed.
Показать полностью
M.Goodall, A.Tagg British Aircraft before the Great War (Schiffer)
Deleted by request of (c)Schiffer Publishing
S116-118, S119-121 and S151-162 Tractor seaplanes Admiralty Type 830 (Nos.828-830, 819-821 and 1335-1346)
S122-127 Tractor seaplanes Admiralty Type 827 (Nos.822-827) The development of the smaller version of the Type 135 (S88) resulted in contracts for two batches of three and four aircraft incorporating improvements, which became known as the Admiralty Type 830. Delivery of the first batch was made between November 1914 and January 1915 and the second batch between December 1914 and January 1915. A further batch of twelve ordered in 1915 were delivered in that year. S151-162 (Nos.1335-1346)
Aircraft Nos.828-830 had the 135hp Salmson engine, as fitted in the original machine S88, but Nos.819-821 had the 150hp Sunbeam, later known as the Nubian. A further batch of six aircraft, which were not delivered until 1915, were designated the Admiralty Type 827. In other respects the two versions were similar, but differed from the original Type 135 (S88) by the use of kingpost and wire bracing to the top wing extensions.
In addition to the aircraft built by Shorts at Rochester, Parnalls, Faireys, Sunbeam and Brush produced the 827 in quantity in wartime, and the type continued in service throughout the period of hostilities; quantities of some nineteen of Type 830, and 107 Type 827 aircraft were ordered. Certain of the later aircraft had wings with stiff, as opposed to wired, trailing edges and parallel chord, double acting ailerons.
Type 827.
Power: 150hp Sunbeam eight-cylinder water-cooled vee, later named Nubian.
Data
Span 53ft 11in
Area 506 sq. ft
Length 35ft 3in
Weight 2,700 lb.
Weight allup 3,400lb.
Max speed 62 mph
Endurance 3 l/2hr
Type 830.
Power: 135hp Salmson (Canton-Unne) nine-cylinder single-row water-cooled radial.
Data
Span 53ft 11in
Area 506 sq. ft
Length 35ft 3in
Weight 2,624 lb.
Weight allup 3,324lb.
Max speed 70 mph
Endurance 3 l/2hr
Abandoned Short Types of 1914
No doubt a number of types were projected of which there is no remaining evidence. However in June 1914 a prototype Short Type B two-seater tractor biplane, Admiralty serial No. 178 with 200hp Salmson or Le Rhone engine, to be built at Eastchurch, was ordered. This was to be followed by nine production aircraft ordered in July, Nos. 190-198. None of these was produced and actual manufacture had probably not commenced before cancellation, since no construction numbers were allocated.
Показать полностью
J.Bruce British Aeroplanes 1914-1918 (Putnam)
Short Seaplane, Admiralty Types 827 and 830
ALMOST contemporary with the Short 166 was the slightly smaller floatplane which was powered with either the 135 h.p. Salmson radial engine or the 150 h.p. Sunbeam Nubian water-cooled vee-eight. The first batch of twelve, numbered 819-830, were ordered in the summer of 1914; it was intended that six machines should have the Salmson engine and six the Sunbeam. The Salmson-powered seaplanes were to be 819-821 and 828-830, but 827 also had that engine at one time.
Under the Admiralty’s illogical and unpredictable system of nomenclature, the Sunbeam-powered Short was known as the Short Seaplane Type 827, whilst that with the Salmson was designated Type 830.
In structure and appearance the Short 827/830 bore a very close resemblance to the Short 166. Identification of the Short 827 was facilitated by its Sunbeam engine, and the 830 could be distinguished from the Short 166 by the straight trailing edge on its inversely tapered ailerons, which extended inboard of the outer struts; by the plain steel-tube interplane struts, the slight forward rake of the rear centresection struts, and by the slightly less bulky engine. There were two bays of interplane bracing, and the extensions of the upper wings were braced by cables. The mainplanes could be folded. Once again there was a large radiator block mounted on top of the fuselage in front of the wings, for the 135 h.p. Salmson, like the 200 h.p. engine of the same make, was a water-cooled radial. The Short 827/830 was not designed to carry a torpedo. The first Short of the new type was delivered to the R.N.A.S. in 1914.
A number of Short 830s were built, but the Sunbeam engine was standardised for the type and the Short 827s ultimately outnumbered the 830s. The only visible differences between the airframes were those necessitated by the use of the vee-eight engine in place of the radial. The Short 827 was built by Parnall & Sons, the Fairey Aviation Company, the Sunbeam Motor Car Company, and the Brush Electrical Engineering Company, in addition to the parent firm.
An improved version of the 830 existed. It had rigid trailing edges on the mainplanes in place of the wire which was used on the standard machine; and constant-chord ailerons were fitted. The observer had a Lewis gun mounted in an opening in the upper centre-section.
The Short 827s began to appear in numbers in 1915, and the type remained in service until the Armistice. In home waters it was used for oversea patrols from stations such as Calshot and Great Yarmouth. One of the Yarmouth 827s bombed the German Fleet at 4.05 a.m. on April 25th, 1916, when the enemy carried out his bombardment of Lowestoft.
The Short 827 was used in other theatres of war. Three were sent to Mombasa in July, 1915, where they were to have been collected by the R.N.A.S. personnel who had assisted in the destruction of the cruiser Konigsberg and were on their way to participate in the campaign in German East Africa. However, by the time the party reached Mombasa orders had already been received for the Shorts to go to Mesopotamia.
Despite the transfer of these three Short 827s the type nevertheless participated in the East African campaign, for in March, 1916, an R.N.A.S. detachment arrived at Zanzibar equipped with four Voisins and four Short 827s. This unit was later known as No. 8 (Naval) Squadron. The seaplanes operated from Chukwani Bay, but greater mobility was obtained by using three ships as seaplane carriers: the armed liner Laconia, the armed merchant cruiser Himalaya, and the aircraft carrier Manica each had one Short 827.
These seaplanes did a good deal of useful work in the coastal operations of the East African campaign. They contributed to the success of the operations at Dar-es-Salaam in August, 1916, and in the following month the attack on Bagamoyo was based on air photographs taken by the Mamed’s seaplane. The landings at Lindi, Sudi Bay, Kilwa and Kisiju were all covered by the Short 827s. In June, 1917, Flight Sub-Lieutenant C. F. M. Chambers and his observer, Petty Officer Mechanic F. Wilmshurst, flying the Manicds Short 827, contributed reconnaissance charts which were used in the preparation of maps for the advance from Lindi.
Four Short 827s were ultimately handed over to the Belgian forces in East Africa. If they were in fact the four which were used by No. 8 (Naval) Squadron, their serviceability record must have been unequalled by any contemporary seaplanes.
The three Short 827s which had left Mombasa for Mesopotamia in July, 1915, reached Basra at the beginning of September; these machines were all equipped with wireless transmitters. They proved to be of little use, however, for they were unable to get an adequate take-off run from the waters of the Tigris; once airborne their rate of climb in the hot climate was too poor.
Aircraft were sorely needed at that time, and in October two of the Short 827s were converted to landplanes by the substitution of “home-made” wheel undercarriages for the floats. At the beginning of December, 1915, these Shorts took part in the bombing of the Turkish forces advancing on Kut al Imara.
The Shorts were withdrawn to Basra for refit on December 4th. In January, 1916, it was decided to form a composite Flight of R.N.A.S. and R.F.C. personnel at Ora, and the Shorts were flown there. One was wrecked on January 31st; a second was damaged in a bad landing on February 4th; and on February 14th the third turned over on landing and was wrecked.
A small number of Short 827s were used in the Mediterranean: they were based at Otranto, whence four were sent early in 1917.
SPECIFICATION
Manufacturers: Short Brothers, Rochester.
Other Contractors: The Brush Electrical Engineering Co., Ltd., Loughborough; The Fairey Aviation Co., Ltd., Hayes, Middlesex; Parnall & Sons, Ltd., Mivart Street, Eastville, Bristol; The Sunbeam Motor Car Co., Wolverhampton.
Power: 135 h.p. Salmson (Canton-Unne); 150 h.p. Sunbeam Nubian.
Dimensions: Span: upper 53 ft 11 in., lower 40 ft. Length: 35 ft 3 in. Height: 13 ft 6 in. Chord: 5 ft. Gap: 5 ft 6 in. Stagger: nil. Dihedral: nil.
Areas: Wings: 506 sq ft.
Weights: 135 h.p. Salmson. Empty: 2,622 lb. Military load: nil. Crew: 360 lb. Fuel and oil: 342 lb. Weight loaded: 3,324 lb. 150 h.p. Sunbeam. Weight loaded: 3,400 lb.
Performance: Salmson. Maximum speed at 2,000 ft: 70 m.p.h. Climb to 2,000 ft: 10 min 25 sec. Endurance: 3 1/2 hours. Sunbeam. Maximum speed: 61 m.p.h.
Armament: Bombs could be carried on racks under the fuselage. A Lewis machine-gun could be carried: on one Short 830 the gun was fitted on a special mounting in the upper centre-section.
Service Use: R.N.A.S. Stations, Calshot, Dundee, Killingholme, Isle of Grain and Great Yarmouth. Short 830 used on aircraft carriers Engadine and Ben-my-Chree. East Africa: No. 8 (Naval) Squadron: four Short 827s, three of which were disposed on board the armed liner Laconia, the armed merchant cruiser Himalaya, and the aircraft carrier Manica. Four 827s were later handed over to the Belgians in East Africa. Mesopotamia: R.N.A.S. Flight at Basra. Mediterranean: Seaplane station at Otranto. Seaplane carriers Raven II and Ben-my-Chree.
Production and Allocation: Serial numbers indicate that at least nineteen Short 830s and 107 Short 827s were ordered. On October 31st, 1918, the R.A.F. had four Short 827s on charge. Three were at seaplane stations in the United Kingdom and one was in the Mediterranean.
Serial Numbers: Short 830: 819-821, 827-830 and 1335-1346 were built by Short Brothers. Short 827: 822-826: built by Short Brothers. 3063-3072: built by Short Brothers. 3093-3112: built by Short Brothers. 3321-3332: built by Brush Electrical Engineering Co. 8218-8229: built by Parnall & Sons. 8230-8237: built by Brush Electrical Engineering Co. 8250-8257: built by Parnall & Sons. 8550-8561: built by Fairey. 8630-8649: built by Sunbeam.
Notes on Individual Machines: Used by R.N.A.S., Great Yarmouth: 3104, 3105, 3108, 3109, 8222, 8637. Used by R.N.A.S., Calshot: 3326, 3332, 8228, 8229, 8551, 8559. Other machines: 820 and 821: used on H.M.S. Ben- my-Chree. 829: R.N.A.S., Isle of Grain; interned by Holland, November nth, 1914. 3093-3095 were sent to East Africa and were later handed over to the Belgians. 3096-3098 were presented by the Overseas League; 3098 was used in East Africa. 8219 was handed over to the Belgians in East Africa. 8226-8229 were fitted with dual control. 8226: R.N.A.S., Killingholme. 8645: R.N.A.S., Dundee.
Short (140 h.p. Salmson) Seaplane, 1916
THIS seaplane has come to be regarded as a close relative of the Short 827 and 830, though it was in fact a new design. There were certain points of similarity between the types, but the later Salmson-powered seaplane was a somewhat larger aircraft than the Short 827/830.
Possibly the use of the single-row Salmson radial engine suggested a closer relationship to the Short 830 than existed in fact. There was a general similarity in the disposition of the cockpits and interplane struts; and only bracing details distinguished the undercarriage of the later machine from that of the 827 and 830.
However, the Salmson-powered seaplane of 1916 had a lengthened fuselage, larger fin, and wings of increased span. Double-acting ailerons were fitted to the upper wings, and all interplane struts were faired. The centre-section had a large circular aperture, presumably to give the observer ready access to the retrieving sling and to facilitate hoisting-in. It may also have been possible to mount a Lewis gun on the centre-section. The wings could be folded.
Only ten machines were built. No doubt the 140 h.p. Salmson-Short proved to be underpowered in relation to the Service needs of its time; and by that time the Short 184 had been adopted as the standard patrol seaplane.
SPECIFICATION
Manufacturers: Short Brothers, Rochester.
Power: 140 h.p. Salmson.
Service Use: R.N.A.S. Station, Calshot.
Production: Ten Short seaplanes of this type were built.
Serial Numbers: 9781-9790.
Показать полностью
O.Thetford British Naval Aircraft since 1912 (Putnam)
Short 827/830 Seaplane
Very similar in appearance to the Short 166 Seaplane, the Short 827/830 was of somewhat smaller dimensions and had two alternative power plants. The Type 827 could be more readily distinguished from the Type 166 in that it had an in-line Sunbeam engine, whereas the Type 830 had a Salmson water-cooled radial as in the Type 166.
The Admiralty's first contract for 12 aircraft was placed in the summer of 1914: it covered six Type 827s (Nos.822 to 827) and six Type 830s (Nos.819 to 821 and 828 to 830). Ultimately, the Type 827 predominated and 108 were ordered, against 28 of the Type 830. The Short 827 enjoyed a remarkably long operational life, for it served from 1915 until the Armistice.
Unlike the Short 830, which was built by the parent firm only, the Short 827 was manufactured by four firms in addition to Short Bros and, indeed, 12 aircraft of this type (Nos.8550 to 8561) were the first aircraft ever built by Fairey before they turned to their own designs.
Both the Short 827 and 830 were used from seaplane carriers, from RNAS, coastal air stations and overseas. In March 1916 four Short 827s accompanied four Voisins to Zanzibar to form a unit which became No.8 Squadron, RNAS. They did much useful work in the East African campaign and a number of successful attacks were planned after photographic reconnaissance by a Short 827 operating from the seaplane carrier Manica. Short 827s operated in Mesopotamia from September 1915 and in December two were converted as landplanes to bomb the Turks advancing on Kut al Imara.
The following year, on 25 April 1916, a Short 827 (No.3108) from Great Yarmouth bombed the German warships that were shelling Lowestoft.
UNITS ALLOCATED
No.8 Squadron, RNAS (East Africa). Seaplane carriers: Ben-my-Chree, Engadine, Manica and Raven II. Armed merchant vessels: Himalaya and Laconia. RNAS coaslal air stations: Calshot, Dundee. Great Yarmouth, Isle of Grain and Killingholme. Overseas: Basra and Otranto.
TECHNICAL DATA (SHORT 827)
Description: Two-seat reconnaissance and bombing seaplane. Wooden structure, fabric covered.
Manufacturers: Short Bros (827s serialled 822-827, 3063-3072, 3093-3112 and 830s serialled 819-821, 828-830, 1335-1346 and 9781-9790). Subcontracted 827s by Brush Electrical (serialled 3321-3332 and 8230-8237), by Parnall (8218-8229 and 8250-8257), by Fairey (8550-8561) and by Sunbeam (8630-8649).
Power Plant: One 150 hp Sunbeam Nubian.
Dimensions: Span, 53 ft 11 in. Length, 35 ft 3 in. Height, 13 ft 6 in. Wing area, 506 sq ft.
Weights: Empty, 2,700 lb. Loaded, 3,400 lb.
Performance: Maximum speed, 61 mph. Endurance, 3 1/2 hr.
Armament: One free-mounted Lewis machine-gun. Bomb-racks below fuselage.
SHORT (140 hp SALMSON) SEAPLANE
Ten seaplanes of this type were built, Nos.9781 to 9790, and No.9790 is illustrated. They served with the RNAS seaplane station at Calshot from 1916. The engine was a 140 hp Salmson radial.
Показать полностью
H.King Armament of British Aircraft (Putnam)
The seaplanes Types 166, 827 and 830 and that which had had the 140-hp Salmson engine all carried bombs under the fuselage. The first Westland-built 166s had arched cross-bracing struts between the floats to enable them to carry a 14-in torpedo, but all later examples had a standardized installation of three 112-lb bombs. These same aircraft could have a Lewis gun in the rear cockpit, provided with six 47-round drums. A Lewis gun on a centre-section mounting was carried by at least one Type 830, and a similar installation appears to have been made on the 140-hp Salmson type.
Показать полностью